Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1439
Revised: September 9, 2004
Accepted: September 15, 2004
Published online: March 14, 2005
AIM: To evaluate the factors affecting the early tumor recurrence within one year in cirrhotic patients having a single small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after complete tumor necrosis by radiofrequency ablation (RFA) therapy.
METHODS: Thirty patients with a single small HCC received RFA therapy by a RFA 2000 generator with LeVeen needle. Tri-phase computerized tomogram was followed every 2 to 3 mo after RFA. The clinical effects and tumor recurrence were recorded.
RESULTS: The initial complete tumor necrosis rate was 86.7%. Twenty-two patients were followed for more than one year. The local and overall recurrence rates were 13.6% and 36.4%, 33.3% and 56.2%, 46.6% and 56.2% at 12, 24 and 30 mo, respectively. No major complication or procedure-related mortality was found. The risk factors for early local tumor recurrence within one year were larger tumor size, poor pathologic differentiation of tumor cells and advanced tumor staging. The age of patients with new tumor formation within one year was relatively younger (55.1±8.3 vs 66.7±10.8, P = 0.029).
CONCLUSION: Large tumor size, poor pathologic differentiation of tumor cells and advanced tumor staging are the risk factors for early local tumor recurrence within one year, and young age is the positive predictor for new tumor formation within one year.
- Citation: Yu HC, Cheng JS, Lai KH, Lin CP, Lo GH, Lin CK, Hsu PI, Chan HH, Lo CC, Tsai WL, Chen WC. Factors for early tumor recurrence of single small hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(10): 1439-1444
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i10/1439.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1439
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignancy worldwide and about 70% of HCC is found in Asia[1]. There is an increasing incidence in the western countries[2]. In Taiwan, HCC is a leading neoplasm due to the high prevalence of chronic viral hepatitis[3-5].
Surgical resection, liver transplantation and local ablation therapy are considered potentially curative therapies for HCC nowadays[6,7]. However, only 9% to 27% of patients are suitable for operation[8,9]. For the patients who are not candidates for surgical treatment, local ablation therapy is another choice for controlling this neoplasm. Many modalities, such as percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI), percutaneous acetic acid injection (PAI), cryotherapy, percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy (PMCT), and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) are available for local therapy. These minimally invasive techniques have the advantages of preserving the uninvolved liver parenchyma with less complication and mortality than surgery. However, inadequate treatment and recurrence of tumor are still common.
RFA first described by Rossi and coworkers[10] is a new technique of local thermal ablation therapy for HCC. It allows focal coagulation necrosis of hepatic tumors by producing thermal energy with an alternating electric current generator at a radiofrequency of 200 to 1200 kHz through a needle electrode. Tumor cells are destroyed by heating to a temperature of about 80 °C to 100 °C. Previous reports have shown that RFA has a better complete necrosis rate, lower local recurrence rate, fewer treatment sessions and longer survival interval than PEI[11,12]. However, despite the high complete necrosis rate of RFA, early tumor recurrence within one year, either local tumor recurrence or new tumor formation, can still be found. A series of studies discussed the factors for tumor recurrence including the tumor size, subcapsular lesion, operative procedure, underlying liver disease and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels, but the results were not well documented[13-15,23]. The factors for the early tumor recurrence within one year were never discussed independently.
In our study, we followed our patients with a single small HCC after RFA and analyzed the results including complete tumor necrosis, local and overall tumor recurrence, safety of procedure, clinical morbidity and mortality and the factors responsible for early tumor recurrence within one year.
From September 2000 to February 2003, 30 cirrhotic patients with a single small HCC received ultrasound-guided percutaneous RFA therapy in our hospital. The enrolled criteria included: (1) HCC was pathologically proved before therapy by ultrasound-guided cutting biopsy; (2) the largest tumor size was smaller than 4 cm in diameter and the number of tumor was single; (3) there was no bleeding tendency (prolongation of prothrombin time was ≤3 s and platelet count was ≥60000/mm) or uncontrollable ascites; (4) no extra-hepatic metastases could be found by clinical or image studies (computed tomogram, abdominal ultrasound and chest X-ray) before procedure; (5) tumor location was detectable under ultrasound-guided approach and was far away from major vessels and main bile ducts at least by 1.0 cm (to prevent major complication and heat-sink effect by major vessels); (6) patients refused surgery or were not candidates for surgical treatment and (7) there was no previous therapy for HCC.
Patients were given full explanation of the procedure and written consent was obtained from each patient. This study was approved by the Department of Medical Research and Education of Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital.
The cirrhotic condition was defined by Child-Pugh classification and the tumor staging was defined by BCLC staging system[16]. The pathologic grading was defined by Edmondson and Steiner classification[17] and the grade I and II was defined as well-differentiation and the grade III and IV was defined as poor differentiation.
All patients received intra-muscular injection of pethidine 50 mg and oral diclofenac potassium 25 mg (if serum creatinine level was <2 mg/dL and no peptic ulcer by endoscopy) about 30 min before RFA after they had fasted for 4 h. In patients with impaired renal function (serum creatinine was ≥2 mg/dL) or peptic ulcers, diclofenac potassium would be held to prevent the advanced effect and acetaminophen 500 mg would be given orally. Local anesthesia with 10 CC of 2% Xylocaine was injected at the puncture site before introducing the needle. RFA machine of 2000 generator (Boston Scientific Co.) and LeVeen needle electrode (15 gauge, 25 cm in length, 8-10 hooks, maximum dimension 2.0, 3.0 and 3.5 cm on full expanded) were used. Under real-time ultrasound guidance, the electrode needle was introduced percutaneously into the center or lower part of hepatic tumor, and then expanded the tines of the tip fully before ablation. The selection of needle size depended on the location and diameter of the tumor.
The initial output was set at 30-50 W with an increment of 10 W every 60 s till the power of about 60-90 W, which was maintained for 5 min, and then, increasing the power again to the maximum level (90-130 W) step by step. The selection of the power level depended on the size of needle. Ablation was maintained for at least 15 min unless there was a rapid drop in the power output coincident with marked increase in tissue impedance due to coagulation necrosis (roll-off phenomenon). If no roll-off occurred after ablation for 15 min, the second ablation as the previous procedure would be performed till the roll-off occurred or 10 min of the treatment time had elapsed. No more than 25 min of radiofrequency energy was applied with each deployment of the needle electrode.
After initial ablation, the tines of the tip were fully retracted and if needed, the needle was withdrawn about 1 to 2 cm along the needle tract and re-expanded the tines for another ablation to cover the main tumor area and to create the safe margin of about 0.5 to 1 cm as possible. If no more ablation was needed, we withdrew the needle to the point about 1 cm near the liver surface and re-expanded the tines about 1/4 to 1/5 on extensions. Then, another ablation with initial power was performed till roll-off occurred (usually within 2 min) for coagulating the needle tract to prevent bleeding and needle tract tumor seeding. Patients received sand bag compression for 2 h to prevent internal bleeding after procedure. The complete course of procedure was defined as one therapeutic session. The number of sessions needed for ablating the whole tumor was dependent on the tumor size and needle introducing position. The second session would be performed within one week if indicated. For subcapsular lesions, we inserted the electrode into the HCC nodule through non-cancerous liver tissue without making artificial ascites. Heat coagulation was performed carefully under real-time ultrasound monitor to prevent adjacent organ injury. Intra-muscular injection of ketoprofen 50 mg (in patients with serum creatinine <2 mg/dL and no peptic ulcer) or pethidine 50 mg (in patients with serum creatinine ≥2 mg/dL or peptic ulcer) for further pain control during or after procedure would be given, if needed. Any complications, associated symptoms and signs were recorded and treated.
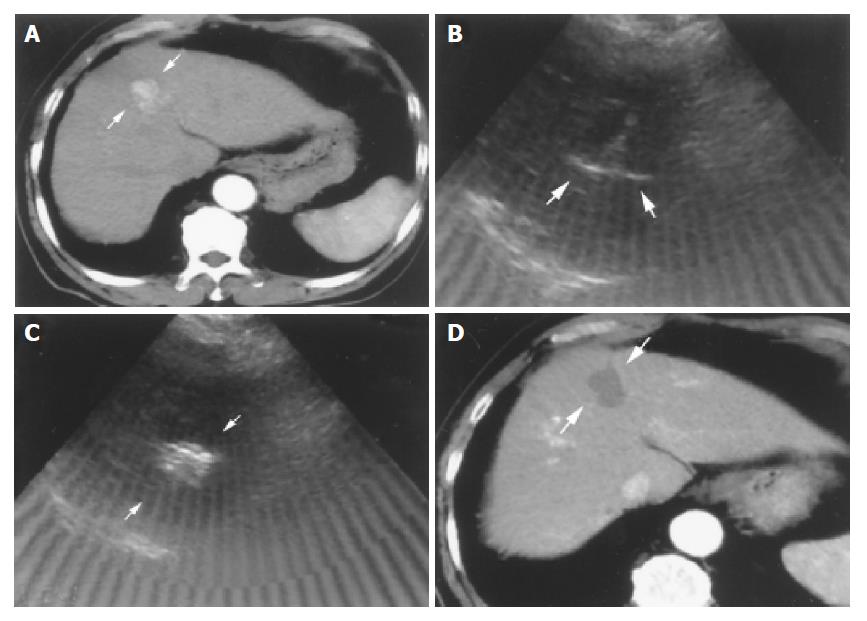
Tri-phase computerized tomography (CT) was performed after RFA therapy one month later for detecting the effect. Successful complete tumor necrosis was defined as no enhanced lesion could be found at previous ablative site. (Figure 1). On the other hand, patients with enhanced lesions were considered as treatment failure; another course of RFA or shifted to other therapies such as transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE), PAI or PEI would be arranged.
Regular follow-up with the tri-phase CT scan, liver biochemistries and AFP level every 2-3 mo was performed after initial successful treatment. The local recurrence was defined as enhanced lesions over the previous ablative area. Enhanced lesions over different segments or faraway from the previous ablative site were defined as new tumor formation. If any recurrence or new tumor developed, proper therapy would be performed according to the patient’s condition.
The data were expressed as mean±SD. χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test (F-test) were used for comparison of categorical data. Mann-Whitney analysis was performed for comparisons of continuous variables. Statistical significance was defined as P<0.05. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used for tumor recurrent curve.
Thirty patients with single HCC were enrolled for RFA therapy. The tumor size ranged from 1.1 to 3.9 cm. There were 37 sessions totally (one session in 24 tumors, two sessions in 6 tumors). Ablative duration ranged from 3 to 48 min. One patient developed severe pain during RFA and the procedure was prematurely terminated. Three patients failed to reach successful complete tumor necrosis after RFA by CT images one month later. They were excluded from our follow-up study. Further RFA therapy was refused and they were referred for TAE therapy. The initial successfully completed tumor necrosis rate was 86.7% (26 in 30).
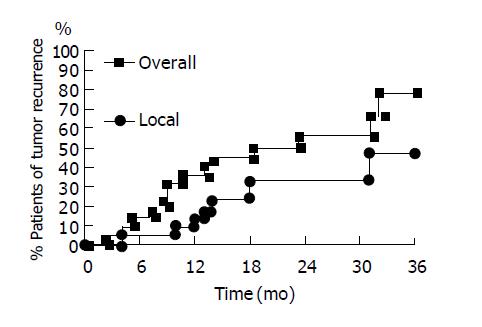
In the 26 patients with successful initial complete tumor necrosis, three patients were lost for follow-up within 6 mo. One patient died of sepsis 9 mo after RFA without tumor recurrence. These patients were also excluded from our study. There were 22 patients who received long-term regular follow-up for more than one year. The baseline data was shown in Table 1. The results of RFA were shown in Table 2. The mean follow-up duration was 28.8±9.0 mo (from 15 to 45 mo). The accumulative local tumor recurrence rates were 13.6%, 33.3% and 46.6% at 12, 24 and 30 mo respectively. Overall tumor recurrence rates (including new tumor formation and local tumor recurrence) were 36.4%, 56.2% and 56.2% at 12, 24 and 30 mo respectively (Figure 2). The tumor-free interval was 18.5±11.4 mo (from 2 to 45 mo) (Table 2). One patient died of hepatic failure 15 mo after RFA. The survival interval was 28.7±9.1 mo (from 15 to 45 mo). Except for three patients lost for follow-up, 25 of 27 patients survived till July 2004. The accumulative mortality rate was 7.4% (2 in 27).
| Sex (male/ female) | 16/6 |
| Age (yr, range) | 62.5±11.3 (40-82) |
| HBV/HCV/HBV+HCV/others | 9/10/2/1 |
| Child's classification | |
| A / B / C | 18/4/0 |
| Esophageal varices (+/-) | 11/11 |
| Ascites (+/-) | 1/21 |
| Tumor size (cm, range) | 2.3±0.7 (1.1-3.9) |
| ≤2 cm / > 2 cm | 10/12 |
| Tumor location | |
| Right lobe/Left lobe | 16/6 |
| Subcapsular lesion (+/-) | 4/18 |
| Histological classification | |
| Well1/Poor2 | 21/1 |
| Tumor staging (BCLC stage)3 | |
| Ia / Ib / Ic | 11/10/1 |
| Total sessions of RFA | 26 |
| One session/ Two sessions | 18/4 |
| Average sessions | 1.20.4 |
| Ablative time (min, range) | 21.3±13.7 (3-48) |
| F/U1 duration (mo, range) | 28.8±9.0 (15-45) |
| Roll-off (+/-) | 21/1 |
| Complications | |
| Local pain | 11 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 4 |
| Fever | 1 |
| Local-free interval (M2, range) | 22.2±10.0 (4-45) |
| Tumor-free interval (M2, range) | 18.5±11.4 (2-45) |
| Local recurrence rate | |
| 12M/24M/30M | 13.6% / 33.3% /46.6% |
| Overall recurrence rate | |
| 12M/24M/30M | 36.4%/56.2%/56.2% |
| Survival interval (M2, range) | 28.7±9.1 (15-45) |
| Pre-RFA / Post-RFA3 | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8±0.5/4.20.6 |
| GOT (U/L) | 63.5±32.9/70.434.2 |
| GPT (U/L) | 71.1±40.0/79.234.2 |
| T. Bili.4 (mg/dL) | 1.1±0.5/1.00.5 |
| Alk-P5 (U/L) | 116.0±46.3/123.546.1 |
| AFP6 level (ng/mL) | |
| Pre-treatment (range) | 223.5±663.1 (3-2870) |
| Post-treatment | 41.3±90.6 (3-422) |
| Decrease AFP > 50% post RFA | |
| Yes / No | 8/14 |
Eight patients had new tumor formation within one year and 14 patients had no new tumor formation. By analysis, young age (55.1±8.3 vs 66.7±10.8, P = 0.029, Mann-Whitney test) was the independent risk factor for early new tumor formation within one year. There were no differences in sex, age, Child-Pugh classification, underlying etiology of cirrhosis, presentation of esophageal varices, duration of tumor ablation, tumor size, tumor location, tumor staging, therapeutic sessions, roll-off phenomenon, histological classification, follow-up duration and the liver biochemistries and AFP level before and after RFA (Table 3).
| New tumor(n = 8) | No new tumor(n = 14) | P | |
| Age (yr) | 55.1±8.3 | 66.7±10.8 | 0.029 |
| Sex (male/female) | 6/2 | 10/4 | NS6 |
| Child1 (A/B) | 5/3 | 13/1 | 0.076 |
| Right lobe/Left lobe | 5/3 | 11/3 | NS |
| Subcapsular (+/-) | 2/6 | 2/12 | NS |
| HBV/HCV/others | 3/4/1 | 6/6/2 | NS |
| EV2 (+/-) | 2/6 | 9/5 | 0.076 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 2.4±0.8 | 2.2±0.8 | NS |
| Tumor >2 cm (+/-) | 5/3 | 7/7 | NS |
| Histology | |||
| (Well/Poor)3 | 7/1 | 14/0 | NS |
| BCLC stage4 Ia/Ib/Ic | 2/5/1 | 9/5/0 | NS |
| Roll-off (+/-) | 8/0 | 13/1 | NS |
| Ablative time (min) | 20.8±10.8 | 21.6±15.5 | NS |
| Sessions | 1.1±0.4 | 1.2±0.4 | NS |
| Follow-up (mo) | 26.8±10.4 | 30.0±8.3 | NS |
| Pre-RFA/Post-RFA | |||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.6±0.5/4.1±0.7 | 4.0±0.4/4.2±0.5 | 0.059/NS |
| T.Bili (mg/dL) | 1.3±0.6/1.0±0.3 | 1.0±0.4/1.1±0.6 | NS/NS |
| GOT (U/L) | 54.3±18.1/61.0±23.1 | 68.7±38.5 /75.8±38.9 | NS/NS |
| GPT (U/L) | 63.336.5/82.141.1 | 75.6±42.5/77.6±31.1 | NS/NS |
| Alk-P (U/L) | 117.0±33.3/126.9±45.1 | 115.5±53.5/121.6±48.2 | NS/NS |
| AFP5 (ng/mL) | 388.5±1 003.2/77.9±142.4 | 129.2±376.8/20.4±32.4 | NS/NS |
| Decrease AFP > 50% | 4/4 | 4/10 | NS |
| Post-RFA(+/-) |
Three patients had early local tumor recurrence within one year after RFA. Tumor size was the significant factor for early local tumor recurrence within one year. (3.2±0.7 vs 2.2±0.7, P = 0.03, Mann-Whitney test). Besides, poor differentiation of tumor cells (P = 0.01, χ2 test) and advanced tumor staging (P = 0.036, χ2 test) were other risk factors for early local tumor recurrence within one year (Table 4).
| Local recurrence (n = 3) | No local recurrence(n = 19) | P | |
| Age (yr) | 57.7±9.3 | 63.3±11.6 | NS6 |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 2/1 | 14/5 | NS |
| Child1 (A/B) | 3/0 | 15/4 | NS |
| Right lobe/Left lobe | 2/1 | 14/5 | NS |
| Subcapsular (+/-) | 1/2 | 3/16 | NS |
| HBV/HCV/others | 1/2/0 | 8/8/3 | NS |
| EV2 (+/-) | 1/2 | 10/9 | NS |
| Tumor size (cm) | 3.2±0.7 | 2.2±0.7 | 0.03 |
| Tumor >2 cm (+/-) | 3/0 | 9/10 | 0.089 |
| Histology | |||
| (Well/Poor)3 | 2/1 | 19/0 | 0.01 |
| BCLCstage4 Ia/Ib/Ic | 1/1/1 | 10/9 | 0.036 |
| Roll-off (+/-) | 3/0 | 18/1 | NS |
| Ablative time (min) | 27.0±12.3 | 20.4±14.0 | NS |
| Sessions | 1.3±0.6 | 1.2±0.4 | NS |
| Follow-up (mo) | 35.0±6.6 | 27.8±9.1 | NS |
| Pre-RFA/Post-RFA | |||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.6±0.3/4.0±1.0 | 3.9±0.5/4.2±0.5 | NS/NS |
| T. Bili. (mg/dL) | 1.2±0.6/1.1±0.2 | 1.0±0.5/1.0±0.5 | NS/NS |
| GOT (U/L) | 56.3±16.2/49.3±14.0 | 64.6±34.9/73.3±35.4 | NS/NS |
| GPT (U/L) | 50.0±24.4/56.3±20.1 | 74.4±41.4/82.8±34.9 | NS/NS |
| Alk-P (U/L) | 106.3±26.3/109.3±31.0 | 117.6±49.1/125.7±48.3 | NS/NS |
| AFP5 (ng/mL) | 967.7±1647.5/145.0±240.0 | 106.0±323.3/24.9±33.3 | NS/NS |
| Decrease AFP > 50% | 2/1 | 6/13 | NS |
| Post-RFA(+/-) |
Some minor advanced events such as local heat and pain (11 cases), low-grade fever (<38 °C) (1 case) and nausea or vomiting (4 cases) were found (Table 2). They were controlled by conservative treatment. No procedure-related mortality was noted.
In our study, the high complete tumor necrosis rate (86.7%) after RFA is comparable with other trials (65-100%, average 83%)[18,22-24]. The local recurrence rates of HCC after RFA are 2.1 to 39% for variable methods, variable follow-up duration and tumor characters reported by several studies[22-28]. Our local tumor recurrence rates are 13.6% and 33.3% at 12 and 24 mo respectively, which are comparable with other reports. However, the local tumor recurrence rate increases to 46.6% at 30 mo after the so-called “complete necrosis” by RFA therapy.
As we know, successful RFA therapy requires an adequate safe margin to prevent the local tumor recurrence due to microscopic invasion around the periphery of the tumor. Just like hepatic resection, 0.5 to 1.0 cm is the acceptable thickness for this purpose when RFA is performed[20,21]. Two or more sessions and a longer ablative duration will be needed to create the area compared to only ablating the main tumor area without adequate safe margin. Unfortunately, repeated insertion and positioning of an electrode may result in inaccurate positioning because the safe margin is difficult to identify after the first treatment under sonogram, probably due to echogenic gas formation by the initial RFA[29]. Inadequate safe margin may be created due to the interference especially for larger tumor that needs repeated sessions. So, further studies for development of a new technique or a protocol to create enough ablative area and a safe margin with lesser sessions may increase the success rate[30]. Chen and his colleagues reported protocol and clinical application for RFA therapy[31] and Poon and his colleagues reported the learning curve for RFA therapy[32]. Both suggest the need to improve the technique to reach the goal for an adequate creation of safe margins. The incomplete treatment due to technical defect may be one of the causes for high local recurrence rate for our study after 2.5 years post-RFA therapy.
On the other hand, despite the high initial complete necrosis rate of RFA therapy, early local tumor recurrence still can be found in some cases. Some trials reported risk factors relating to local tumor recurrence but the early tumor recurrence within one year was not discussed independently, earlier. In our study, we evaluated the factors for this issue. Larger tumor size, poor pathologic differentiation of tumor cells and advanced tumor staging are the major risk factors for early local tumor recurrence within one year as per our analysis.
Komorizono and colleagues reported that the tumor of more than 2 cm in size and the subcapsular lesions were the risk factors of local tumor recurrence[13]. In our study, tumor size >2 cm has the trend for early local tumor recurrence (P = 0.089, Mann-Whitney test) (Table 4). We also performed RFA for subcapsular lesions without making artificial ascites. However, no significant relation to early tumor recurrence was found by analysis (P = 0.464, χ2 test). Harrison and colleagues reported frequent local tumor recurrence after RFA for HCC in 46 patients[14]. They found that the independent predictors of tumor recurrence are tumor size, serum AFP levels and presence of hepatitis. In our study, the AFP level or presence of hepatitis were not related to early local tumor recurrence (Table 4). Kosari and his colleagues[15] and Llovet and his coworkers[23] also reported that the tumor size was the independent predictor for tumor recurrence after RFA. Our results are comparable with them (3.2±0.7 vs 2.2±0.7, P = 0.03, Mann-Whitney test).
As we know, the cooling effect due to heat-sink by blood flow when lesions are adjacent to major vessels will decrease the efficacy of RFA. In our study, we excluded lesions near the main portal vain or major vessels (<1 cm in distance) to avoid the cooling effect. These patients received other treatments such as TAE or PEI. In addition, except for the tumor size that is comparable to other trials, poor pathologic differentiation of tumor cells (P = 0.01, χ2 test) and advanced tumor staging (P = 0.036, χ2 test) are the other predictors for early local tumor recurrence within one year (Table 4). The results are reasonable due to the usually poor prognosis and aggressive tumor progression in patients with poorly differentiated tumor cells and advanced tumor stage.
New tumor formation is frequent in patients with chronic liver disease such as cirrhosis. Ikeda and colleagues reported that the new tumor formation invariably reflected the advanced stage of chronic liver disease. In our study, the markers of advanced cirrhosis such low pre-treatment albumin level (P = 0.059, Mann-Whitney test), advanced Child-Pugh classification (P = 0.076, χ2 test) and presence of portal hypertension (esophageal varices) (P = 0.076, χ2 test) were shown to have the trend related to the early new tumor formation after RFA therapy (Table 3). In addition, the most important process in hepatocarcinogenesis is genomic instability caused by chronic hepatitis associated with repeated destruction and regeneration of hepatocytes. In our study, younger age (55.1±8.3 vs 66.7±10.8, P = 0.029, Mann-Whitney test) was found in the early new tumor formation group (Table 3). The cellular reproductive ability and the growth of tumor cells may be faster in younger patients than the old. There is no study that reported earlier the relationship between young age and rapid new tumor formation. It may need further study with larger case numbers to evaluate.
The complication rates in other studies are around 2-5.7% and 6-6.3% in minor and major complications[18,19]. The procedure-related mortality rate is 0.5-1.4%[18,19]. In our study, no major complication or procedure-related mortality could be noted. One patient died of sepsis about 9 mo after RFA and one patient died of hepatic failure due to rapid tumor progression 15 mo after RFA. The accumulative mortality rate is 7.4% (2 in 27). All minor complications are tolerable and mild. They subsided after supportive treatment.
In conclusion, RFA therapy is an effective treatment for small HCC. Large tumor size, poor pathologic differentiation of tumor cells and advanced tumor staging are the risk factors for early local tumor recurrence taking place within one year, after initial successful complete tumor necrosis by RFA therapy. In addition, young age is the predictor for new tumor formation within one year.
This study was sponsored by the grants from Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital (VGHKS 92104). The authors would like to thank Miss Wan-Ling Li for her kind help in data collection.
Co-first-authors: Jin-Shiung Cheng
Edited by Li WZ Language Editor Elsevier HK
| 1. | Bosch FX. Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tabor E. Liver Cancer. New York: Churchill Livingstone 1997; 13-28. |
| 2. | Bosch FX, Ribes J, Borràs J. Epidemiology of primary liver cancer. Semin Liver Dis. 1999;19:271-285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 671] [Cited by in RCA: 671] [Article Influence: 25.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Beasley RP. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1988;61:1942-1956. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Yeh FS, Yu MC, Mo CC, Luo S, Tong MJ, Henderson BE. Hepatitis B virus, aflatoxins, and hepatocellular carcinoma in southern Guangxi, China. Cancer Res. 1989;49:2506-2509. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Liaw YF, Tai DI, Chu CM, Lin DY, Sheen IS, Chen TJ, Pao CC. Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic type B hepatitis. A prospective study. Gastroenterology. 1986;90:263-267. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Ng IO, Liu CL, Lam CM, Wong J. Improving survival results after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study of 377 patients over 10 years. Ann Surg. 2001;234:63-70. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 451] [Cited by in RCA: 467] [Article Influence: 19.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Roayaie S, Haim MB, Emre S, Fishbein TM, Sheiner PA, Miller CM, Schwartz ME. Comparison of surgical outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B versus hepatitis C: a western experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2000;7:764-770. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 82] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Primary liver cancers in Japan. Cancer. 1980;45:2663-2669. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Lai EC, Fan ST, Lo CM, Chu KM, Liu CL, Wong J. Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. An audit of 343 patients. Ann Surg. 1995;221:291-298. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 302] [Cited by in RCA: 319] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Rossi S, Fornari F, Buscarini L. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency electrocautery for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Interv Radiol. 1993;8:97-103. |
| 11. | Lencioni RA, Allgaier HP, Cioni D, Olschewski M, Deibert P, Crocetti L, Frings H, Laubenberger J, Zuber I, Blum HE. Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology. 2003;228:235-240. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 731] [Cited by in RCA: 674] [Article Influence: 30.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology. 1999;210:655-661. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 994] [Cited by in RCA: 878] [Article Influence: 33.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Komorizono Y, Oketani M, Sako K, Yamasaki N, Shibatou T, Maeda M, Kohara K, Shigenobu S, Ishibashi K, Arima T. Risk factors for local recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma tumors after a single session, single application of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Cancer. 2003;97:1253-1262. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 253] [Cited by in RCA: 255] [Article Influence: 11.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Harrison LE, Koneru B, Baramipour P, Fisher A, Barone A, Wilson D, Dela Torre A, Cho KC, Contractor D, Korogodsky M. Locoregional recurrences are frequent after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2003;197:759-764. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 100] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Kosari K, Gomes M, Hunter D, Hess DJ, Greeno E, Sielaff TD. Local, intrahepatic, and systemic recurrence patterns after radiofrequency ablation of hepatic malignancies. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002;6:255-263. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Befeler AS, Di Bisceglie AM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1609-1619. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 395] [Cited by in RCA: 417] [Article Influence: 18.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Edmondson HA, Steiner PE. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954;7:462-503. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Scaife CL, Curley SA. Complication, local recurrence, and survival rates after radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2003;12:243-255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | de Baère T, Risse O, Kuoch V, Dromain C, Sengel C, Smayra T, Gamal El Din M, Letoublon C, Elias D. Adverse events during radiofrequency treatment of 582 hepatic tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181:695-700. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 362] [Cited by in RCA: 331] [Article Influence: 15.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Regimbeau JM, Kianmanesh R, Farges O, Dondero F, Sauvanet A, Belghiti J. Extent of liver resection influences the outcome in patients with cirrhosis and small hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery. 2002;131:311-317. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 218] [Cited by in RCA: 219] [Article Influence: 9.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Wong J. Significance of resection margin in hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A critical reappraisal. Ann Surg. 2000;231:544-551. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 266] [Cited by in RCA: 293] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, Nicolas Vauthey J, Vallone P. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 2000;232:381-391. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 574] [Cited by in RCA: 530] [Article Influence: 21.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Llovet JM, Vilana R, Brú C, Bianchi L, Salmeron JM, Boix L, Ganau S, Sala M, Pagès M, Ayuso C. Increased risk of tumor seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2001;33:1124-1129. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 583] [Cited by in RCA: 529] [Article Influence: 22.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Meloni F, Dellanoce M, Cova L, Halpern EF, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 117 patients. Radiology. 2001;221:159-166. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 688] [Cited by in RCA: 601] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, Di Stasi M, Quaretti P, Rago M, Zangrandi A, Andreola S, Silverman D, Buscarini L. Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;170:1015-1022. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 442] [Cited by in RCA: 397] [Article Influence: 14.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E, Quaretti P, Garbagnati F, Squassante L, Paties CT, Silverman DE, Buscarini L. Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167:759-768. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 566] [Cited by in RCA: 508] [Article Influence: 17.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Poggi G, Gatti C, Cupella F, Fiori M, Avanza F, Baldi M. Percutaneous US-guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas: results in 15 patients. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:739-742. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M, Vallisa D, Quaretti P, Rocca A. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:914-921. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 232] [Cited by in RCA: 207] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Cha CH, Lee FT, Gurney JM, Markhardt BK, Warner TF, Kelcz F, Mahvi DM. CT versus sonography for monitoring radiofrequency ablation in a porcine liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175:705-711. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Kuvshinoff BW, Ota DM. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: influence of technique and tumor size. Surgery. 2002;132:605-611; discussion 611-612. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 162] [Cited by in RCA: 161] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K, Zou MW, Solbiati L, Liu JB, Dai Y. Large liver tumors: protocol for radiofrequency ablation and its clinical application in 110 patients--mathematic model, overlapping mode, and electrode placement process. Radiology. 2004;232:260-271. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 196] [Cited by in RCA: 181] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Poon RT, Ng KK, Lam CM, Ai V, Yuen J, Fan ST, Wong J. Learning curve for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: prospective analysis of initial 100 patients in a tertiary institution. Ann Surg. 2004;239:441-449. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 151] [Cited by in RCA: 159] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |