Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2726
Revised: September 25, 2004
Accepted: November 19, 2004
Published online: May 14, 2005
AIM: It is controversial whether patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD) respond differently to Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) eradication treatment than those with peptic ulcer disease (PUD). To review the evidence for any difference in H pylori eradication rates between PUD and NUD patients.
METHODS: A literature search for full articles and meeting abstracts to July 2004 was conducted. We included studies evaluating the efficacy of a proton pump inhibitor (P) or ranitidine bismuth citrate (RBC) plus two antibiotics of clarithromycin (C), amoxicillin (A), metronidazole (M), or P-based quadruple therapies for eradicating the infection.
RESULTS: Twenty-two studies met the criteria. No significant difference in eradication rates was found between PUD and NUD patients when treated with 7-d RBCCA, 10-d PCA or P-based quadruple therapies. When the 7-d PCA was used, the pooled H pylori eradication rate was 82.1% (431/525) and 72.6% (448/617) for PUD and NUD patients, respectively, yielding a RR of 1.15 (95%CI 1.01-1.29). However, the statistically significant difference was seen only in meeting abstracts, but not in full publications.
CONCLUSION: There is no convincing evidence to suggest that NUD patients respond to H pylori eradication treatments differently from those with PUD, although a trend exists with the 7-d PCA therapy.
-
Citation: Huang JQ, Zheng GF, Hunt RH, Wong WM, Lam SK, Karlberg J, Wong BCY. Do patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia respond differently to
Helicobacter pylori eradication treatments from those with peptic ulcer disease? A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(18): 2726-2732 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i18/2726.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2726
It has been over 17 years since the first randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) eradication was published[1]. Treatment to cure the infection has evolved from single agents to combination treatment regimens with up to four drugs. Currently, the most commonly recommended combination treatments consist of a proton pump inhibitor (P), clarithromycin (C) and amoxicillin (A) or metronidazole (M)[2-4]. However, the success of treatment with these combination regimens varies considerably between reports[5]. Several factors have been identified to contribute to the variability of the treatment outcomes. These include patient- and treatment-related factors[5]. However, conflicting results have been reported with regard to whether H pylori eradication treatment is more effective in patients with peptic ulcer disease (PUD) than in those with non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD) or other non-ulcer gastric diseases[6-11], especially when patients are treated with the PCA combination regimen. We undertook this meta-analysis to review systematically the literature on H pylori eradication in patients with PUD or with NUD and to evaluate the magnitude of any difference in H pylori eradication rates between the two groups of patients when treated with the most commonly recommended treatment regimens.
A computerized literature search for relevant studies was performed in Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, MEDLINE, PubMed, and EMBASE databases to June 2004 in all languages using the following MeSH terms or textwords in various combinations: dyspepsia, NUD, functional dyspepsia, peptic ulcer, PUD, H pylori, duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, eradication. Several other online trials’ registries were also searched including United Kingdom National Research Register (http://www.doh.gov.uk/research/nrr.htm), Current Science register of controlled trials (http://www.controlled-trials.com), ClinicalTrials.gov developed by the National Library of Medicine (http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct). A recursive hand search of reference lists, review articles, editorials and abstracts from major relevant international meetings was also conducted to supplement electronic searches: American Digestive Disease Week 1997-2004, the United European Gastroenterological Week 1997-2003, American College of Gastroenterology Annual Meetings 1997-2003, the European H pylori Study Group Meetings 1997-2003 and the World Congress of Gastroenterology 1998-2002.
Because the research question of this study sought any difference in H pylori eradication rates between patients with PUD or NUD, the relative efficacy of different treatment regimens was neither compared nor analyzed. Therefore, we included all clinical trial designs if studies met the following criteria: (1) any clinical trial in adults involving one of the following combination regimens given in the recommended doses: a PPI or ranitidine bismuth citrate (RBC) plus two antibiotics (clarithromycin, amoxicillin, metronidazole or tinidazole), and proton pump inhibitor-based quadruple therapies; (2) studies which provided comparative data on H pylori eradication rates between patients with PUD and those with NUD; (3) studies which provided raw data for intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis or ITT data could be derived from the paper; (4) H pylori infection was diagnosed by at least one of the following methods: rapid urease test, histology, culture or urea breath test; eradication was confirmed at least 4 wk after stopping all medications. We excluded studies that reported mixed eradication data or were identified as duplicate publications. Studies of patients with chronic gastritis alone were also excluded.
The eligibility criteria were assessed by two independent reviewers (JQH and GFZ). Any disagreement about the decision was solved through discussion to reach consensus between the reviewers.
Two independent reviewers (JQH and GFZ) extracted the data from the qualified studies and any disagreement was resolved by discussions to reach consensus between the reviewers. The following major items were extracted from each qualified study: name of the first author, source and date of publication, study design, demographics of patients, diagnosis of H pylori infection and methods used for confirmation of eradication, details of treatment regimen (number of drugs, dose, dose frequency and treatment duration), number of patients randomized, treated and dropped-out, and number of patients with H pylori infection eradicated by ITT analysis and by disease category (e.g., PUD, or duodenal ulcer or gastric ulcer or NUD).
The only outcome concerned in this study was the H pylori eradication rate by ITT analysis in patients with PUD compared to those with NUD. Although we also extracted eradication rates by per-protocol analysis, the data were not presented due to concerns over the methodological problems, such as information on drop-outs which was poorly reported.
The quality assessment was done independently by JQH and GFZ. Because of the nature of our research question, no existing scoring instruments could be used for conducting the quality assessment. Therefore, we focused primarily on the quality of presentation of study results such as whether ITT H pylori eradication rates were clearly presented, etc.
Studies were grouped by combination regimens including different doses, treatment durations and types of publication (meeting abstract, full article).
The minimum number of studies required for statistical pooling was arbitrarily set at three and above. If only two studies were available for any subgroup analysis, results from the two studies were described and no pooling was undertaken. The following statistical techniques were used to analyze the data, wherever appropriate. Summary relative risk, risk difference and 95% CI were calculated from the raw data of the studies using a random-effects model. The number-needed-to-treat (NNT) was also calculated. The Cochrane Q method was used to test for homogeneity. P<0.1 was considered to be statistically significant for test of homogeneity. In the presence of statistical heterogeneity, we searched for sources of methodological heterogeneity. We also examined publication bias by the method of Egger’s regression[12]. All analyses were performed with EasyMa software 2001 (M. Cucherat, Lyon, France).
The literature search generated 502 citations. Browsing the titles and abstracts reduced the number of citations to 246. Of these potentially useful citations, 224 were subsequently excluded for various reasons including review articles (n = 8), no raw data (n = 104), unclear patient population (n = 68), unlisted treatment regimens (n = 17), re-treatment (n = 15) and duplicate publications (n = 13). A detailed list of the excluded studies is available upon request.
Twenty-one studies met the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria and were subject to analysis[6-11,13-27].
RBC-containing triple or quadruple regimens were studied in 6 trials involving 10 treatment comparisons[6,9,13-16]. Five studies were published in full[6,13-16] and one in abstract form[9]. The treatment-related information from these studies is tabulated in Table 1.
| Refs | Combination regimens | Dose | Treatment duration | Eradication rate (ITT) | P | |
| PUD | NUD | |||||
| N/T.N (%) | N/T.N (%) | |||||
| Triple therapies | ||||||
| RBCCA | ||||||
| 6 | RBC/Cla/Amo | 400 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 d | 20/23 (86.96) | 18/22 (81.8) | |
| 15 | RBC/Cla/Amo | 400 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 d | 13/18 (72.2) | 48/57 (84.2) | |
| 16 | RBC/Cla/Amo | 400 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 d | 19/23 (82.6) | 66/76 (86.8) | |
| Others | 52/64 (81.3) | 132/155 (85.2)1 | ||||
| 13 | RBC/Cla/Tin | 400 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d. | 5 d | 20/27 (74.1) | 23/39 (58.97) | 0.32 |
| 9 | RBC/Cla/Tin | 400 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d. | 5 d | 6/9 (66.7) | 9/12 (75) | 0.95 |
| 16 | RBC/Cla/Met | 400 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./400 mg b.i.d. | 7 d | 20/21 (95.2) | 69/78 (88.5) | 0.61 |
| 16 | RBC/Met/Tet | 400 mg b.i.d./400 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 d | 38/46 (82.6) | 43/54 (79.6) | 0.9 |
| 14 | RBC/Fur/Tet | 350 mg b.i.d./100 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d. | 7 d | 20/24 (83.3) | 31/36 (86.1) | 0.94 |
| 14 | RBC/Fur/Amo | 350 mg b.i.d./100 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 d | 15/19 (78.95) | 34/41 (82.9) | 0.99 |
| Quadruple therapy | ||||||
| 6 | RBC/Cla/Amo/Met | 400 mg b.i.d./400 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d. | 5 d | 174/174 (100) | 62/71 (87.3) | <0.05 |
A total of 7 different combination regimens and 10 treatment arms were reported. Among the 10 treatment arms, 7 were given for 7 d and three for 5 d. Because of the large variability in drug combinations, meta-analysis was not possible for most combination treatments (Table 1). Triple therapies consisting of RBC (R), clarithromycin (C) and tinidazole (T) were reported in two studies from the same lead author. However, personal communication with the corresponding author has excluded any duplication of patients. No statistically significant difference in H pylori eradication rate was observed in patients with PUD or NUD treated with the 5-d RBT combination regimen in both reports[9,13].
Three reports, involving RBC 400 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg and amoxicillin 1 g, all given twice daily for 7 d, were considered appropriate for meta-analysis[6,15,16]. H pylori eradication was achieved in 81.3% (52/64) of patients with PUD and 85.2% (132/155) in those with NUD, yielding a summary relative risk of 0.96 (95%CI 0.84-1.11); indicating that triple therapy consisting of RBC, clarithromycin and amoxicillin was similarly effective for eradicating H pylori infection in patients with PUD compared to those with NUD. The test of homogeneity was not statistically significant (Q value = 1.1429, P = 0.56).
We found five studies consisting of six treatment arms that provided comparative H pylori eradication data in PUD and NUD patients[8,13,17-19]. Of these, four were published in full[13,17-19] and one in abstract form[8]. Table 2 tabulates the treatment-related characteristics of these studies. Because of the large variability in the drug combinations, dose and treatment duration among these studies, meta-analysis was not possible. However, within study comparison did not reveal any statistically significant difference in H pylori eradication rates between patients with PUD and those with NUD in any of the combination regimens (Table 2).
| Refs | Combination regimens | Dose | Treatment duration | Eradication rate (ITT) | P | |
| PUD | NUD | |||||
| N/T.N (%) | N/T.N (%) | |||||
| 17 | CBS/Met/Tet/Lan | 120 mg ×8/250 mg ×8/250 mg ×8/30 mg b.i.d. | 1d | 22/33 (66.7) | 5/13 (38.5) | 0.16 |
| 17 | CBS/Met/Tet/Lan | 120 mg ×8/250 mg ×8/250 mg ×8/30 mg b.i.d. | 2 d | 26/35 (74.3) | 20/40 (50) | 0.06 |
| 13 | Amo/Cla/Tin/Ome | 1 g b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./20 mg b.i.d. | 5 d12 | 30/31 (96.8) | 31/34 (91.2) | 0.68 |
| 18 | Bis/Met/Tet/Lan | 120 mg q.i.d./400 mg t.i.d./500 mg q.i.d./30 mg q.d. | 7 d | 91/101 (90.1) | 107/118 (90.7) | 0.93 |
| 19 | Bis/Met/Tet/Ome | 120 mg q.i.d./400 mg t.i.d./500 mg q.i.d./30 mg q.d. | 10 d | 53/57 (93) | 46/49 (93.9) | 0.84 |
| 8 | Bis/Met/Tet/Ome | 120 mg q.i.d./500 mg t.i.d./500 mg q.i.d./20 mg b.i.d. | 14 d | 9/11 (81.8) | 8/13 (61.5) | 0.53 |
Nine studies and 10 treatment arms reported comparative data involving triple therapies consisting of a PPI, clarithromycin and amoxicillin[7-11,20-22,27]. Of these, seven studies were only in abstract form[7-10,20-22] and two were published in full[11,27].
Table 3 summarizes treatment-related information from these studies.
| Refs | Combination regimens | Dose | Treatmentduration (d) | Eradication rate (ITT) | P | |
| PUD | NUD | |||||
| N/T.N (%) | N/T.N (%) | |||||
| 22 | Ome/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 | 134/161 (83.2) | 34/42 (81) | |
| 7 | Ome/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d.1/500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 | 60/65 (92.3) | 30/50 (60) | |
| 9 | PPI/Cla/Amo | PPI b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d . | 7 | 27/34 (79.4) | 15/21 (71.4) | |
| 11 | Rab/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 | 101/135 (74.8) | 288/392 (73.5) | |
| 20 | Pan/Cla/Amo | 40 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 | 27/29 (93.1) | 13/19 (68.4) | |
| 27 | Rab/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 | 82/101 (81.2) | 68/93 (73) | |
| 431/525 (82.1) | 448/617 (72.6)2 | |||||
| 10 | Ome/Cla/Amo | 40 mg b.i.d./800 mg b.i.d./2 g b.i.d. | 7 | 87/98 (88.8) | 6/6 (100) | 0.388 |
| 10 | Ome/Cla/Amo | 40 mg b.i.d./1.6 g b.i.d./2 g b.i.d. | 7 | 51/51 (100) | 49/50 (98) | 0.313 |
| 8 | Lan/Cla/Amo | 30 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 10 | 13/13 (100) | 65/71 (91.6) | |
| 21 | Ome/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 10 | 63/96 (65.6) | 20/27 (74.1) | |
| 27 | Rab/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 10 | 75/97 (77.3) | 78/99 (78.8) | |
| 27 | Ome/Cla/Amo | 20 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 10 | 77/103 (74.8) | 68/103 (73.1) | |
| 231/309 (74.8) | 231/300 (77)3 | |||||
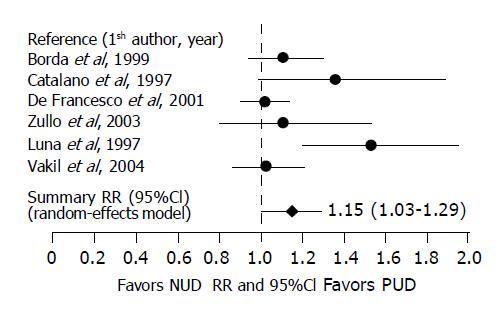
Seven-day treatment involving a standard dose of PPI, clarithromycin 500 mg and amoxicillin 1 g, all given twice daily for 7 d, was used in six studies including 525 PUD patients and 617 NUD patients[7,9,11,20,22,27]. H pylori eradication was achieved in 82.1% of the 525 patients with PUD and 72.6% of the 617 patients with NUD, yielding a RR of 1.15 (95%CI 1.01-1.29). However, the test of homogeneity showed the presence of statistically significant between-study heterogeneity (Q Cochrane = 11.81, df = 5, P = 0.037). Scrutiny of these studies found that the heterogeneity was most likely caused by a large differential difference in H pylori eradication rates between studies. Therefore, a random-effects model was used, which yielded a RR of 1.15 (95%CI 1.01-1.29). The result suggests that the 7-d PCA combination regimen given in the recommended doses cured significantly more H pylori infections in patients with PUD than in those with NUD. The summary risk difference was estimated at 0.11 (95%CI -0.01-0.22), giving an estimated NNT of 9. The Egger’s regression test for the detection of publication bias was not statistically significant (r = -0.64, P = 0.08) for the 7-d PCA triple therapy.
Figure 1 depicts the individual and summary relative risks and 95%CI.
A subgroup analysis was conducted according to the type of publication. Of the six studies, four were published in abstract form[7,9,20,22] and two as full articles[11,27]. The pooled eradication rates from the four meeting abstracts were 85.8% for patients with PUD and 69.7% for those with NUD, yielding a RR of 1.19 (95%CI 1.06-1.33). However, the test of homogeneity was statistically significant (Q Cochrane: 8.47, P = 0.037). A reanalysis of the data using a random-effects model generated a RR of 1.23 (95%CI 1.00-1.52), demonstrating a borderline statistically significant difference, indicating a trend that patients with PUD respond to the 7-d PCA combination treatment better than those with NUD.
Similar eradication rates were observed in the two reports published as full articles[11,27]. An Italian study reported by Zullo and colleagues showed similar H pylori eradication rates between patients with PUD (74.8%) and those with NUD (73.5%)[11] (Table 3). A US study reported by Vakil et al[27], demonstrated that PCA eradicated 8.2% more H pylori infections in patients with PUD than in those with NUD (Table 3). However, this difference was not statistically significant.
Sato and colleagues reported one study, involving two treatment arms, in which higher doses of antibiotics were used in 7-d PCA combination[10]. However, no significant difference in H pylori eradication rates between the two groups of patients was reported (Table 3).
Three studies reported efficacy data obtained with a 10-d standard dose PCA combination regimen involving 309 PUD patients and 300 NUD patients[8,21,27]. The pooled eradication rate was 74.8% (231/309) for PUD patients and 77% (231/300) for NUD patients, respectively, yielding a RR of 1.03 (95%CI 0.95-1.12). The test of homogeneity was not statistically significant (Q Cochrane: 2.81, P = 0.42). Thus, there was no statistically significant difference in H pylori eradication rate between the two groups of patients.
Four studies (five arms) reported comparative eradication data involving triple therapies consisting of a PPI, metronidazole and clarithromycin or amoxicillin[23-26]. The results of these studies are tabulated in Table 4. However, no statistically significant difference in H pylori eradication rates between patients with PUD and those with NUD was reported in any of the studies[23-26].
| Refs | Combination regimens | Dose | Treatment duration | Eradication rate (ITT) | P | |
| PUD | NUD | |||||
| N/T.N (%) | N/T.N (%) | |||||
| 23 | Pan/Met/Cla | 40 mg q.d./400 mg b.i.d./250 mg b.i.d. | 7 d | 54/65 (83.1) | 21/24 (87.5) | 0.613 |
| 23 | Pan/Met/Cla | 40 mg b.i.d./400 mg b.i.d./250 mg b.i.d. | 7 d | 54/64 (84.4) | 18/22 (81.8) | 0.781 |
| 24 | Ome/Met/Cla | 40 mg q.d./500 mg b.i.d./250 mg b.i.d. | 7 d | 15/19 (78.95) | 5/6 (83.3) | 0.819 |
| 25 | Pan/Met/Amo | 40 mg b.i.d./500 mg b.i.d./1 g b.i.d. | 7 d | 14/19 (73.7) | 7/11 (63.6) | 0.569 |
| 26 | Ome/Met/Amo | 40 mg q.d./400 mg t.i.d.1/750 mg b.i.d. | 14 d | 22/27 (81.5) | 22/37 (59.5) | 0.063 |
Individual studies suggest that patients with PUD may respond better to H pylori eradication treatment than patients with NUD. However, the results have been conflicting between studies[6-11]. Several factors may have contributed to the conflicting reports, which include a small sample size[10,17,24,25], use of sub-optimal doses or inadequate treatment duration[13,17]. In order to systematically examine this question, we comprehensively reviewed all relevant clinical trials that provided data on H pylori eradication between patients with PUD and those with NUD.
Although there are numerous combination treatment regimens for eradicating H pylori infection, only a few choices of treatments are currently recommended[2-4,28,29]. Therefore, we focused on the combination treatment regimens that are currently recommended by the majority of authorities or consensus groups. These include triple therapies consisting of a PPI or RBC plus two antibiotics (clarithromycin, amoxicillin or metronidazole) or PPI-based quadruple therapies[2-4,28,29].
No significant difference in the H pylori eradication rate was observed between patients with PUD and those with NUD when RBC-based triple therapies were used, irrespective of the combination of antibiotics, dose regimens and treatment duration (Table 1). Similar results were also found in patients treated with PPI-based quadruple therapies (Table 2), suggesting that both RBC-based triple therapies and PPI-based quadruple combination therapies are similarly effective for eradicating H pylori infection in patients with PUD or with NUD.
PPI-based triple therapies are the most commonly recommended treatment choice for eradicating H pylori infection because of their highly consistent efficacy and excellent safety record[30,31]. However, the number of studies that included both PUD and NUD patients was limited and this has prohibited us from conducting a reliable meta-analysis of all the recommended PPI-based triple therapies. We found that, with the exception of the 7-d PCA combination, no significant differences in H pylori eradication rates have been observed in patients with PUD or NUD when other PPI-based triple therapies were used (Table 4). Among the six studies using the recommended PCA treatment, 9.5% more H pylori infections were cured in patients with PUD compared to those with NUD, which is statistically significant. However, the results from the subgroup analysis by publication type showed that the difference was caused by a large differential difference (16.1%) observed in the meeting abstracts because there was no statistically significant difference in the H pylori eradication rates between the two groups of patients in the two full articles[11,27]. Therefore, according to the current literature, there is no convincing evidence that patients with NUD respond to the 7-d PCA combination treatment significantly different from those with PUD. This is especially the case when the PCA combination treatment is used for 10 d and similar H pylori eradication rates are achieved in both groups of patients[8,21,27].
Nevertheless, Houben and colleagues observed that PPI-based triple therapies eradicated 8.8% more H pylori infections in patients with PUD than in those with NUD (P = 0.036)[32]. However, this study was published in abstract form and no detailed information on treatment regimens was provided[32]. A similar, but statistically non-significant difference was also reported by Kamberoglou et al[33], in a study involving 106 NUD and 142 PUD patients treated with either PPI- or RBC-based triple therapies in which 8.1% more H pylori infections were cured in patients with PUD than in those with NUD. Similarly, the study was only available in abstract form. Furthermore, the authors did not separate patients treated with PPI-based therapies from those receiving RBC-based regimens, making it difficult to ascertain which combination treatment contributed most to the observed difference.
Why patients with NUD and PUD respond differently to the 7-d PCA combination regimen remains unclear. Several hypotheses suggested by Gisbert and colleagues indicate that infection with different strains of H pylori, different severities of inflammation or patient compliance, age and gender may contribute to differences in H pylori eradication rates between patients with PUD and NUD[6]. Nevertheless, it is not clear why the difference was only seen with the 7-d PCA combination treatment, but not with other treatment regimens.
We combined patients with duodenal ulcer or gastric ulcer in this study because the evidence from individual studies suggests no significant difference in H pylori eradication rates between patients with duodenal or gastric ulcer when the PCA combination[10,21,22] or other PPI-based triple therapy[19] was used. The results show that H pylori infection-related gastric or duodenal ulcers respond similarly to eradication treatment.
There are several limitations to our study. First, the nature of the study question which we assessed indicates that there are no randomized controlled clinical trials. Therefore, we included all study designs in the analysis and these may suffer from certain methodological weaknesses. Second, the number of trials available for analysis was limited especially for non-PCA combination regimens. Therefore, a type II error cannot be excluded. The small number of studies also prohibited us from conducting several clinically important subgroup analyses to assess the potential impact of bacterial resistance, different strains of H pylori and the country of study on the difference in H pylori eradication rates.
In conclusion, although individual studies may have suggested that patients with PUD respond better to H pylori eradication treatment than those with NUD, we have not found any convincing evidence that this is the case across different combination treatment regimens although a trend exists with the recommended 7-d triple therapy consisting of a standard dose proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and amoxicillin.
We would like to thank Professor Angelo Zullo of Italy, Javier P. Gisbert of Spain, Fernando Borda of Spain, Francis Megraud of France and Filippo Catalano of Italy for generously providing information on their studies.
Science Editor Guo SY Language Editor Elsevier HK
| 1. | McNulty CA, Gearty JC, Crump B, Davis M, Donovan IA, Melikian V, Lister DM, Wise R. Campylobacter pyloridis and associated gastritis: investigator blind, placebo controlled trial of bismuth salicylate and erythromycin ethylsuccinate. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293:645-649. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 274] [Cited by in RCA: 231] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Peterson WL, Fendrick AM, Cave DR, Peura DA, Garabedian-Ruffalo SM, Laine L. Helicobacter pylori-related disease: guidelines for testing and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:1285-1291. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Lam SK, Talley NJ. Report of the 1997 Asia Pacific Consensus Conference on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:1-12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 309] [Cited by in RCA: 288] [Article Influence: 10.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, Hungin AP, Jones R, Axon A, Graham DY, Tytgat G. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection--the Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:167-180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 846] [Cited by in RCA: 843] [Article Influence: 36.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Huang JQ, Hunt RH. Treatment after failure: the problem of "non-responders". Gut. 1999;45 Suppl 1:I40-I44. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Gisbert JP, Marcos S, Gisbert JL, Pajares JM. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy is more effective in peptic ulcer than in non-ulcer dyspepsia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13:1303-1307. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Catalano F, Catanzaro R, Brogna A. Duodenal ulcer and functional dyspepsia: different susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to eradicating therapy. Gastroenterology. 1997;112: A84. |
| 8. | Gutierrez O, Otero W, Melo M. Helicobacter pylori eradication: duodenal ulcer vs functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:A142. |
| 9. | De Francesco V, Sgarro C, Cela E. Helicobacter pylori Eradication Rates In Non-ulcer Dyspepsia (nud) And Duodenal Ulcer (du) Patients. Gut. 2001;49:A94. |
| 10. | Sato J, Yanaka A, Yokota H. High-dose clarithromycin in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:A279. |
| 11. | Zullo A, Vaira D, Vakil N, Hassan C, Gatta L, Ricci C, De Francesco V, Menegatti M, Tampieri A, Perna F. High eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori with a new sequential treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:719-726. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 160] [Cited by in RCA: 166] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629-634. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34245] [Cited by in RCA: 40493] [Article Influence: 1446.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 13. | De Francesco V, Zullo A, Hassan C, Faleo D, Ierardi E, Panella C, Morini S. Two new treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a randomised study. Dig Liver Dis. 2001;33:676-679. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Lu H, Zhang DZ, Hu PJ, Li ZS, Lu XH, Fang XC, Xiao SD. One-week regimens containing ranitidine bismuth citrate, furazolidone and either amoxicillin or tetracycline effectively eradicate Helicobacter pylori: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15:1975-1979. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Gisbert JP, Carpio D, Marcos S, Gisbert JL, García Grávalos R, Pajares JM. One-week therapy with pantoprazole versus ranitidine bismuth citrate plus two antibiotics for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;12:489-495. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Sung JJ, Chan FK, Wu JC, Leung WK, Suen R, Ling TK, Lee YT, Cheng AF, Chung SC. One-week ranitidine bismuth citrate in combinations with metronidazole, amoxycillin and clarithromycin in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: the RBC-MACH study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999;13:1079-1084. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | van Doorn LJ, Schneeberger PM, Nouhan N, Plaisier AP, Quint WG, de Boer WA. Importance of Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA status for the efficacy of antibiotic treatment. Gut. 2000;46:321-326. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Korman MG, Bolin TD, Nicholson FB, Engelman JL. Lansoprazole quadruple therapy is effective in curing Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 1998;3:202-205. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | O'Morain C, Borody T, Farley A, De Boer WA, Dallaire C, Schuman R, Piotrowski J, Fallone CA, Tytgat G, Mégraud F. Efficacy and safety of single-triple capsules of bismuth biskalcitrate, metronidazole and tetracycline, given with omeprazole, for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori: an international multicentre study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:415-420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Luna P, del Castillo G, Farias R. Efficacy and tolerability of a seven-day triple scheme with pantoprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin for eradicarion of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:A202. |
| 21. | Mantzaris GJ, Archavlis EM, Amberiadis P. Is the Activity and Severity of Gastritis and Helicobacter Pylori Load Related to the Outcome of Anti-H pylori Treastment? Gastroenterology. 1998;114:A214. |
| 22. | Borda F, Martinez A, Elizalde I, Pastor G, Echarri A, Rodriguez A. Does the efficacy of eradication treatment with OCA-7 decrease in non-ulcer gastroduodenal disease? Gut. 1999;45:A270. |
| 23. | Bardhan KD, Dillon J, Axon AT, Cooper BT, Tildesley G, Wyatt JI, Gatz G, Braun W. Triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a comparison of pantoprazole once versus twice daily. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000;14:59-67. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Della Libera E, Rohr MR, Moraes M, Siqueira ES, Ferrari AP. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer and non-ulcer dyspepsia and analysis of one-year reinfection rates. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2001;34:753-757. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Adamek RJ, Pfaffenbach B, Szymanski C. Cure of H. pylori infection using a 7-day triple therapy combining pantoprazole with two antibiotics. Helicobacter. 1998;3:206-211. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Bate CM, Keeling PWN, Crowe JP, Axon ATR, Tildesley G, Harris SJ, Powell JA. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia and duodenal ulcer disease using two omeprazole treatment regimens – a 12 mo follow-up study. J Clin Res. 1998;1:103-118. |
| 27. | Vakil N, Lanza F, Schwartz H, Barth J. Seven-day therapy for Helicobacter pylori in the United States. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20:99-107. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 126] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Hunt RH, Fallone CA, Thomson AB. Canadian Helicobacter pylori Consensus Conference update: infections in adults. Canadian Helicobacter Study Group. Can J Gastroenterol. 1999;13:213-217. [PubMed] |
| 29. | Coelho LG, León-Barúa R, Quigley EM. Latin-American Consensus Conference on Helicobacter pylori infection. Latin-American National Gastroenterological Societies affiliated with the Inter-American Association of Gastroenterology (AIGE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:2688-2691. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Gisbert JP, González L, Calvet X, García N, López T, Roqué M, Gabriel R, Pajares JM. Proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and either amoxycillin or nitroimidazole: a meta-analysis of eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000;14:1319-1328. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 127] [Cited by in RCA: 123] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Huang J, Hunt RH. The importance of clarithromycin dose in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: a meta-analysis of triple therapies with a proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and amoxycillin or metronidazole. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999;13:719-729. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |