Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 15, 2003; 9(1): 44-49
Published online Jan 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.44
Published online Jan 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.44
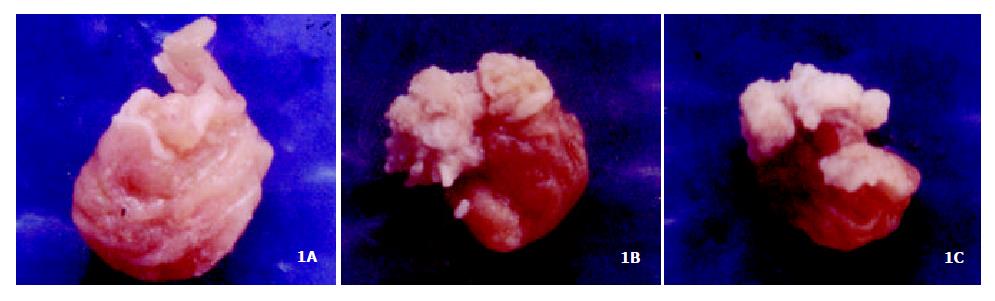
Figure 1 The establishment of mouse neoplasia model induced by B (a) P.
(A): normal forestomach; (B, C): forestomach neoplasia.
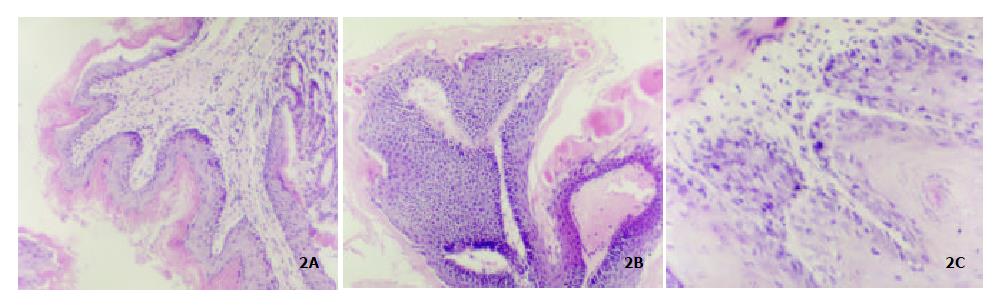
Figure 2 The pathological analysis of mouse forestomach.
(A): normal forestomach × 10; (B): Atypical hyperplasia × 10; (C): Carci-noma in situ× 4.
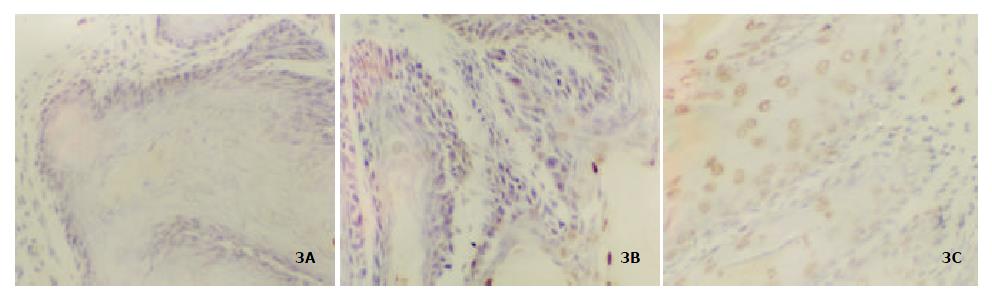
Figure 3 Apoptosis induced by CLA in mice forestomach.
(A or B): there were few apoptotic cells in group A and B; (C): the apoptosis induced by CLA. Arrow showed apoptotic cells × 40.
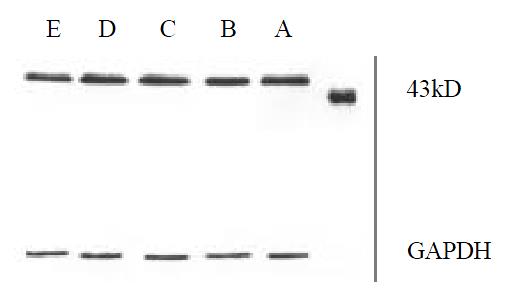
Figure 4 The effect of CLA on the expression of MEK-1 protein.
Figure 5 The effect of CLA on the expression of ERK-1 protein.
Figure 6 The effect of CLA on the expression of MKP-1 protein.
- Citation: Chen BQ, Xue YB, Liu JR, Yang YM, Zheng YM, Wang XL, Liu RH. Inhibition of conjugated linoleic acid on mouse forestomach neoplasia induced by benzo (a) pyrene and chemopreventive mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(1): 44-49
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i1/44.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.44