INTRODUCTION
Biliary cystadenocarcinoma is a very rare malignant cystic tumor of the liver. It is often misdiagnosed because of an insufficient recognition of it[1,2] and is hard to differentiate it from benign cystic lesions, such as simple cysts, hydatid cysts and its benign counterpart, cystadenoma. Although these cystic lesions of the liver are more frequently discovered because of the advances in abdominal imaging over the past several years, they are often incorrectly diagnosed, resulting in inadequate therapy[1-5]. In recent years, real time contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) has gained substantial attention in liver imaging, and its role in differentiating benign from malignant focal liver lesions has been well established. The enhancement characteristics of common benign and malignant focal liver lesions on CEUS have been well described and analyzed, some of which are considered criteria for the differential diagnosis of focal liver lesions[6-8]. However, to the best of our knowledge, no reports are available on the enhancement characteristics of biliary cystadenocarcinoma on real time CEUS, or on comparison between CEUS, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. We report a case of a 60-year-old man with a surgically proven biliary cystadenocarcinoma with its CEUS, CT, MRI and histopathologic findings compared.
CASE REPORT
A 60-year-old man was admitted to a local hospital due to an intermittent abdominal pain for 9 d, which was especially severe in the epigastrium. Physical examination revealed a palpable upper abdominal mass with tenderness in the epigastrium. Except for a 5-year history of diabetes mellitus, laboratory test showed normal carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), and anti-hepatitis B surface antigens (anti-HBs), but an elevated serum CA19-9 level of 1090 U/mL.
CT scan performed in the local hospital revealed a large irregular cystic lesion in the left liver lobe with no clear septations and solid components (Figure 1). After admitted to our hospital, two-dimensional ultrasonography and CEUS were performed with Philips iU22 (Philips Medical Systems, Bothell, WA) using a 1.0-5.0 MHz probe C5-1 transducer with a pure wave crystal technology to obtain B-mode and color Doppler images. The acoustic power output was adjusted to a low mechanical index of approximately 0.04 for CEUS.
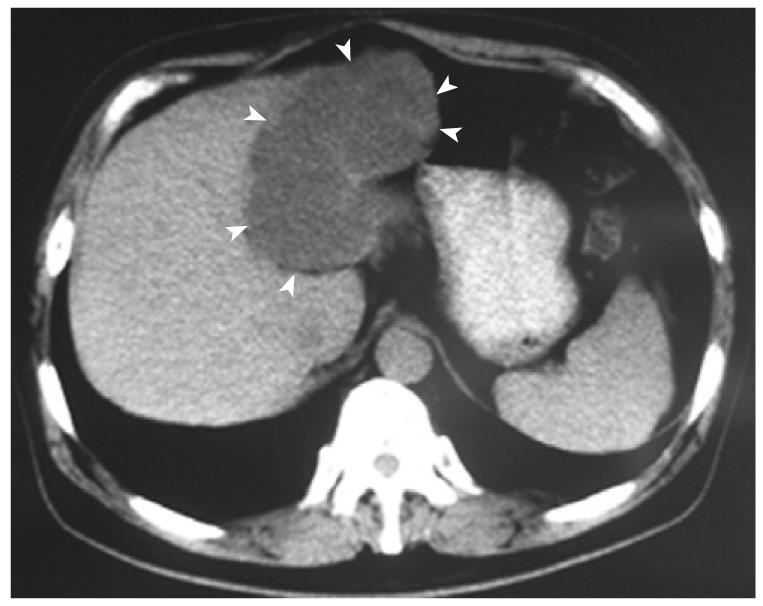
Figure 1 Biliary cystadenocarcinoma.
Computed tomography shows a huge cystic tumor (arrowheads) in the left liver lobe, with no clear septations and solid components.
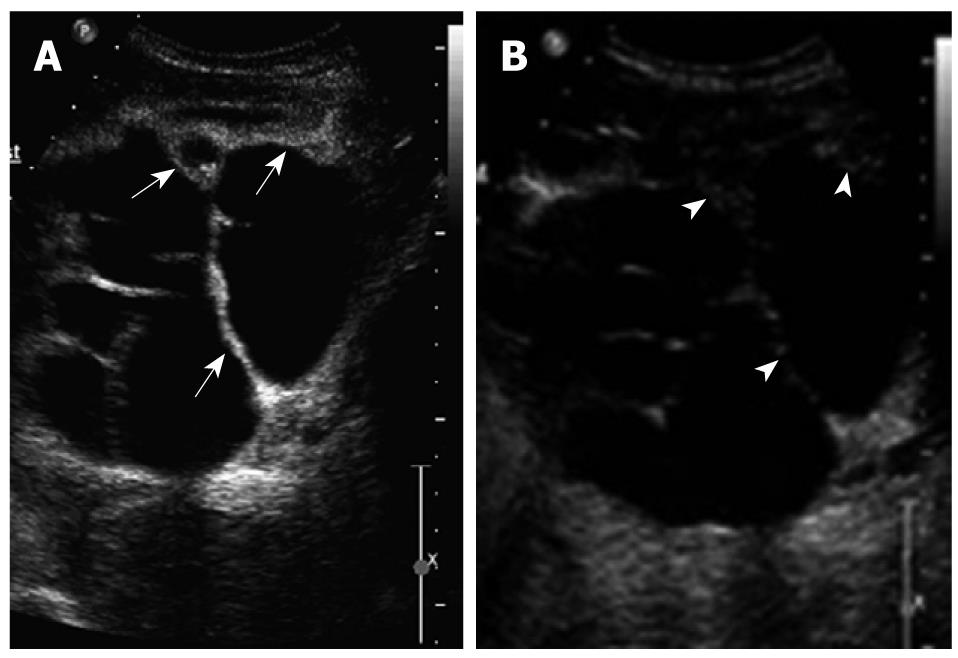
B-mode ultrasonography showed a 12.5 cm × 10.6 cm × 8.2 cm anechoic cystic mass with a well-defined thick wall, mural nodules, and multiple internal septa (Figure 2A), as well as multiple thick and coarse mural and septal calcifications or stones within the septated cysts (Figure 2B). Color Doppler image demonstrated affluent blood flow in the internal septa (Figure 2C). After a conventional sonographic examination to depict the size, location, echogenicity, and internal color Doppler flow signals of the mass, pulse inversion harmonic imaging mode was initiated to examine the real-time CEUS using a sulfur hexafluoride microbubble contrast agent (SonoVue; Bracco SpA, Milan, Italy). A contrast agent (2.4 mL) was administrated intravenously in a bolus fashion via an antecubital vein, followed by a flush of 5 mL normal saline solution. CEUS displayed hyper-enhancement of the cystic wall, internal septations and intra-cystic solid portions in the arterial phase at 18 s after contrast agent injection. The intensity reached its peak at 31 s and the enhancement was washed out progressively and depicted as hypo-enhancement in the portal and late phases (Figure 3). MRI showed an irregular cystic occupying lesion with separations (Figure 4).
Figure 2 Biliary cystadenocarcinoma.
A: Conventional sonography shows a multilocular cystic lesion in left lobe of the liver with nodular thickening of internal septa and mural nodules projecting into the cyst (arrow); B: Conventional sonography shows septal calcifications or stones (arrowhead); C: Color doppler flow imaging (CDFI) shows affluent vascularity in the internal septa (arrows).
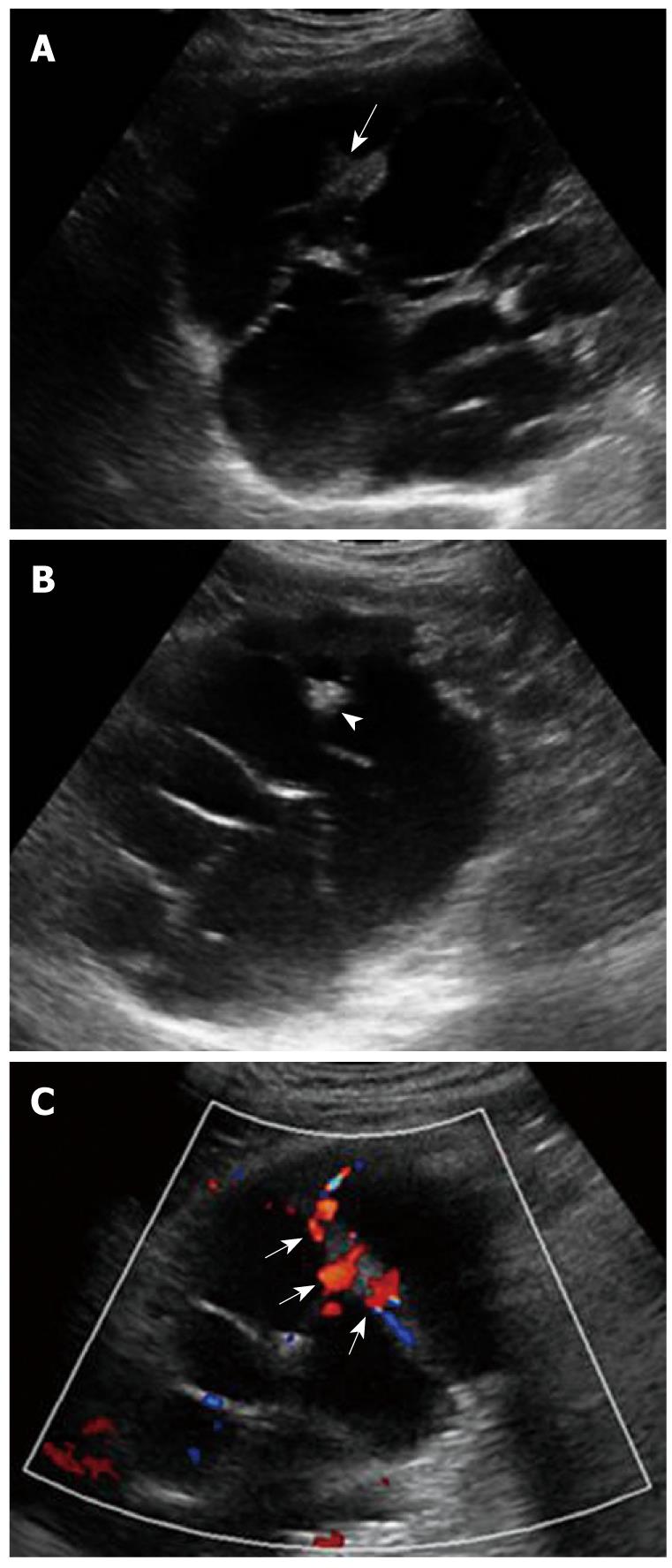
Figure 3 Biliary cystadenocarcinoma.
A: Contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) shows hyperenhancement of the cystic wall, internal septations and intracystic solid portions during the arterial phase (arrows); B: CEUS shows hypoenhancement of the cystic wass, internal septations and intracystic solid portions during the portal and late phases (arrowheads).
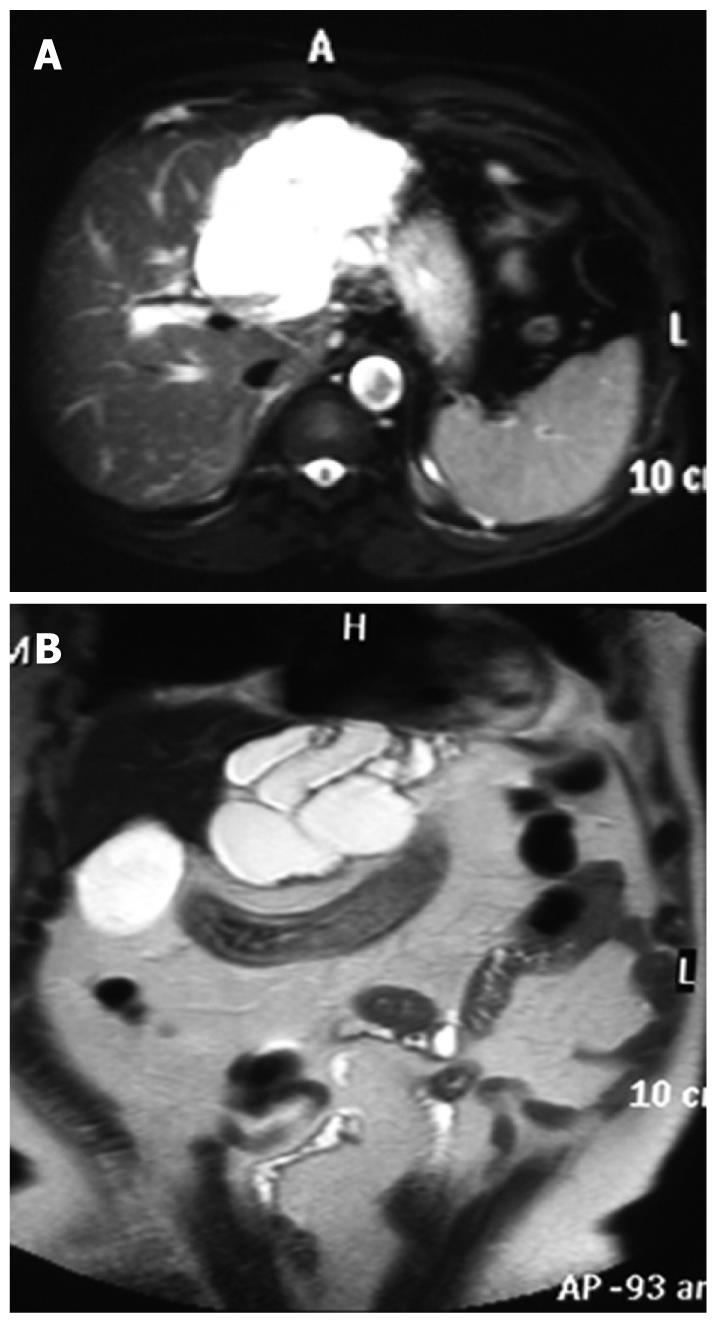
Figure 4 Biliary cystadenocarcinoma.
A and B: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans showing a multilocular cyst in the left lobe of the liver.
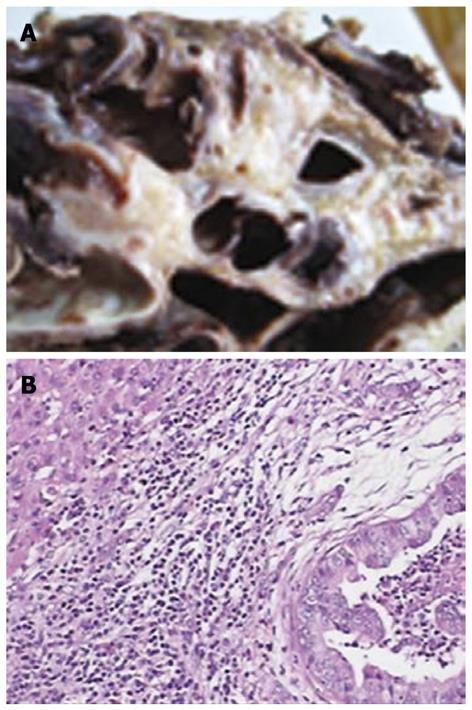
Finally, hepatic lobectomy was performed during which a large cystic mass was found with mucinous fluid present in some portions of the lesion. The mass was finally diagnosed as a biliary cystadenocarcinoma based on the pathological findings which confirmed the thick and coarse calcifications and stones on ultrasonography (Figure 5).
Figure 5 Biliary cystadenocarcinoma.
A: Gross appearance of a cross-section of the formalin fixed specimen showing a multilocular mucinous cyst; B: Microscopically, tumor tissues showing moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma with a papillary growth pattern (HE, original magnification × 100).
DISCUSSION
Biliary cystadenocarcinoma is a very rare malignant cystic tumor of the liver with an incidence of 0.41%[1]. Since it was first reported in 1943[9], only a few cases of biliary cystadenocarcinoma have been reported in the literature[2,9]. Most biliary cystadenocarcinomas are primary malignant tumors originating from the intra-hepatic bile duct or from congenital intra-hepatic biliary malformation, or from benign cystadenoma[10-12], or from very slowly growing bile ducts[2].
Symptoms of biliary cystadenocarcinoma include abdominal pain, infection, dyspepsia, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally, jaundice due to ductal compression. Most biliary cystadenocarcinoma patients are symptomatic with palpable upper abdominal masses[2]. Abdominal pain and a palpable upper abdominal mass were noted in our case with no jaundice. Because of insufficient knowledge about the biliary cystadenocarcinoma and its indistinctive clinical presentations, it is often misdiagnosed as a hepatic abscess, or a hydatid cyst, or a metastatic tumor with cystic degeneration, or even a simple cyst. It is most difficult to differentiate biliary cystadenocarcinoma from cystadenoma, due to their very similar clinical presentations and imaging features. Cystadenoma occurs predominately in women while 38%-44% of biliary cystadenocarcinomas occur in men[13-15]. Choi et al[16] reported that involvement of the left liver lobe is much more common. The majority of biliary cystadenocarcinomas are large in size, usually exceeding 10 cm in diameter, ranging 3.5-25 cm[16,17]. In our case, the lesion was found in the left liver lobe with a diameter of 12.5 cm.
Preoperative imaging studies are of key importance in differential diagnosis. The characteristic CT finding in these tumors is low-density intra-hepatic lesions with internal septa and mural nodules. Contrast enhancement can be seen along the internal septa and wall[2,3,5,17]. In our case, however, CT scan only revealed a large irregular cystic lesion in the left liver lobe with no clear septations and solid components, while sonography showed internal septa and affluent blood signals. It was reported that CT scan fails to show any definite or probable septa while sonography reveals internal septa in the same cases. Because contrast enhanced CT was not performed for our case, CT enhancement characteristics of biliary cystadenocarcinoma could not be observed, suggesting that sonography is somewhat more sensitive than CT in detecting the septa of a cystic lesion[5,16] and is thus superior to CT in displaying the morphology of cystic hepatic lesions.
Although MRI can show small differences in tissue and provide further information concerning the nature of fluid in the cyst, and is therefore extraordinarily helpful in characterizing hepatic lesions. In our case, MRI showed an irregular cystic occupying lesion with separations. However, biliary cystadenocarcinoma could not be diagnosed in our hospital due to an insufficient recognition of it. In order to understand its enhancing characteristics and make a correct diagnosis, CEUS was performed with Philips iU22, which showed hyper-enhancement of the cystic wall with internal septations and intra-cystic solid portions in the arterial phase and reached its peak intensity in late arterial phase. However, the enhancement was washed out progressively and depicted as hypo-enhancement in the portal and late phases. An initial diagnosis of biliary adenocarcinoma was made by comparing the results in our study with published enhanced CT characteristics, which was confirmed at surgery. The hyper-enhancement in arterial phase and the hypo-enhancement in portal or late phase on CEUS in this case may indicate the malignant nature of the lesion. However, Xu et al[18] have reported the hyper-enhancement of the cystic wall, internal septations, and intra-cystic solid portion in the arterial phase in 1 case with benign intrahepatic biliary cystadenoma on CEUS. The enhancement was washed out progressively and depicted as hypo-enhancement in the portal and late phases, suggesting that inadequate differences in enhancement characteristics can differentiate benign intrahepatic biliary cystadenoma from cystadenocarcinoma.
In addition to the features mentioned above, Li et al[19] and Koffron et al[20] have reported increased levels of CA125 and CA19-9. The CA19-9 level was also elevated in our case. Macroscopy can discover large monolocular or multilocular cystic lesions with mural nodules projecting into the cyst in most cases. Most of the cysts are filled with a great deal of clear, yellow mucous like fluid. The cystic fluid can be coffee-colored when complicated by intra-cystic hemorrhage and bile-like if the cyst communicates with intra-hepatic bile ducts[21]. Microscopy can display moderately-differentiated adenocarcinoma with a papillary growth pattern. The papillary structure is lined by monolayer columnar or pseudo-stratified epithelial cells. The tumor cells are characterized by loss of polarity, karyomegaly, and allotypic and pathologic mitotic figures. Although percutaneous liver biopsy contributes to a definite diagnosis, it is risky to induce peritoneal implantation metastasis[22].
Biliary cystadenocarcinoma should be suspected when CT or ultrasonography reveals an elevated mass or nodule in cystic wall or in folding. However, it is extremely difficult to differentiate cystadenoma from adenocarcinoma by imaging alone. In our case, benign hepatic cyst was considered at admission. It has been reported that tumor markers, carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 are increased in serum or cystic fluid of biliary cystic tumor[23-25]. However, tumor markers cannot distinguish cystadenocarcinoma from cystadenoma or both from other cystic lesions of the liver. The increased level of serum CA125 and CA19-9 contributes to the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors and is a useful index for the prognosis of biliary cystadenocarcinoma patients[23-25].
In conclusion, biliary cystadenocarcinoma is asymptomatic. When patients have a large cystic lesion in the liver, especially accompanying elevated serum CA125 and CA19-9 levels, a diagnosis of biliary adenocarcinoma can be established. Its definitive diagnosis is difficult to be made based on ultrasonography, CT and MRI findings. CEUS is useful in depicting the enhancing characteristics of cystic wall, internal septations and intra-cystic solid portions of biliary cystadenocarcinoma but cannot give a definite diagnosis. Further study is needed.