Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1307-1311
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1307
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1307
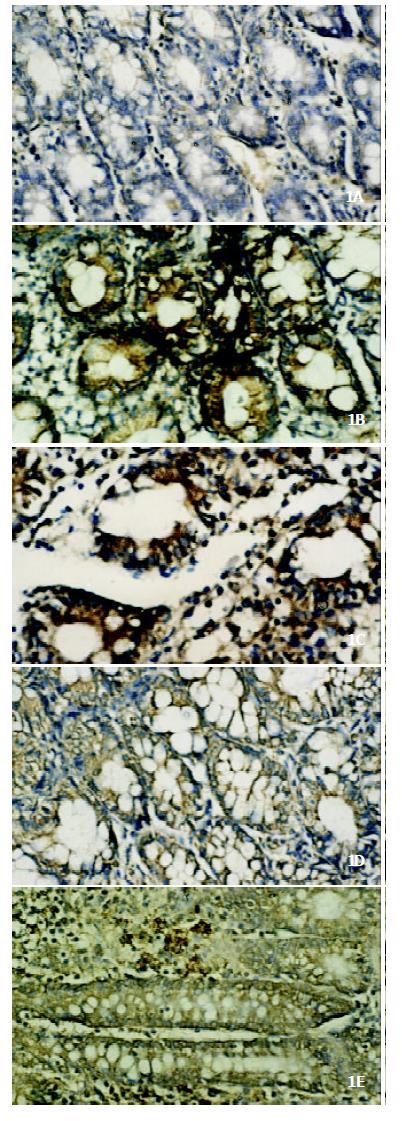
Figure 1 Abnormal expression of iNOS in colonic tissue of rats with cloitis induced by both acetic acid and TNBS enemas and its improvement by melatonin.
A. Immunohistochemical localization of iNOS in normal control, which was manifested as fine brown granules distributed mainly in the cytoplasm of histocytes, neutrophils and smooth muscle cells. B. Positively stained granules for iNOS were significantly increased in both number and intensity in colonic tissue of model control rats. (a) Acetic acid treated rats; (b) TNBS treated rats. C. The colonic iNOS expression was significantly reduced in both acetic acid (d) and TNBS (e) treated rats after intervened with 10.0 mg•kg-1 of melatonin.
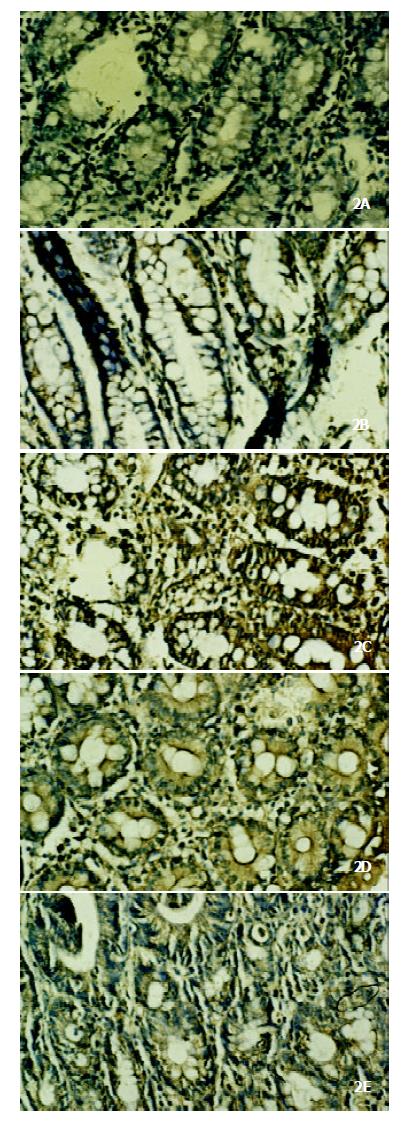
Figure 2 Abnormal expression of COX-2 in colonic tissue of rats with colitis induced by acetic acid or TNBS enema and its improvement by melatonin, which was in accordance with the observation in clonic iNOS expression.
A. Positively stained COX-2 granules in colonic tissue of normal control rats. B. iNOS expression was significantly increased as manifested by the augmented and intensified positively stained granules in colonic tissue of model control rats. (a) Acetic acid treated rats; (b) TNBS treated rats. C. The colonic COX-2 expression was significantly reduced in both acetic acid (d) and TNBS (e) treated rats after intervened with 10.0 mg•kg-1 of melatonin.
- Citation: Dong WG, Mei Q, Yu JP, Xu JM, Xiang L, Xu Y. Effects of melatonin on the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in rat models of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1307-1311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1307.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1307