Published online Nov 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5648
Revised: August 25, 2007
Accepted: September 14, 2007
Published online: November 14, 2007
AIM: To assess the long-term clinical benefit of sustained virological response (SVR) in patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) cirrhosis treated by antiviral therapy using mostly ribavirin plus interferon either standard or pegylated.
METHODS: One hundred and thirteen patients with uncomplicated HCV biopsy-proven cirrhosis, treated by at least one course of antiviral treatment ≥ 3 mo and followed ≥ 30 mo were included. The occurrence of clinical events [hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), decompensation and death] was compared in SVR and non SVR patients.
RESULTS: Seventy eight patients received bitherapy and 63 had repeat treatments. SVR was achieved in 37 patients (33%). During a mean follow-up of 7.7 years, clinical events occurred more frequently in non SVR than in SVR patients, with a significant difference for HCC (24/76 vs 1/37, P = 0.01). No SVR patient died while 20/76 non-SVR did (P = 0.002), mainly in relation to HCC (45%).
CONCLUSION: In patients with HCV-related cirrhosis, SVR is associated with a significant decrease in the incidence of HCC and mortality during a follow-up period of 7.7 years. This result is a strong argument to perform and repeat antiviral treatments in patients with compensated cirrhosis.
- Citation: Braks RE, Ganne-Carrié N, Fontaine H, Paries J, Grando-Lemaire V, Beaugrand M, Pol S, Trinchet JC. Effect of sustained virological response on long-term clinical outcome in 113 patients with compensated hepatitis C-related cirrhosis treated by interferon alpha and ribavirin. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(42): 5648-5653
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i42/5648.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5648
In patients with chronic liver diseases, the prognosis strongly depends on the extent of liver fibrosis, as life-threatening complications mainly occur in patients with cirrhosis. In chronic hepatitis C in particular, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is observed only in case of cirrhosis or severe fibrosis (some of them presumably with under diagnosed cirrhosis due to sampling error of liver biopsy). In patients with compensated hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related cirrhosis, the annual incidence of HCC, decompensation and death reach around 3%, 4% and 3%, respectively[1-4] and the main cause of death is HCC[1].
Interferon-α was approved for use in chronic hepatitis C in 1991. During the past 15 years, subsequent improvements have included extension of therapy to 48 wk, the combination of interferon-α with ribavirin, and the use of pegylated interferon. These progresses have resulted in improvement in the sustained virological response (SVR) rate in patients included in randomized trials from less than 10% with the initially recommended 24-wk course of Interferon-α monotherapy to as high as 50%-60% with the combination of peg interferon and ribavirin for 48 wk. In unselected patients, the percentage of SVR is expected to be lower particularly in patients with cirrhosis.
Most studies of antiviral therapy of HCV have been limited to 6 mo of follow-up after the end of treatment and have not included HCC, liver decompensation or death as end points. Therefore, studies of the effect of antiviral therapy on clinical outcome of HCV-cirrhosis have largely been retrospective analyses of therapeutic trials using Interferon-α alone, focusing on patients with cirrhosis[4-11]. Only three randomized trials have assessed this effect, giving conflicting results[12-15]. Recent meta-analysis suggested a slight, but significant preventive effect of standard Interferon-α monotherapy on HCC occurrence in patients with HCV-cirrhosis, especially in those who achieve SVR, who intrinsically represent a small proportion of patients in these trials[16,17]. The influence of Interferon-α on the incidence of decompensation or death in patients with HCV-cirrhosis was less studied and more controversial[4,8,10,12,14,18].
At present, bitherapy with standard then pegylated interferon plus ribavirin has created a new perspective for patients with HCV because of the higher rate of SVR reported[19,20]. The clinical long-term benefit of bitherapy with standard interferon-α has been recently assessed in Chinese patients with HCV-cirrhosis[21]. Such data are still not available in Western patients. Therefore, to assess the impact of achievement of a SVR on clinical long-term outcome of cirrhosis, we conducted a long-term, retrospective, bi-centre analysis of prospective collected data from a cohort of 113 French patients with histological proven HCV cirrhosis treated at least 3 mo by different regimens including ribavirin plus standard or pegylated interferon, and periodically followed and screened for HCC according to standardized criteria.
We retrospectively selected all the consecutive patients followed-up in two French liver centres between 1989 and 2006 fulfilling the following criteria: (1) HCV-related cirrhosis defined by association of positive serum anti-HCV antibodies and RNA, with typical liver histology; (2) absence of complication before or at inclusion (Child-Pugh class A); (3) absence of HBV or HIV co infection (negative serum HBsAg and HIV antibodies); (4) daily alcohol consumption < 50 g; (5) absence of contra-indication to antiviral treatment, particularly platelet and polymorphonuclear counts ≥ 80000/mm3 and 1500/mm3, respectively; (6) at least a 3 mo course of antiviral treatment using standard or pegylated interferon with or without ribavirin, according to therapeutic advance over time and international guidelines; (7) a regular follow-up ≥ 30 mo after the starting of the first treatment; (8) absence of HCC or even suspicious findings such as liver nodule or serum level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) above 50 ng/mL; (9) residence in France allowing regular follow up.
SVR was defined as undetectable serum HCV RNA 6-mo after discontinuation of the last treatment. Non responder patients to a first line treatment were retreated once or more each time it was possible with the same or a different regimen according to therapeutic advance over time. Serum HCV RNA was measured annually during follow-up and at the time of the last visit. According to final virological response, patients were separated into SVR and non SVR groups. Patients not fulfilling SVR criteria, including all patients who relapsed after the achievement of the end of treatment response, were classified as non-SVR.
All patients were prospectively followed-up according to the same schedule in both centres. Complete physical examination, standard biochemical tests, serum AFP determination and abdominal ultrasonography (US) were repeated every 6 mo, whatever the virological response. Baseline then annual endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract allows assessment of the presence of gastrooesophageal varices. In case of significant endoscopic portal hypertension, prophylactic treatment (propranolol and/or endoscopic treatment) was started. The length of the study was calculated from the starting date of antiviral therapy and ended at death or at the last follow-up visit.
When a focal liver lesion or increased AFP levels were detected, tomodensitometry and, whenever possible, fine needle guided liver biopsy were performed. Diagnostic criteria for HCC were: (1) histological and (2) clinical, in patients with AFP value greater than 400 ng/mL and evidence of focal liver lesion at imaging techniques. After 2002, the HCC diagnosis was based on the guidelines of the European Association for the Study of the Liver[22].
Liver-related complications (ascites, upper gastro-intestinal bleeding, and hepatic encephalopathy) were considered an endpoint in all patients with or without the occurrence of HCC. In the subjects who developed HCC, liver complications were recorded only when they occurred before tumour development. Ascites was diagnosed by clinical examination and/or US detection. Porto-systemic encephalopathy was defined by clinical parameters. The source of gastro oesophageal bleeding was confirmed by endoscopy whenever possible.
Dates and causes of deaths were recorded. Liver transplantation was considered as liver-related death endpoint. Reference date was February 2006.
Continuous variables are reported as mean and standard deviation, and categorical variables as absolute and relative frequencies. The Mann-Whitney rank-sum test (M-W) and the Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric analysis of variance (K-W) were applied to compare the means. The associations between Non-SVR or SVR status and events in 2 × 2 cross tabulations were tested using Fisher's exact test. In case of larger cross tabulations, we tested the correlation by computing Pearson's Chi-square, or by computing either the exact probability value, or the Monte Carlo estimate of the exact probability value. Cumulative incidence curves of liver-related complications, HCC and mortality according to response to interferon treatment were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method. The differences between groups were assessed using log-rank tests. Data was censored when individuals died, received a liver transplantation or were lost during follow-up. The variables which proved to be significant at univariate analysis were tested by the multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model to assess their independent effect on the development of events during the follow-up. The results were expressed as hazard ratio (HR) and their 95% confidence interval (CI). Data handling and analysis were performed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS 13.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) and STATXACT. All tests were 2-sided and P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
One hundred thirteen patients fulfilled inclusion criteria (mean age: 54 ± 11 years, males: 61%, HCV genotype 1: 51%) (Table 1). As a whole, the mean (± SD) cumulated duration of treatment was 15.3 ± 9 (range: 3-42, median 12) mo. Treatment courses were performed 1, 2, 3 and 4 times in 50 (44.2%), 42 (37.2%), 19 (16.8%) and 2 (1.8%) patients respectively (Table 2). Interferon-ribavirin bitherapy was administered in 78 patients (69%), using pegylated interferon in 38 cases. SVR was obtained in 37 patients (33%). Nineteen out of 113 treated patients (16.8%) became SVR after the first treatment, 15/113 (13.3%) after the second, 3/113 (2.7%) after the third and 0/113 (0%) after the fourth treatment. Among the 37 SVR patients, 11 (29.7%) received only a monotherapy versus 24 (31.6%) in the 76 non SVR group (P = 1.00). Cumulated duration of antiviral treatment (14 mo ± 6 mo vs 16 mo ± 10 mo) did not significantly differ between SVR and non SVR patients (P = 0.99). There was no significant difference between the 2 groups regarding the number and the patterns of treatment (Table 2). Furthermore, there was no heterogeneity among the 2 centres in terms of duration and patterns of treatment.
| Characteristics | All n = 113 | SVR n = 37 | Non SVR n = 76 | P1 |
| Male gender (%) | 69 (61.1%) | 31 (83.8%) | 38 (50.0%) | 0.0005 |
| Age (mean, yr) | 54.1 ± 11.2 | 50.6 ± 11.1 | 55.8 ± 10.9 | 0.02 |
| Alcohol (g/d) | 0.4 | |||
| 0 | 71 (62.8%) | 21 (56.8%) | 50 (65.8%) | |
| < 20 | 20 (17.7%) | 9 (24.3%) | 11 (14.5%) | |
| ≥ 20 | 22 (19.5%) | 7 (18.9%) | 15 (19.7%) | |
| HCV genotype2 | 0.0001 | |||
| 1 | 58 (61.1%) | 11 (35.5%) | 47 (73.4%) | |
| 2 | 10 (10.5%) | 7 (22.6%) | 3 (4.7%) | |
| 3 | 15 (15.8%) | 8 (25.8%) | 7 (10.9%) | |
| 4 | 8 (8.4%) | 1 (3.2%) | 7 (10.9%) | |
| 5 | 2 (2.1%) | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| 6 | 2 (2.1%) | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.9 ± 4.0 | 24.6 ± 3.8 | 26.5 ± 4.0 | 0.015 |
| Platelets (103/mm3) | 149.4 ± 56.2 | 152.9 ± 50.1 | 147.9 ± 59.2 | 0.4 |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 43.0 ± 5.0 | 45.4 ± 6.1 | 41.8 ± 4.0 | 0.001 |
| Bilirubin (μmol/L) | 14.6 ± 9.6 | 14.3 ± 7.5 | 14.8 ± 10.5 | 0.6 |
| Prothrombin activity (%) | 83.7 ± 13.3 | 84.5 ± 12.6 | 83.4 ± 13.8 | 0.7 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 14.4 ± 25.2 | 8.7 ± 12.9 | 17.3 ± 29.2 | 0.008 |
| AST (× ULN) | 2.9 ± 2.0 | 2.4 ± 1.4 | 3.1 ± 2.3 | 0.2 |
| ALT (× ULN) | 3.1 ± 1.9 | 3.1 ± 1.9 | 3.1 ± 2.0 | 0.7 |
| All n = 113 | SVR n = 37 | Non SVR n = 76 | P1 | |
| Follow-up from the first liver biopsy (mean ± SD, yr) | 8.2 ± 3.1 | 8.2 ± 2.7 | 8.2 ± 3.3 | 0.7 |
| Follow-up from the beginning of first treatment (mean ± SD, yr) | 7.7 ± 3.0 | 7.7 ± 2.6 | 7.6 ± 3.1 | 0.6 |
| Number of treatment courses | 0.25 | |||
| 1 | 50 (44.2%) | 19 (51.4%) | 31 (40.8%) | |
| 2 | 42 (37.2%) | 15 (40.5%) | 27 (35.5%) | |
| 3 | 19 (16.8%) | 3 (8.1%) | 16 (21.1%) | |
| 4 | 2 (1.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.6%) | |
| Type of treatment | 1.00 | |||
| α-interferon monotherapy | 35 (31.0%) | 11 (29.7%) | 24 (31.6%) | |
| Bitherapy | 78 (69.0%) | 26 (70.3%) | 52 (68.4%) | |
| Type of bitherapy | < 0.0001 | |||
| α-interferon + ribavirin | 40 (51.3%) | 22 (84.6%) | 18 (34.6%) | |
| Peg-interferon + ribavirin | 38 (48.7%) | 4 (15.4%) | 34 (65.4%) | |
| Total duration of treatment (mo) | 15.3 ± 9.05 | 14.3 ± 6.4 | 15.8 ± 10.1 | 0.4 |
The main patients' baseline characteristics according to final response are reported in Table 1. Compared to non SVR, SVR patients were more often males (84% vs 50%, P = 0.0005), younger (51 ± 11 vs 56 ± 11 years, P = 0.02), leaner (25 vs 26.5 kg/m2, P = 0.015), less frequently infected with HCV genotype 1 (35.5% vs 73.4%, P = 0.0001), and had higher serum albumin levels (45 vs 42 g/L, P = 0.001) and lower AFP serum level (8.7 vs 17.3 ng/ mL, P = 0.008).
The mean duration of follow-up was 7.7 ± 3.0 years from the beginning of the first treatment in the whole population. SVR and non SVR patients did not differ in term of follow-up (7.7 ± 2.6 vs 7.6 ± 3.1 years, P = 0.6) (Table 2).
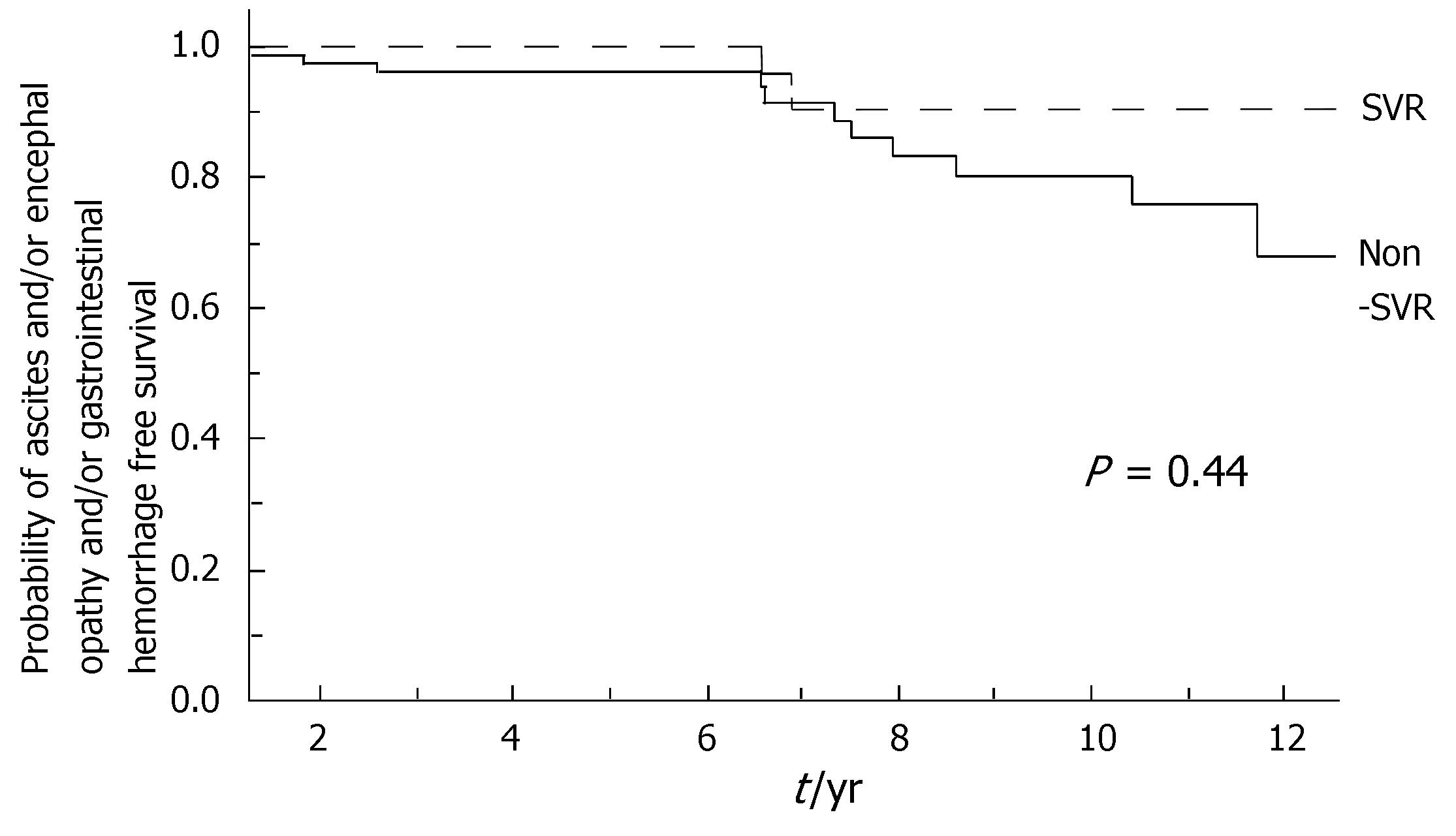
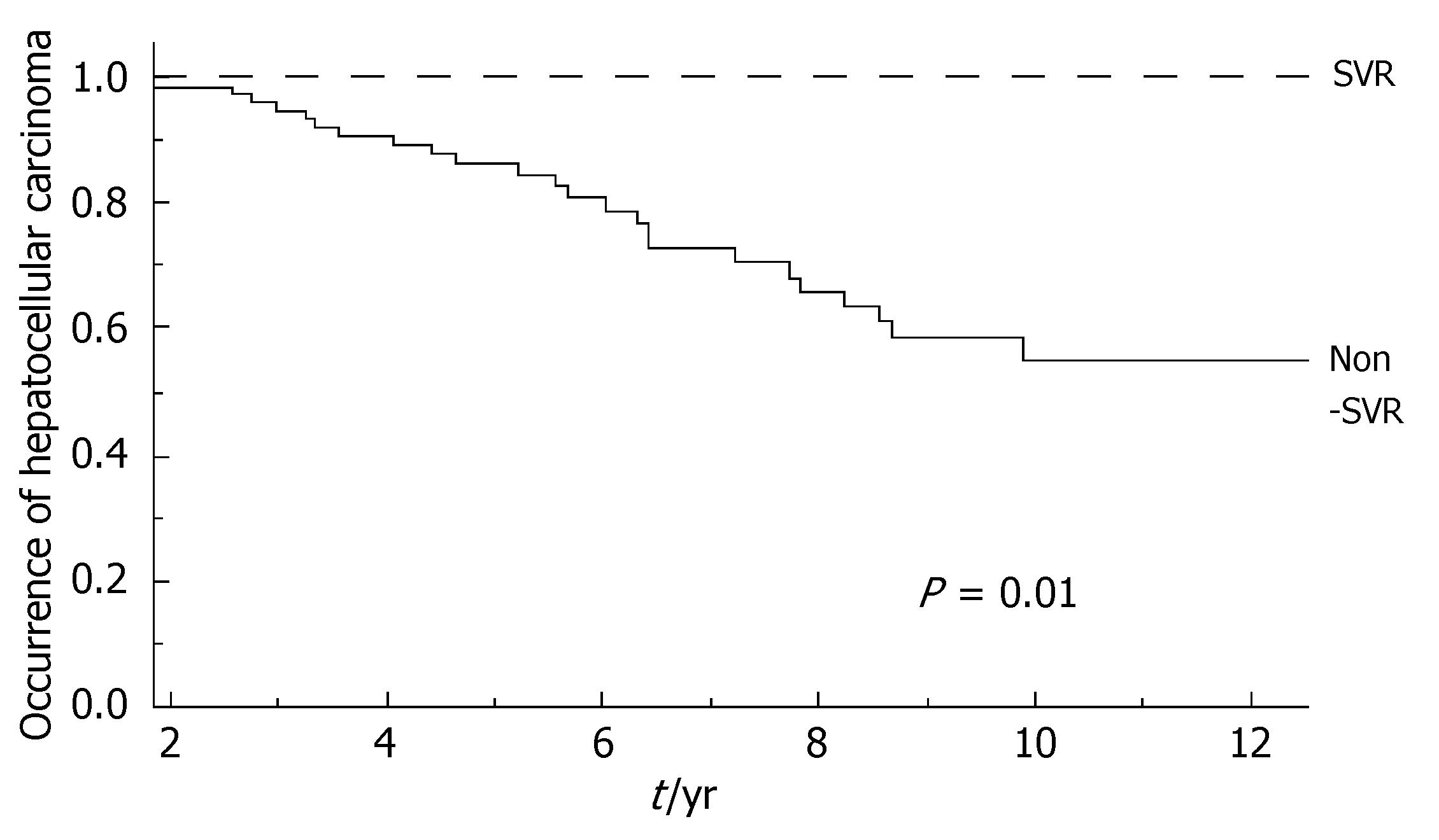
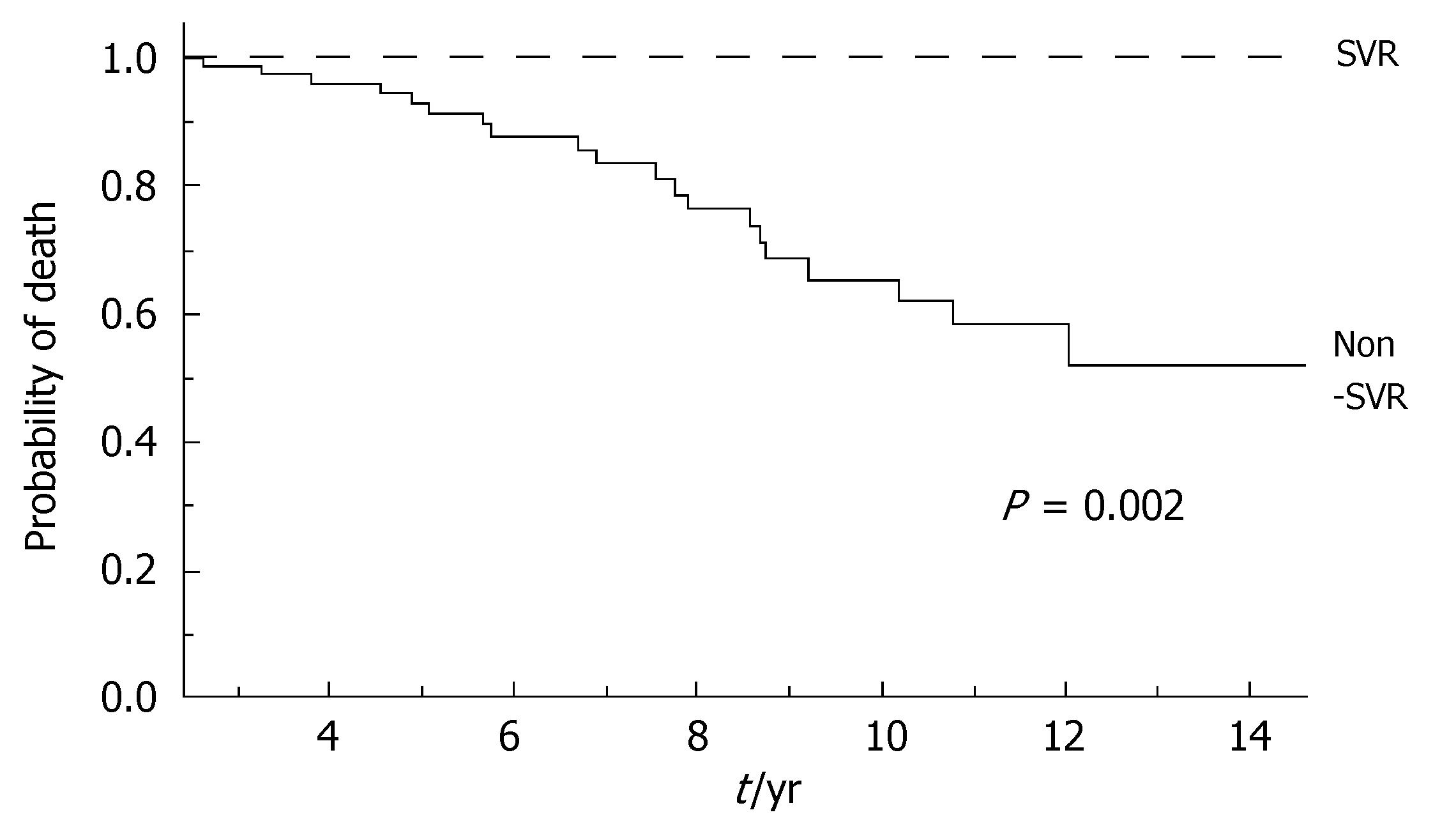
During the follow-up, at least one severe clinical event (HCC or ascites or hepatic encephalopathy or gastrointestinal bleeding or death) occurred in 37 patients with a significant higher frequency in non-SVR (44.7% versus 8.1%, Hazard Ratio 6.3 (95% Confidence Interval 1.9-20.4), P = 0.002). Ascites, hepatic encephalopathy or gastrointestinal bleeding occurred in 11/76 non-SVR and in 3/37 SVR (Figure 1); HCC occurred in 24/76 non-SVR and in 1/37 SVR (Figure 2). The difference between the two groups was significant only for HCC [P = 0.01, Hazard Ratio 13.6 (95% Confidence Interval 1.8-100.5)], while there was no significant difference for the occurrence of other clinical events [ascites, hepatic encephalopathy or gastrointestinal bleeding: P = 0.44, Hazard Ratio 1.65 (95% Confidence Interval 0.46-5.9)] (Table 3). The diagnosis of HCC was assessed by histology in 9 patients (before June 2002) and according to guidelines of European Association for the Study of the Liver[22] in 16 patients (after July 2002). The median number of nodules was 1.5 (range, 1-8) and the median size 30 (range, 10-65) mm. The median times from the beginning of the first treatment until complications were not different in SVR and non-SVR: 6.99 years in SVR and 6.36 years in non-SVR for the occurrence of HCC (P = 0.150); 6.91 years in SVR and 6.78 years in non-SVR for the onset of decompensation or upper GI bleeding (P = 0.531). For the 37 patients who achieved a SVR, the median time from SVR (i.e., 6 mo after the end of the successful antiviral treatment) to the occurrence of complication was 4.79 years for HCC and 4.66 for decompensation. Death rate was significantly higher in case of non-SVR patients (20/76 vs 0/37; P = 0.002, Figure 3). Deaths were mainly related to liver disease and HCC was causative of 45% of the deaths. There was no heterogeneity among the 2 centres in terms of patterns of the duration of follow-up and of the number of events observed.
| SVR n = 37 | Non SVR n = 76 | P | |
| Number of patients with at least one liver-related events or death during follow-up (%) | 31 (8.1%) | 342 (44.7%) | 0.002 |
| Number of patients (%) with | |||
| HCC | 1 (2.7%) | 24 (31.6%) | 0.01 |
| Ascites | 2 (5.4%) | 8 (10.5%) | 0.43 |
| Digestive haemorrhage | 1 (2.7%) | 4 (5.3%) | 0.62 |
| Encephalopathy | 0 | 2 (5.4%) | 0.56 |
| Number of deaths | 0 | 20 (26.3%) | 0.002 |
| Liver-related | 0 | 17 | |
| Liver failure | 0 | 7 | |
| GI haemorrhage | 0 | 1 | |
| HCC | 0 | 9 | |
| Non liver-related | 0 | 3 | |
| Suicide | 0 | 1 | |
| Miscellaneous | 0 | 2 |
The multivariate analysis (Cox model) found two independent predictive factors for clinical events: SVR [P = 0.001, HR 7.1 (95% CI 2.2; 23.2)] and duration of treatment [P = 0.001, HR 0.93 (95% CI 0.89; 0.97)]. In other words, the Hazard for HCC was 7% lower for each additional year of treatment.
There was no significant difference with age, gender, or viral genotype for HCC occurrence.
Our study demonstrates a significant difference in long-term outcome between initially uncomplicated HCV cirrhotic patients with and without SVR after antiviral treatment. Over a mean follow-up period of 7.7 years, there were no deaths and virtually no severe clinical events in patients with SVR. At the opposite, HCC and liver decompensation occurred in patients without SVR with incidence rates similar to those previously reported in untreated cirrhotic patients[23].. We should emphasize that HCC was carefully screened before treatment, which eliminates HCC of small size appearing a few months after antiviral treatment.
Several studies performed in patients with chronic hepatitis C have suggested that successful antiviral treatment could result in a dramatic decrease in severe clinical events and mortality, life expectancy of patients with SVR being close to general population[6,9,10,24,25]. However, those studies used only interferon-α. In the past, interferon-α monotherapy resulted in a small rate of SVR in patients with cirrhosis due to low virological efficacy and poor tolerance resulting in a high rate of premature interruption of treatment. Accordingly, in the studies including a subset of cirrhotic patients, SVR rates in those populations did not usually exceed 15%.
Our study has several differences. Firstly, it was strictly restricted to patients with histological proven cirrhosis. This population is clearly at high risk of severe short-term complications occurrence as demonstrated by previous studies[1,26]. Secondly bitherapy using interferon-α and ribavirin was used in about 70% of cases in our study, with pegylated interferon in 38 cases. Thirdly antiviral treatment was repeated each time it was possible due to the absence of a priori contra-indication to treatment in those patients. Overall, after one (51.4%) or repeated (48.6%) antiviral treatments, 33% of our patients achieved HCV eradication, which is a rate twice higher than those obtained in previous studies.
Due to the lack of randomization, patients with SVR were obviously different from non SVR. Particularly, they were younger, more often men and significantly more frequently infected with HCV genotypes 2 or 3 than non SVR patients, as observed by Bruno et al[10]. Excepted male gender, these factors had been previously identified as predictive factors of SVR and it is not surprising to identify them in our study. The reduced rate of serious events in patients with SVR could result more from the presence of protective factors than from antiviral treatment. Patients with SVR were younger and this could result in a lower risk to develop complications as demonstrated for HCC occurrence. The role of genotype in spontaneous outcome of HCV-related cirrhosis although still debated does not seem to be a determinant factor in this setting and the male sex is a favouring factor of fibrosis progression and HCC occurrence. Subsequently the absence of serious event seems related to the complete response to treatment.
Several successive treatment courses have been performed in most of the patients, representing a cumulated time of treatment of 15.3 ± 9 mo. It could explain why clinical event incidence was decreased with a linear fashion from the start of treatment even if viral eradication was obtained later with further treatment. About half of SVR patients had no HCV eradication after the first course of treatment. It could seem questionable that severe events incidence have been reduced even before eradication was achieved in those patients. We postulate that it could reflect a more complete blockade of HCV replication in those patients occurring from the first course of treatment and due to higher sensitivity of virus. The fact that patients received similar duration of treatment in both groups is in favour of this hypothesis and against a non specific effect of treatment such as antifibrotic and/or antiproliferative effects of interferon.
The association between SVR and a significantly reduced number of clinical events has been previously reported[10,16,17,25]. However, this result cannot be applied to the whole population of patients with HCV-cirrhosis. In this study as in others, patients were selected and those with initial major contra-indication to treatment were excluded. These patients are probably the most severe with the higher risk of developing complications such as HCC. In addition, due to the selection of patients, the risk of death related to co morbidity was very low in our study.
Even in case of SVR, the periodic follow-up of cirrhotic patients should be recommended, particularly HCC screening as it is worth noting that the only HCC observed in SVR occurred 4.8 years after the achievement of viral clearance. In spite of a significant decrease in the incidence of HCC in case of SVR, several isolated cases of HCC were reported 4.5 to 6.6 years after the achievement of a SVR[27-30].
In conclusion, repeated antiviral therapy actually results in SVR in 33% of patients with HCV-cirrhosis. Virological cure seems to be associated with a strong decrease in the incidence of complications particularly HCC. These results are a strong argument to perform and repeat antiviral treatments in patients with compensated cirrhosis.
HCV cirrhosis is a life threatening disease with annual incidences of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), decompensation and death reaching around 3%, 4% and 3% respectively. The achievement of a sustained viral eradication (SVR) with the initially recommended 24-wk course of interferon-α monotherapy is associated with a slight preventive effect on HCC occurrence but its influence on the incidence of decompensation or death was less studied and more controversial.
Subsequent progresses in the field of HCV treatment (including extension of therapy to 48 wk, the combination of interferon-α with ribavirin, and the use of pegylated interferon) have created a new perspective for patients with HCV-cirrhosis because of the higher rate of SVR. Thus, the clinical long-term benefit of antiviral treatment in patients with HCV cirrhosis needed to be re-assessed.
Long-term effect of standard interferon-α plus ribavirin therapy on incidence of HCC in patients with HCV cirrhosis was recently studied in Chinese patients. Our results are the first in Western patients. In addition, death was a clinical end-point and we showed a significant reduced mortality in patients who achieved SVR.
While firm recommandations on antiviral treatment for patients with compensated HCV-cirrhosis was not made by international conferences, this is a strong argument to perform and repeat antiviral bitherapy in these patients to achieve SVR.
Sustained virological response (SVR) is defined by the absence of detectable serum HCV RNA six months after the end of antiviral treatment and is associated with a durable viral eradication in most patients. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most frequent primary liver cancer and the first cause of death in patients with HCV-cirrhosis.
The manuscript by El Barks et al demonstrates that antiviral treatment in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis decreases the incidence of HCC. The data provided argue for an antiviral treatment in HCV patients. The study was well performed and the data are clearly presented.
S- Editor Zhu LH L- Editor Alpini GD E- Editor Wang HF
| 1. | Benvegnù L, Gios M, Boccato S, Alberti A. Natural history of compensated viral cirrhosis: a prospective study on the incidence and hierarchy of major complications. Gut. 2004;53:744-749. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 328] [Cited by in RCA: 318] [Article Influence: 15.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Degos F, Christidis C, Ganne-Carrie N, Farmachidi JP, Degott C, Guettier C, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M, Chevret S. Hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: time to occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and death. Gut. 2000;47:131-136. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 264] [Cited by in RCA: 256] [Article Influence: 10.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Fattovich G, Giustina G, Degos F, Tremolada F, Diodati G, Almasio P, Nevens F, Solinas A, Mura D, Brouwer JT. Morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type C: a retrospective follow-up study of 384 patients. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:463-472. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1013] [Cited by in RCA: 957] [Article Influence: 34.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Serfaty L, Aumaître H, Chazouillères O, Bonnand AM, Rosmorduc O, Poupon RE, Poupon R. Determinants of outcome of compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998;27:1435-1440. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 291] [Cited by in RCA: 278] [Article Influence: 10.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Suzuki F, Tsubota A, Arase Y, Murashima N, Chayama K, Kumada H. Long-term interferon therapy for 1 year or longer reduces the hepatocellular carcinogenesis rate in patients with liver cirrhosis caused by hepatitis C virus: a pilot study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;16:406-415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Gramenzi A, Andreone P, Fiorino S, Cammà C, Giunta M, Magalotti D, Cursaro C, Calabrese C, Arienti V, Rossi C. Impact of interferon therapy on the natural history of hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis. Gut. 2001;48:843-848. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Effect of interferon-alpha on progression of cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. International Interferon-alpha Hepatocellular Carcinoma Study Group. Lancet. 1998;351:1535-1539. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 198] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Benvegnù L, Chemello L, Noventa F, Fattovich G, Pontisso P, Alberti A. Retrospective analysis of the effect of interferon therapy on the clinical outcome of patients with viral cirrhosis. Cancer. 1998;83:901-909. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Mazzella G, Accogli E, Sottili S, Festi D, Orsini M, Salzetta A, Novelli V, Cipolla A, Fabbri C, Pezzoli A. Alpha interferon treatment may prevent hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV-related liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1996;24:141-147. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 209] [Cited by in RCA: 209] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Bruno S, Stroffolini T, Colombo M, Bollani S, Benvegnù L, Mazzella G, Ascione A, Santantonio T, Piccinino F, Andreone P. Sustained virological response to interferon-alpha is associated with improved outcome in HCV-related cirrhosis: a retrospective study. Hepatology. 2007;45:579-587. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 506] [Cited by in RCA: 475] [Article Influence: 26.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kobayashi S, Takeda T, Enomoto M, Tamori A, Kawada N, Habu D, Sakaguchi H, Kuroda T, Kioka K, Kim SR. Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C who had a sustained virological response to interferon therapy: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study of 1124 patients. Liver Int. 2007;27:186-191. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Fartoux L, Degos F, Trépo C, Goria O, Calès P, Tran A, Buffet C, Poynard T, Capron D, Raabe JJ. Effect of prolonged interferon therapy on the outcome of hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis: a randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:502-507. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Nishiguchi S, Kuroki T, Nakatani S, Morimoto H, Takeda T, Nakajima S, Shiomi S, Seki S, Kobayashi K, Otani S. Randomised trial of effects of interferon-alpha on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic active hepatitis C with cirrhosis. Lancet. 1995;346:1051-1055. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 644] [Cited by in RCA: 607] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Nishiguchi S, Shiomi S, Nakatani S, Takeda T, Fukuda K, Tamori A, Habu D, Tanaka T. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic active hepatitis C and cirrhosis. Lancet. 2001;357:196-197. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 191] [Cited by in RCA: 179] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Valla DC, Chevallier M, Marcellin P, Payen JL, Trepo C, Fonck M, Bourliere M, Boucher E, Miguet JP, Parlier D. Treatment of hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis: a randomized, controlled trial of interferon alfa-2b versus no treatment. Hepatology. 1999;29:1870-1875. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 158] [Cited by in RCA: 151] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Papatheodoridis GV, Davies S, Dhillon AP, Teixeira R, Goulis J, Davidson B, Rolles K, Dusheiko G, Burroughs AK. The role of different immunosuppression in the long-term histological outcome of HCV reinfection after liver transplantation for HCV cirrhosis. Transplantation. 2001;72:412-418. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Cammà C, Giunta M, Andreone P, Craxì A. Interferon and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in viral cirrhosis: an evidence-based approach. J Hepatol. 2001;34:593-602. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 285] [Cited by in RCA: 294] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Shiratori Y, Ito Y, Yokosuka O, Imazeki F, Nakata R, Tanaka N, Arakawa Y, Hashimoto E, Hirota K, Yoshida H. Antiviral therapy for cirrhotic hepatitis C: association with reduced hepatocellular carcinoma development and improved survival. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:105-114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 226] [Cited by in RCA: 207] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975-982. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4847] [Cited by in RCA: 4747] [Article Influence: 206.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958-965. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4736] [Cited by in RCA: 4558] [Article Influence: 189.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Hung CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, Wang JH, Hu TH, Tung HD, Chen CH, Chen WJ, Changchien CS. Long-term effect of interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin therapy on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13:409-414. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 89] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, Christensen E, Pagliaro L, Colombo M, Rodés J. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol. 2001;35:421-430. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3252] [Cited by in RCA: 3240] [Article Influence: 135.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Heathcote EJ. Prevention of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S294-S302. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Cammà C, Di Marco V, Lo Iacono O, Almasio P, Giunta M, Fuschi P, Vaccaro A, Fabiano C, Magrin S, Di Stefano R. Long-term course of interferon-treated chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1998;28:531-537. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Veldt BJ, Saracco G, Boyer N, Cammà C, Bellobuono A, Hopf U, Castillo I, Weiland O, Nevens F, Hansen BE. Long term clinical outcome of chronic hepatitis C patients with sustained virological response to interferon monotherapy. Gut. 2004;53:1504-1508. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Sangiovanni A, Prati GM, Fasani P, Ronchi G, Romeo R, Manini M, Del Ninno E, Morabito A, Colombo M. The natural history of compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus: A 17-year cohort study of 214 patients. Hepatology. 2006;43:1303-1310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 433] [Cited by in RCA: 444] [Article Influence: 23.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Yamaura T, Matsumoto A, Rokuhara A, Ichijo T, Tanaka E, Hanazaki K, Kajikawa S, Kiyosawa K. Development of small hepatocellular carcinoma in a patient with chronic hepatitis C after 77 months of a sustained and complete response to interferon therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:1229-1235. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Yamaguchi K, Omagari K, Kinoshita H, Yoshioka S, Furusu H, Takeshima F, Nanashima A, Yamaguchi H, Kohno S. Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in a patient with chronic hepatitis C after 6 years of a sustained and complete response to IFN-alpha. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999;29:207-209. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Yamada M, Ichikawa M, Matsubara A, Ishiguro Y, Yamada M, Yokoi S. Development of small hepatocellular carcinoma 80 months after clearance of hepatitis C virus with interferon therapy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;12:1029-1032. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Miyano S, Togashi H, Shinzawa H, Sugahara K, Matsuo T, Takeda Y, Saito K, Saito T, Ishiyama S, Kaneko M. Case report: Occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma 4.5 years after successful treatment with virus clearance for chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;14:928-930. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |