Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1256-1260
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1256
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1256
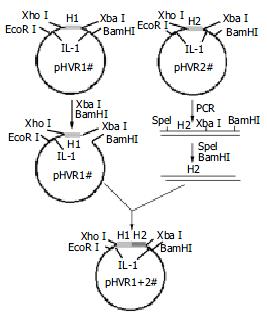
Figure 1 Four different HVR1 gene fragments were cloned on pBVIL-1.
HVR1-2 gene fragment was ligated with pBVIL-1-HVR1-1 (pHVR1#). The new pHVR1+2 had the same site with pHVR1#, and the HVR1-4# gene fragments could be ligated by the same way. After 3 cycles, the chimera HVR1 plamid was constructed.
Figure 2 Derivation of the Chinese consensus sequence.
(A) Consensus pattern of the 123 natural variants of the HCV HVR1 sequence used in this work. Shaded residues accounted alone for 80% of the observed frequency. Residues were listed in decreasing order of observed frequency from top to bottom. The first line was Chinese consensus sequence (CCS). (B) The Chinese consensus sequence (upper) was different with Puntoriero's (lower). Dashes indicate residues identical to the upper line.
Figure 3 The amino acid sequence of 12 representative HVR1 sequences.
Amino acid residues were indicated by standard single-letter codes.
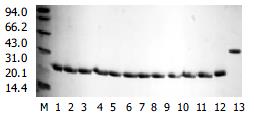
Figure 4 The Coomassic stain after SDS-PAGE of 12 purified representative and chimera HVR1 antigen.
M. marker; 1-12. 12 purified representative HVR1 antigen; 13. chimera HVR1 antigen.
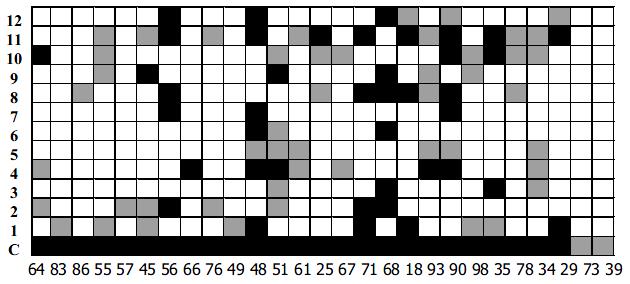
Figure 5 Reaction of the 12 representative HVR1s and chimera HVR1antigen (C) with 27 sera from HCV-infected patients.
HVR1 names are indicated at the left of each column. For each serum (indicated on the bottom of each column) average values (A450) have been determined from two independent experiments. The mean of 10 sera from non-infected individuals plus 4SD defined the cutoff (co). Results were expressed as the difference between the average value of the HCV antibody positive sera and co. Strong positive values (> 0.5) are indicated in black. And weak positive values are indicated in grey (0.15-0.5).
- Citation: Xiu BS, Ling SG, Song XG, Zhang HQ, Chen K, Zhu CX. Cross-reactivity of hypervariable region 1 chimera of hepatitis C virus. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1256-1260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1256.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1256