Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2002; 8(6): 1088-1093
Published online Dec 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1088
Published online Dec 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1088
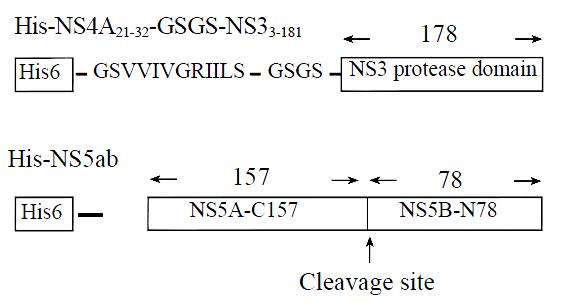
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of constructs expressing single-chain serine protease NS3N4A and substrate NS5ab.
His6, the hexahistidine metal chelation tag; GSVVIVGRIILS, NS4A central peptide (a.a. 21-32) and GSGS, an amino acid linker connecting the NS4A peptide to the NS3 serine protease domain. Cleavage site, representing the cleavage site between NS5A and NS5B.
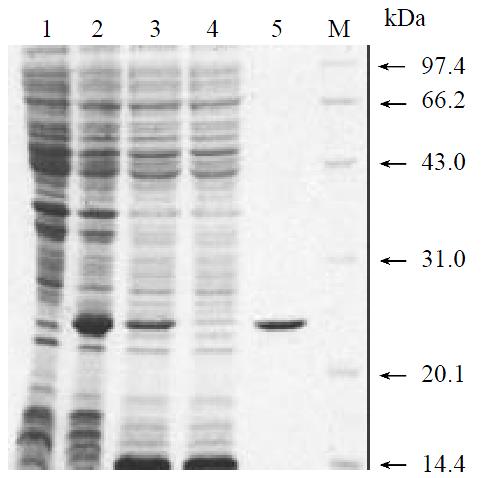
Figure 2 SDS-PAGE analysis for the expression and purity of single-chain serine protease.
Lane 1, Noninduced cells; lane 2, Cells induced with IPTG; lane 3, Cleared lysate; lane 4, Flow-through; lane 5, Purified single-chain serine protease; M, low molecular weight markers.
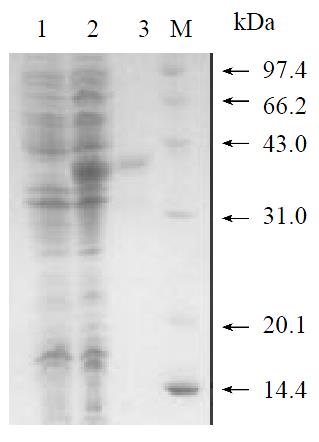
Figure 3 SDS-PAGE analysis for the expression and purity of HCV NS5ab protein.
Lane 1, noninduced E.coli M15 cell lysate; lane 2, lysate of E.coli M15 cells transformed with pQENS5ab plasmids after induction; lane 3, purified HCV NS5ab protein; M, Low molecular weight markers.
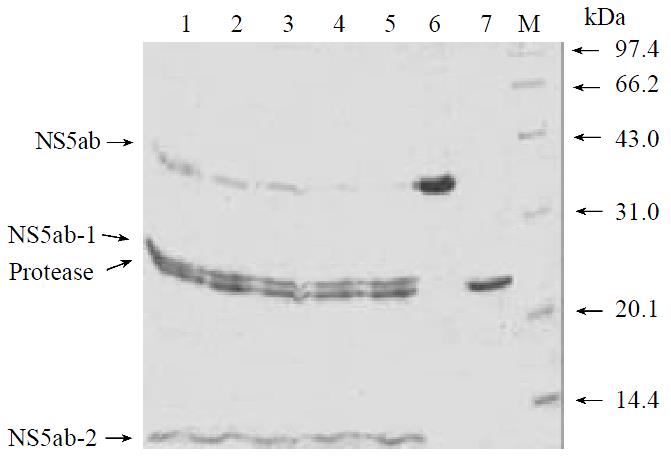
Figure 4 In vitro trans-cleavage at the NS5A/5B site of single-chain serine protease.
Lane 1-5, cleavage reaction after 10, 20, 30, 45 and 60 mins; lane 6, protein substrate NS5ab;lane 7, single-chain serine protease; M, low molecular weight markers.
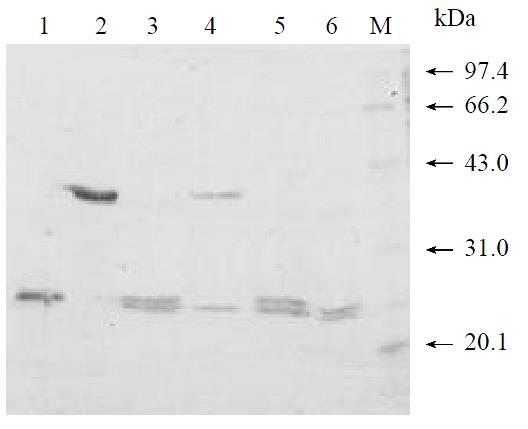
Figure 5 The inhibitory effects of PMSF and EDTA on single-chain protease activity.
M, low molecular weight markers; lane1, single-chain serine protease; lane 2, protein substrate NS5ab; lane 3, without PMSF; lane 4, with 5 mmol/L PMSF; lane 5, without EDTA; lane 6, with 5 mmol/L EDTA.
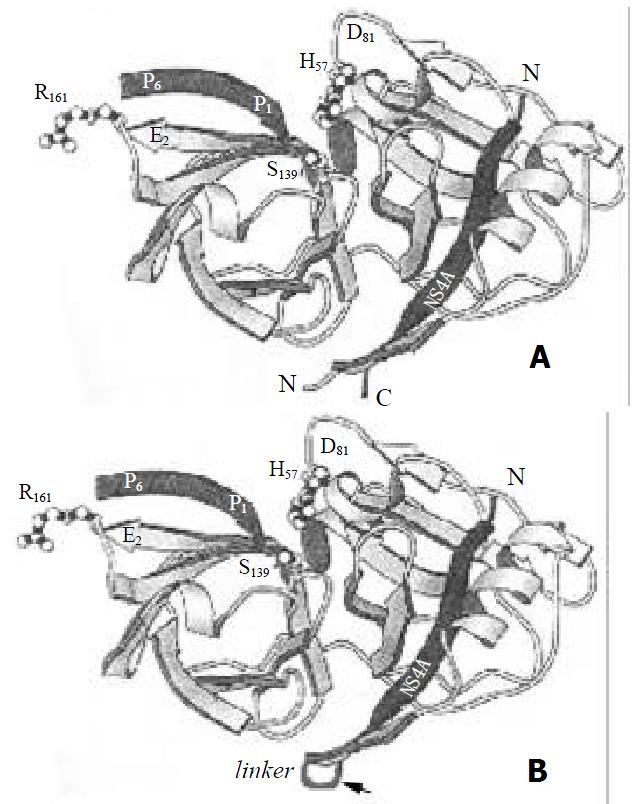
Figure 6 The crystal structure of serine protease domain and NS4A central sequence.
A. cocrystal structure of the NS31-181/ NS4A21-32 complex (adapted from reference 11). B. cocrystal structure of the NS31-181/NS4A21-32 complex with a flexible linker.
-
Citation: Du GX, Hou LH, Guan RB, Tong YG, Wang HT. Establishment of a simple assay
in vitro for hepatitis C virus NS3 serine protease based on recombinant substrate and single-chain protease. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(6): 1088-1093 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i6/1088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1088