Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1292-1295
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1292
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1292
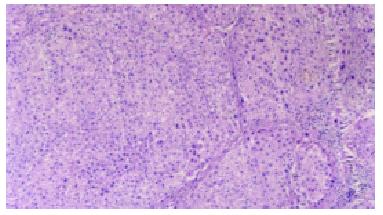
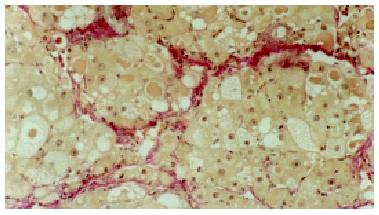
Figure 1 Loss of normal lobular architecture, some had pseudo lobule formation in the CCl4 intoxicated groups.
HE × 100.
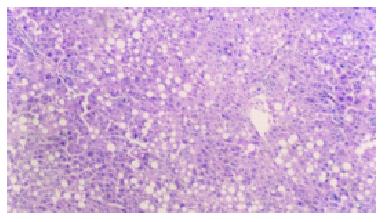
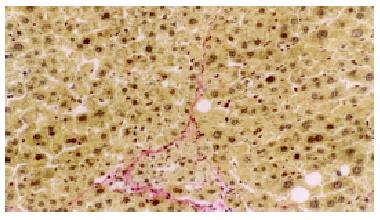
Figure 2 Steatosis was not severe and fibrosis was not so pronounced, without any pseudo -lobule formation in the Ganyanping-treated groups.
HE × 100.
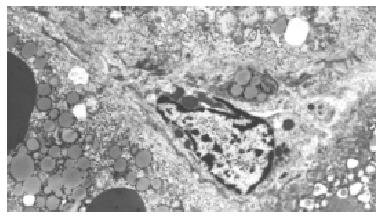
Figure 3 The numbers of hepatic stellate cells and collagen fibrils increased in Disse's space and hepatocellular degeneration were frequently seen in the CCl4 intoxicated groups.
× 4000.
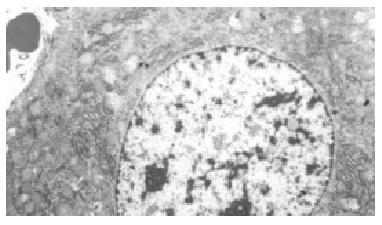
Figure 4 Most of hepatocytes showed basically normal ultrastructure and a few lipid droplets were found in the cytoplasm in the Ganyanping-treated groups.
× 4000.
Figure 5 Hepatic parenchyma separated by the rough, red-stained fibrotic septa in the CCl4 intoxicated groups.
VG × 200.
Figure 6 Collagen fibrosis was less pronounced in the Ganyanping-treated groups.
VG × 200.
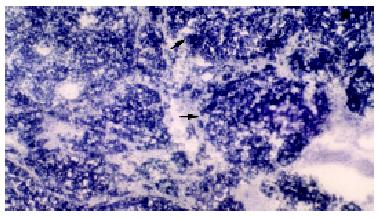
Figure 7 Increase in the activities of MAO(+++) in the CCl4 intoxicated groups.
× 75.
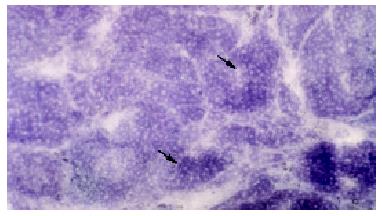
Figure 8 Decrease in the activities of MAO in the Ganyanping-treated groups (++).
× 75.
- Citation: Tang WX, Dan ZL, Yan HM, Wu CH, Zhang G, Liu M, Li Q, Li SB. Experimental study of effect of Ganyanping on fibrosis in rat livers. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1292-1295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1292.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1292