Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2003; 9(10): 2251-2257
Published online Oct 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2251
Published online Oct 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2251
Figure 1 The strategy for disruption of vacA gene by directed mutagenesis.
LA and RA were PCR-amplified from H pylori NCTC 11638 genomic DNA, and the kanamycin resistance gene, from pEGFP-N1. PCR products with different restriction sites on both sides were digested with corresponding endonucleases, and then cloned into pBluescript II SK digested with the same enzymes. Because there is an EcoR II site in RA, pLA and pkmr were firstly joined together, resulting in pLK, which then was joined with pRA, resulting in pLKR. The plasmid pLKR was transformed into H. pyloi NCTC 11638, where the Kmr marked mutation was introduced into the genome by homologous recombination, resulting in the vacA-Kmr mutant strain.
Figure 2 Nucleotide sequence of cysS gene and the downstream sequence amplified from the vacA-Kmr mutant H pylori.
The 1398 bp cysS ORF and the 795 bp kmr ORF are shown. Primers la1, la2, ra1, ra2, and rs for amplifying LA, RA, and ASm are indicated. -35 signal, -10 signal, and rbs of vacA gene serving km r gene in the mutant strain are also shown.
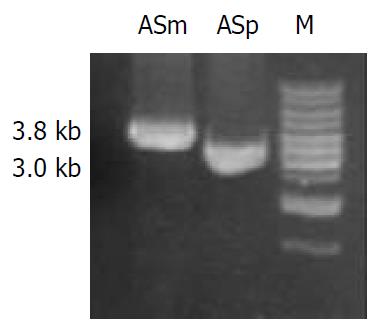
Figure 3 PCR amplification for the determination of homolo-gous recombination in Kmr mutant strain.
Genomic DNA of NCTC 11638 wild strain and Kmr mutant strain were respec-tively PCR-amplified for the fragments ASm and ASp using the primers ra1 and rs. A single 3.8 kb product ASm was am-plified from Kmr mutant strain as compared with the 3.0 kb product ASp amplified from the wild strain.
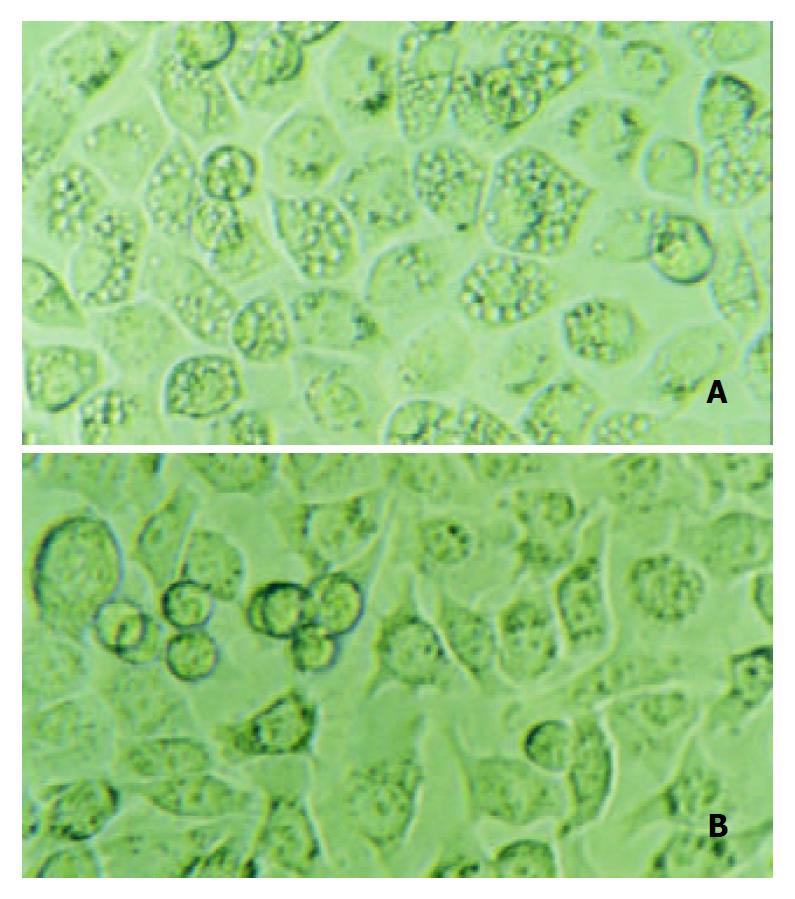
Figure 4 Gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 were co-cultured with the supernatant either from Helicobacter pylori NCTC 11638 or its vacA-knockout mutant strain.
12 h after the incubation, A: cells co-cultured with NCTC 11638 developed vacuoles in the cytosol; B: cells co-cultured with vacA- mutant strain developed no vacuoles at all.
-
Citation: Yuan JP, Li T, Shi XD, Hu BY, Yang GZ, Tong SQ, Guo XK. Deletion of
Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin gene by introduction of directed mutagenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(10): 2251-2257 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i10/2251.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2251