Published online Oct 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5380
Revised: August 3, 2007
Accepted: September 1, 2007
Published online: October 28, 2007
AIM: To elucidate the influences of H pylori infection on oral iron treatment for iron deficiency anemia (IDA).
METHODS: A total of 86 patients were divided into two groups: group A, receiving ferrous succinate combined with triple therapy for H pylori eradication, and group B (control), treated with ferrous succinate only. During treatment of IDA, dynamic changes in hemoglobin (Hb) level, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), serum iron (SI), and serum ferritin (SF) were compared between the groups.
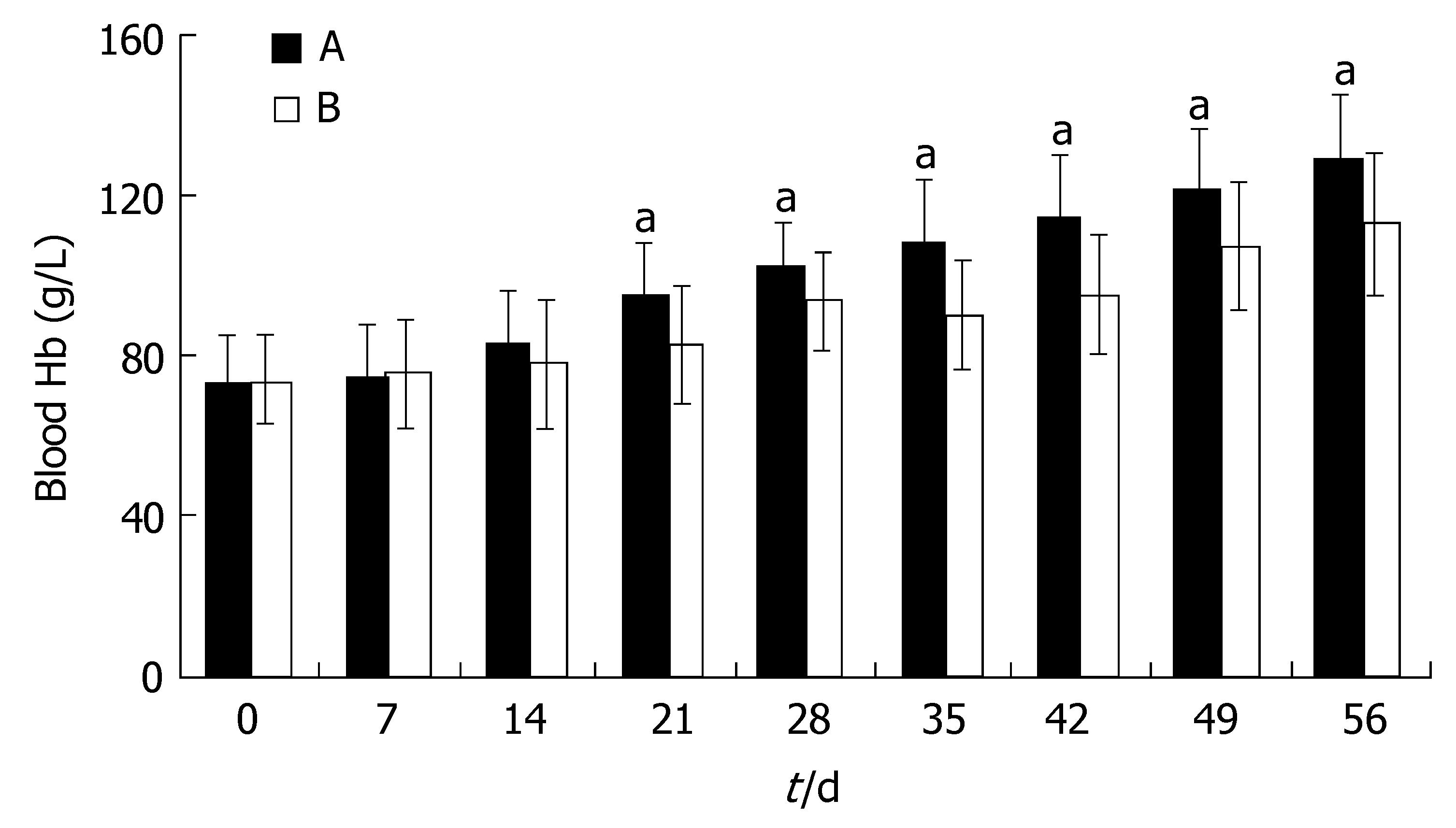
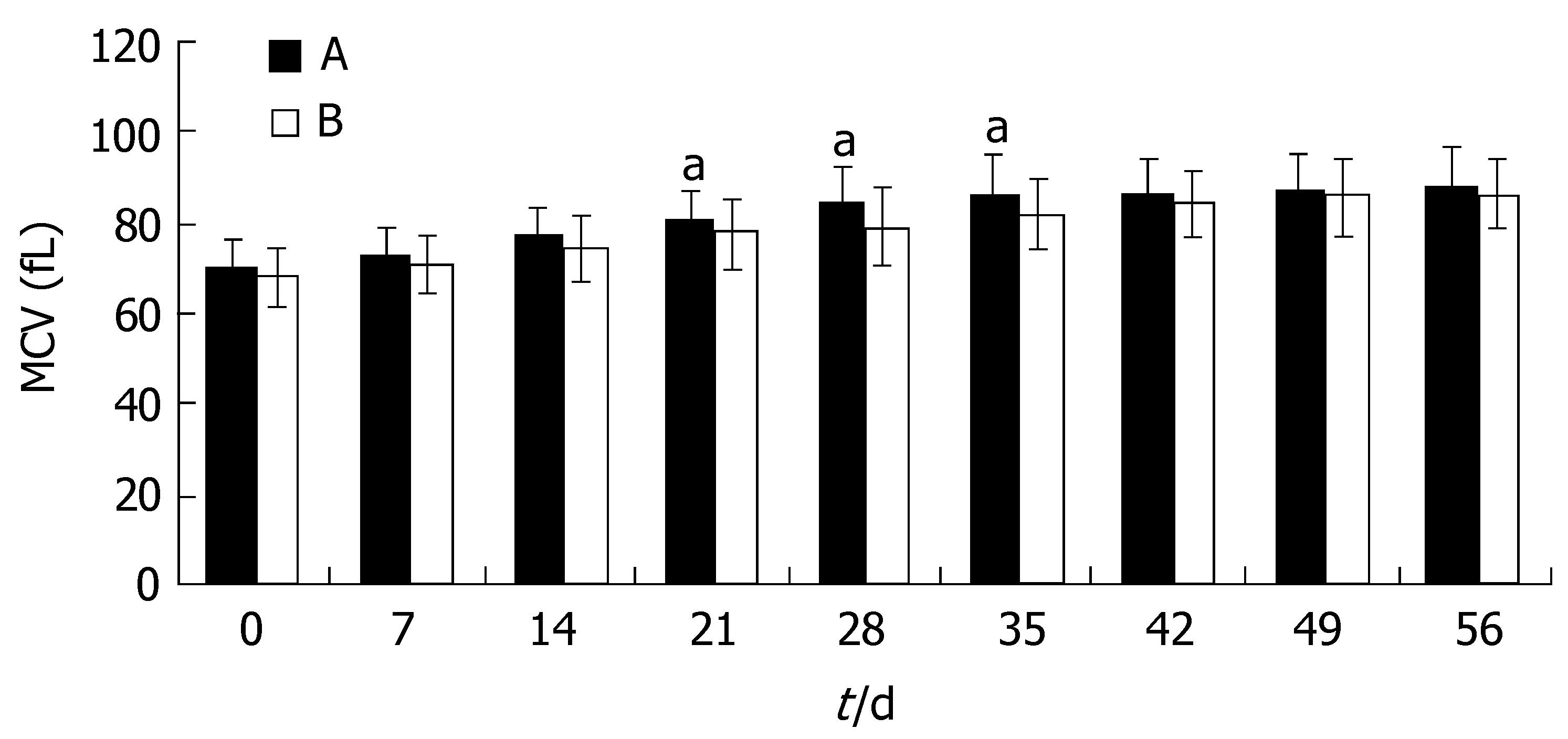
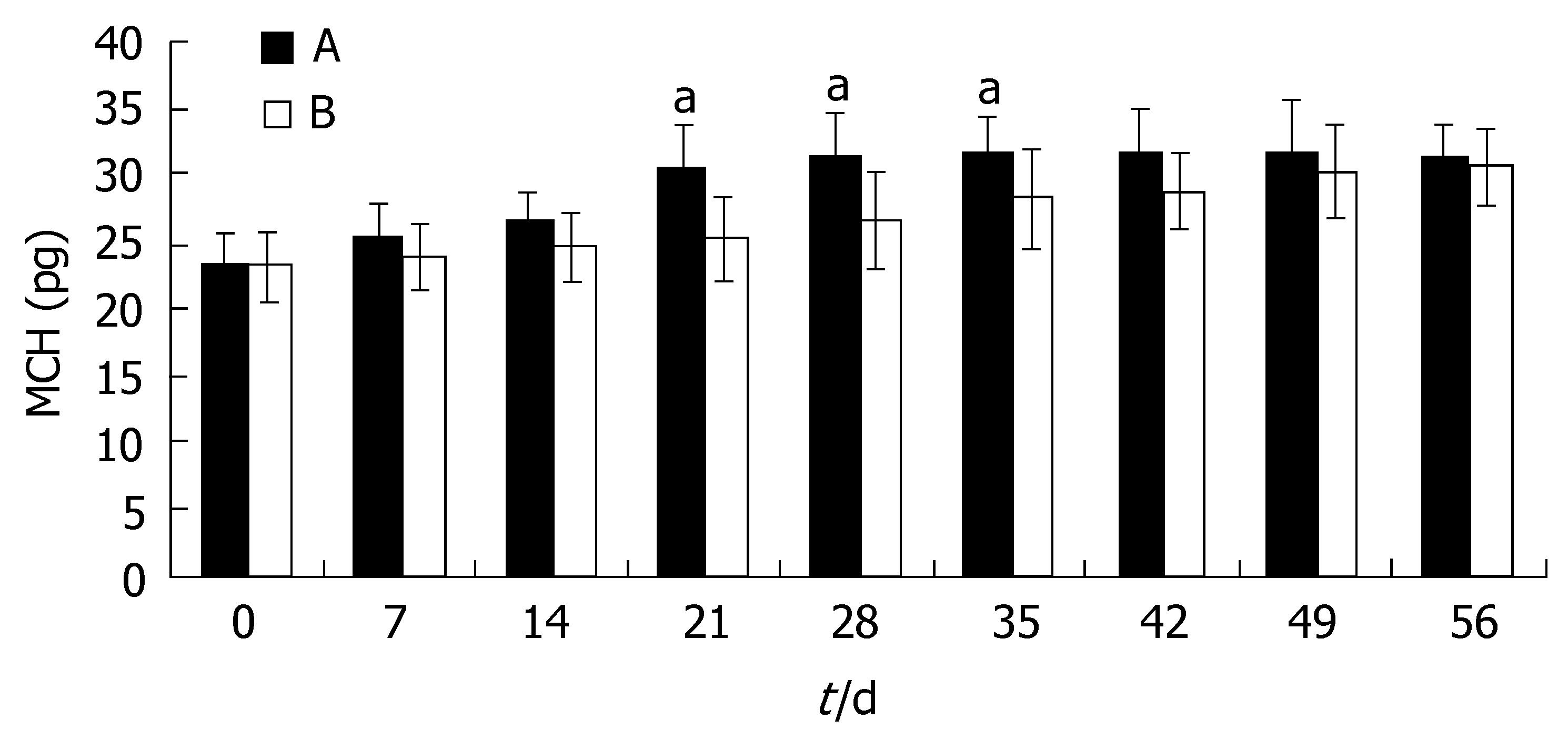
RESULTS: Hb was slightly higher in group A at d 14 after the start of triple therapy for H pylori eradication(P > 0.05). After the therapy, the increase of Hb in group A became significantly faster than that in group B (P < 0.05). At d 56, the mean Hb in group A returned to the normal level, however, in group B, it was lower than that in group A (P < 0.05) although it had also increased compared with that before oral iron treatment. The MCV and MCH in group A recovered to the normal level, and were much higher than those in group B (P < 0.05) at d 21. In Group B, the MCV and MCH remained at lower than normal levels until d 42 after the start of therapy. And then, they reached a plateau in both groups and the differences disappeared (P > 0.05). The SF in group A was higher than that in group B (P < 0.05) 28 d after the treatment and its improvement was quicker in group A (P < 0.05) , and the difference between the two groups was even more significant (P < 0.01) at d 56. The SI in group A was higher than that in group B (P < 0.05) at d 14 and this persisted until d 56 when the follow-up of this research was finished.
CONCLUSION: Treatment of H pylori can enhance the efficacy of ferrous succinate therapy in IDA patients with H pylori-positive chronic gastritis.
-
Citation: Chen LH, Luo HS. Effects of
H pylori therapy on erythrocytic and iron parameters in iron deficiency anemia patients withH pylori -positive chronic gastristis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(40): 5380-5383 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i40/5380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5380
Spontaneous iron excretion in adults is minimal and iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is generally attributed to abnormal blood loss[1]. IDA is often caused by gastrointestinal bleeding due to peptic ulcer and chronic gastritis, or in women of reproductive age by increased menstrual flow and the greater requirements of pregnancy. Recently, several seroepidemiological studies have suggested a link between IDA and H pylori infection[2,3]. A high percentage of H pylori-positive IDA patients exhibit atrophic changes in the gastric body, and the remainders have chronic superficial gastritis extending to the fundic mucosa.
H pylori infection has even been implicated as a cause of IDA refractory to oral iron treatment[4,5]. Some patients with refractory IDA have no gastrointestinal symptoms but H pylori gastritis, as the only cause of their anemia[6]. Most dietary iron is in the non-hemic ferric form, and an acidic intragastric pH is needed to reduce it to the ferrous form for absorption. This reaction is promoted by gastric acidity and ascorbic acid (AA), which is thus considered the most potent regulator of iron absorption[7]. Patients with H pylori gastritis showed an increase in intragastric pH with a median of > 3, a pH that is known to be critical in the process of iron absorption. Moreover, AA is actively secreted from plasma to the gastric juice[8], but the concentration of AA in the gastric juice of patients with H pylori gastritis and IDA is clearly reduced in comparison with both healthy and non-anemic H pylori-positive controls[9-11].
The availability of convenient, non-invasive methods for identifying H pylori gastritis has greatly facilitated the recognition of infected patients, resulting in progressive awareness of its influences and possible role in the causation of IDA[12]. Therefore, we first examined the prevalence of H pylori infection and serum markers of iron deficiency. We then evaluated the effects of subsequent H pylori eradication on the response to oral iron therapy, which could provide valuable information for further clinical applications.
From January 2002 to December 2005, 86 IDA adult patients with H pylori-positive chronic gastritis were enrolled. The participants comprised 36 women and 50 men; median age 53 years, range 18-76. According to Sydney System, the patients were diagnosed as having atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, or antral versus body gastritis, in 34, 27, and 25 cases, respectively. According to the criteria[13], IDA was defined as hemoglobin (Hb) concentration < 120 g/L in the men and< 110 g/L in the women, serum ferritin (SF) < 12 μg/L, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) < 27 pg, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV) < 80 fL. Obvious causes of blood loss, such as active gastrointestinal hemorrhage, menometorrhagia or heavy menstrual loss, and any other non-gastrointestinal disease likely to cause IDA, were exclusion criteria for this study. Also excluded from the study protocol were patients with previous gastric surgery, and those who received anti-H pylori treatment or anti-secretory drugs before. Patients who were lactating or pregnant and those with malnutrition or cancer were also excluded.
The 14C-urease breath test was performed as described previously[14]. Briefly, the patients fasted overnight and were then given urea labeled with 37 kBq of 14C dissolved in water. Breath samples were collected before and 15 min after ingestion, when enzymolysis of labeled urea occurred and 14CO2 had been released into the peripheral circulation. The 14CO2 in these samples was trapped in 1 mmol/L of hyamine hydroxide in ethanol and transferred into scintillation liquid. The 14C content was measured in Bq mode using a liquid β-scintillation counter (Headway, China). Samples with < 3.33 Bq were considered negative for H pylori, while samples with > 3.33 Bq were considered positive. The peripheral hemogram including MCH and MCV was measured with a Sysmex automated analyzer (Kobe, Japan). Biochemical assays for serum iron (SI) and Hb were performed as routine. SF was determined with a chemiluminescent immunometric analyzer and kit from Bayer Co. (Germany).
The 86 patients were randomly divided into two groups of equal size. Group A comprised 43 cases and received oral iron treatment combined with triple therapy for H pylori eradication, while the 43 cases in group B received oral iron treatment only as controls. Oral iron treatment comprised ferrous succinate (with an Fe2+ content of 34%-36%) 200 mg supplemented with ascorbic acid 100 mg three times daily. Treatment was given until the SF recovered to normal. Triple therapy for H pylori eradication included deutero-bismuth citrate 240 mg × 2/d, amoxicillin 500 mg × 2/d, and metronidazole 400 mg × 2/d for 2 wk; in all cases, H pylori was eradicated.
The mean Hb, MCH, and MCV in the peripheral blood of the two groups were recorded before and at d 0, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, and 56 after iron treatment. SI and SF were compared before and at d 0, 14, 28, 42, and 56.
Each assay was made at least three times and data were expressed as the mean ± SD. The differences between groups were determined using t test for paired analysis.P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Hb was slightly higher in group A at d 14 after the start of triple therapy for H pylori eradication, but the difference was not significant (P > 0.05). After the complete course of triple therapy, the increase of Hb in group A became significantly faster than that in group B (P < 0.05). At d 56, the mean Hb in group A returned to the normal level referred to the criteria. In group B, the mean Hb had also increased compared with that before oral iron treatment, but it was still lower than that in group A (P < 0.05, Figure 1).
Similar to the trend seen for Hb, the increase of MCV and MCH in group A was not significantly greater than that in group B (P > 0.05). At d 21, the MCV and MCH in group A became normal, and were much higher than those in group B (P < 0.05). In group B, the MCV and MCH remained at lower than normal levels until 42 d after the start of therapy. At this time, the MCV and MCH reached a plateau in both groups and the differences disappeared(P > 0.05, Figures 2 and 3).
There were no significant differences in parameters of iron status between the two groups at the start of treatment (P > 0.05), but after 28 d the SF in group A was higher than that in group B (P < 0.05). Thereafter, the improvement of SF was much quicker in group A, and at d 56 the difference between the two groups was even more significant (P < 0.01). At d 14, the SI in group A was higher than in group B (P < 0.05) and this persisted until 56 d after the start of oral iron treatment, when the follow-up of this research was finished (Table 1).
H pylori infection has been reported to have various manifestations in adolescents and adults, including IDA. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial performed in adolescents with IDA and H pylori infection suggested that SF was significantly lower in the H pylori-infected group and that H pylori eradication led to resolution of iron deficiency[15,16]. A large serosurvey of H pylori in adults also found that SF was significantly lower in adults positive for H pylori IgG than that in non-infected controls[17,18]. Based on our medical records of adult patients with chronic gastritis, we found that IDA occurred more frequently in H pylori-positive cases. The coexistence of H pylori gastritis in the 86 IDA adult patients enrolled in this study was determined by endoscopy and the urease breath test. To avoid influences from other clinical factors, the subjects were selected according to strict criteria.
It has recently been shown that extension of gastritis to the corporal mucosa occurs in a higher percentage of patients with H pylori infection and IDA compared with non-anemic H pylori-infected controls[19]. The blood loss in chronic gastritis, and bleeding from duodenal or gastric ulcers related to H pylori infection, plays an important role in the development of iron deficiency in adults. In response to H pylori chronic gastric inflammation, the epithelial cells in the mucosa are damaged, leading to detachment and apoptosis. In the absence of bleeding lesions, the possible mechanisms by which H pylori is involved in the development of IDA remain unclear. Preliminary studies suggest that the growth and proliferation of H pylori requires iron from the host and that some H pylori strains have a specific ability to interfere with iron metabolism by binding iron to their outer membrane proteins[20]. However, other studies have demonstrated that neither virulence factors such as Cag-A4 nor mutations in the bacterial genes involved in iron uptake are associated with IDA. Given the high prevalence of H pylori infection, this hypothesis cannot explain why not all patients with H pylori gastritis develop IDA[21].
Besides the occult gastrointestinal bleeding and competition for dietary iron, H pylori infection can affect the gastric body and initiate the development of atrophic body gastritis that can in turn cause decreased gastric acid secretion and increased intragastric pH[5,22]. H pylori infection adversely influences the composition of the gastric juice; for example, in terms of its acidity and ascorbate content, both of which are critical for normal iron absorption[23]. These findings suggest that the physiological mechanisms that are necessary for the absorption of alimentary iron in the duodenal mucosa are impaired in patients with H pylori gastritis and IDA. Thus, we planned to determine the relationship between H pylori infection status and indices of IDA such as the peripheral hemogram and SI. These indices were compared between group A, which received triple therapy combined with oral iron treatment, and group B, which received oral iron treatment only.
Before the completion of H pylori eradication, there were no significant differences in parameters reflecting iron status between the two groups, though the indices were slightly higher in group A. After the 2 wk triple therapy was finished, our observations indicate that the response to oral iron treatment was significantly greater in group A than in group B. Since supplementation with ascorbic acid has been commonly shown to reduce the pH of gastric juice thereby increasing iron absorption, its influence was not evaluated in this research. It has been clearly demonstrated in previous studies that H pylori eradication can reverse the negative effect of H pylori infection on iron absorption and lead to improvement of IDA in case series and in clinical trials in both children and adults[4,15,16]. Successful H pylori eradication resulted first in a significant post-treatment decrease of serum gastrin and H pylori IgG antibody titers, and then an increase in the peripheral hemogram and SI. This normalization of iron metabolism in H pylori-positive patients increased the MCV and MCH to a plateau similar to the normal level.
The H pylori gastritis is increasingly considered a possible cause of IDA refractory to oral iron treatment, and eradication of H pylori may be followed by an improved response to oral iron in previously refractory IDA patients[4,5]. In this study, H pylori infection slowed the trend of recovery from IDA recovery, but the indices in group B still reached normal levels. In our opinion, H pylori eradication is necessary for the resolution of IDA with a lower risk of recurrence. Patients with H pylori infection and IDA should receive oral iron and triple therapy simultaneously.
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is often caused by gastrointestinal bleeding due to peptic ulcer and chronic gastritis. H pylori infection, which has been proved to play the main role in peptic ulcer and chronic gastritis, has been implicated as a cause of IDA refractory to oral iron treatment. The role of H pylori and its eradication in IDA in patients with H pylori-positive gastritis has been unclear.
In some cases, refractory IDA is not sensitive to oral iron treatment, especially in patients with H pylori-positive gastritis. It is important to elucidate the relation of IDA to H pylori infection and the effect of H pylori eradication on the treatment of IDA.
Related publications are rare.
This study showed that the H pylori infection could slow the trend of recovery from IDA and that H pylori eradication is necessary for the resolution of IDA with a lower risk of recurrence. The efficacy of simultaneous oral iron and triple therapy was evaluated.
For the treatment of IDA in patients with H pylori-positive chronic gastritis, it is effective and necessary to eradicate H pylori infection, which can lead to satisfactory recovery of this category of IDA.
H pylori infection: H pylori infection is the main cause of peptic ulcer and chronic gastritis. IDA: iron deficiency anemia is generally attributed to abnormal blood loss, which is often caused by gastrointestinal bleeding due to peptic ulcer and chronic gastritis, or in women of reproductive age by increased menstrual flow and the greater requirements of pregnancy.
This is a good review on an interesting topic with an appropriate number of patients. The major point greatly enhances the conclusions.
S- Editor Ma N L- Editor Ma JY E- Editor Li JL
| 1. | Ross EM. Evaluation and treatment of iron deficiency in adults. Nutr Clin Care. 2002;5:220-224. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Ciacci C, Sabbatini F, Cavallaro R, Castiglione F, Di Bella S, Iovino P, Palumbo A, Tortora R, Amoruso D, Mazzacca G. Helicobacter pylori impairs iron absorption in infected individuals. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:455-460. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Ashorn M. Acid and iron-disturbances related to Helicobacter pylori infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;38:137-139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Konno M, Muraoka S, Takahashi M, Imai T. Iron-deficiency anemia associated with Helicobacter pylori gastritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000;31:52-56. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Hacihanefioglu A, Edebali F, Celebi A, Karakaya T, Senturk O, Hulagu S. Improvement of complete blood count in patients with iron deficiency anemia and Helicobacter pylori infection after the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004;51:313-315. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Annibale B, Capurso G, Chistolini A, D'Ambra G, DiGiulio E, Monarca B, DelleFave G. Gastrointestinal causes of refractory iron deficiency anemia in patients without gastrointestinal symptoms. Am J Med. 2001;111:439-445. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 152] [Cited by in RCA: 142] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Conrad ME, Umbreit JN. Iron absorption and transport-an update. Am J Hematol. 2000;64:287-298. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Schulz HU, Schürer M, Krupp S, Dammann HG, Timm J, Gessner U. Effects of acetylsalicylic acid on ascorbic acid concentrations in plasma, gastric mucosa, gastric juice and urine--a double-blind study in healthy subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004;42:481-487. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Capurso G, Ricci R, Panzuto F, Baccini F, Passi S, Di Giulio E, Delle Fave G, Annibale B. Intragastric ascorbic but not uric acid is depleted in relation with the increased pH in patients with atrophic body gastritis and H. pylori gastritis. Helicobacter. 2003;8:300-306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Park JH, Kim SY, Kim DW, Lee WG, Rhee KH, Youn HS. Correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and vitamin C levels in whole blood, plasma, and gastric juice, and the pH of gastric juice in Korean children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003;37:53-62. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Furuta T, Baba S, Takashima M, Futami H, Arai H, Kajimura M, Hanai H, Kaneko E. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric juice pH. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:357-363. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Kato S, Nakayama K, Minoura T, Konno M, Tajiri H, Matsuhisa T, Iinuma K. Comparison between the 13C-urea breath test and stool antigen test for the diagnosis of childhood Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:1045-1050. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Zhang ZN, Shen T. Standard diagnosis and curative effect of hematologic disease. Beijing: Science Press 1998; 10-19. |
| 14. | Mirbagheri SA, Sohrabpour AA, Hasibi M, Moghimi B, Mohamadnejad M. 14C-urea breath test in patients undergoing anti-tuberculosis therapy. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:1712-1714. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Choe YH, Kim SK, Son BK, Lee DH, Hong YC, Pai SH. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of Helicobacter pylori eradication for iron-deficiency anemia in preadolescent children and adolescents. Helicobacter. 1999;4:135-139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 130] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Choe YH, Kwon YS, Jung MK, Kang SK, Hwang TS, Hong YC. Helicobacter pylori-associated iron-deficiency anemia in adolescent female athletes. J Pediatr. 2001;139:100-104. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 84] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Milman N, Rosenstock S, Andersen L, Jørgensen T, Bonnevie O. Serum ferritin, hemoglobin, and Helicobacter pylori infection: a seroepidemiologic survey comprising 2794 Danish adults. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:268-274. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Parkinson AJ, Gold BD, Bulkow L, Wainwright RB, Swaminathan B, Khanna B, Petersen KM, Fitzgerald MA. High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in the Alaska native population and association with low serum ferritin levels in young adults. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000;7:885-888. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Capurso G, Lahner E, Marcheggiano A, Caruana P, Carnuccio A, Bordi C, Delle Fave G, Annibale B. Involvement of the corporal mucosa and related changes in gastric acid secretion characterize patients with iron deficiency anaemia associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15:1753-1761. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Pérez-Pérez GI, Israel DA. Role of iron in Helicobacter pylori: its influence in outer membrane protein expression and in pathogenicity. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;12:1263-1265. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Annibale B, Negrini R, Caruana P, Lahner E, Grossi C, Bordi C, Delle Fave G. Two-thirds of atrophic body gastritis patients have evidence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2001;6:225-233. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Bini EJ. Helicobacter pylori and iron deficiency anemia: guilty as charged? Am J Med. 2001;111:495-497. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Koike T, Ohara S, Sekine H, Iijima K, Abe Y, Kato K, Toyota T, Shimosegawa T. Helicobacter pylori infection prevents erosive reflux oesophagitis by decreasing gastric acid secretion. Gut. 2001;49:330-334. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 140] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |