Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2002; 8(3): 540-545
Published online Jun 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.540
Published online Jun 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.540
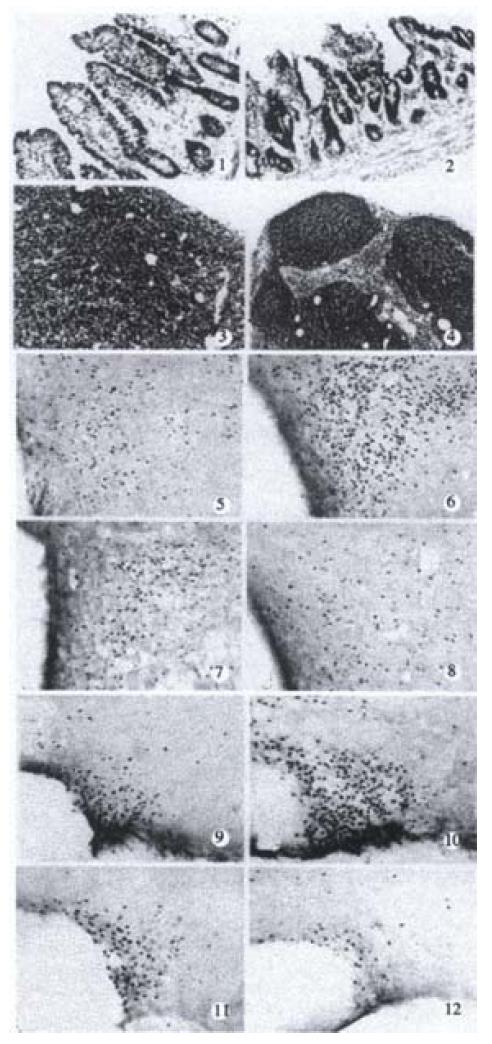
Figure 1 In Figures E1 and E3 show the normal structures of the villus and mesenteric lymph node in saline-injected rats; 2 and 4 show the villus and mesenteric lymph node in STM-challenged rats.
5 and 9 show Fos expression in PVN and SON respectively in NS + sham rats; 6 and 10 show Fos expressions in PVN and SON respectively in STM + sham rat; 7 and 11 show Fos expressions in PVN and SON respectively in STM + vagotomy rat; 8 and 12 show Fos expressions in PVN and SON respectively in NS + vagotomy rat. × 50
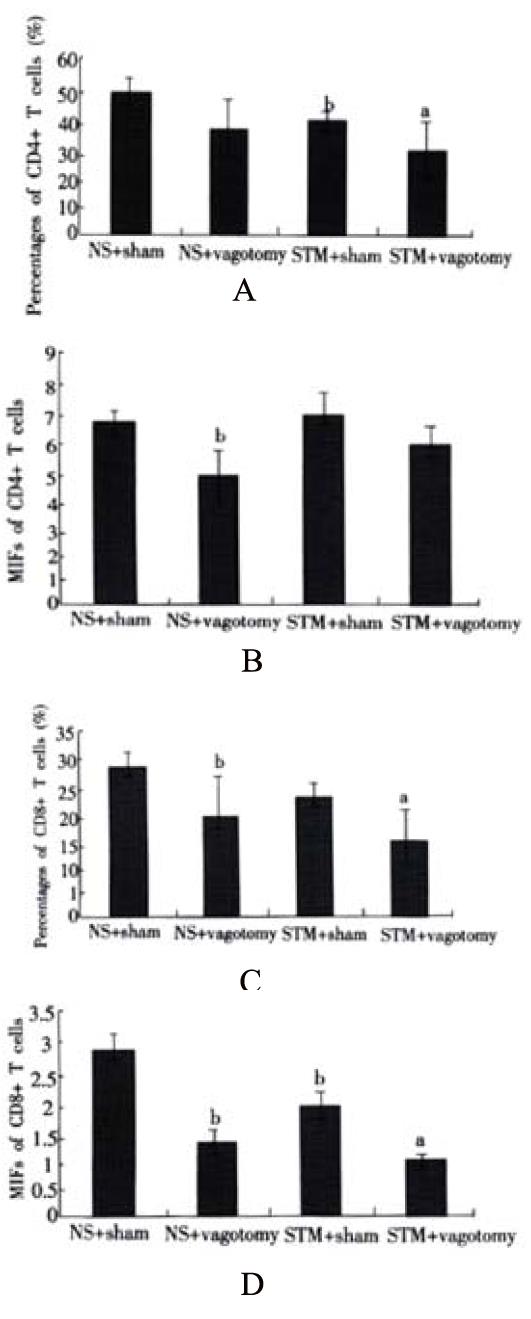
Figure 2 A: Percentages of blood CD4+ T cells.
aP < 0.05 vs. STM + sham, bP < 0.05 vs NS + sham; B: The Mean Intensities of Fluorescence (MIFs) of blood CD4+ T cells. bP < 0.05 vs NS + sham; C: Percentages of blood CD8+ T cells. aP < 0.05 vs STM + sham, bP < 0.05 vs NS + sham; D: The Mean Intensities of Fluorescence (MIFs) of blood CD8+ T cells. aP < 0.05 vs STM + sham; bP < 0.05 vs NS + sham.
- Citation: Wang X, Wang BR, Zhang XJ, Xu Z, Ding YQ, Ju G. Evidences for vagus nerve in maintenance of immune balance and transmission of immune information from gut to brain in STM-infected rats. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(3): 540-545
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i3/540.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.540