Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2001; 7(6): 796-800
Published online Dec 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.796
Published online Dec 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.796
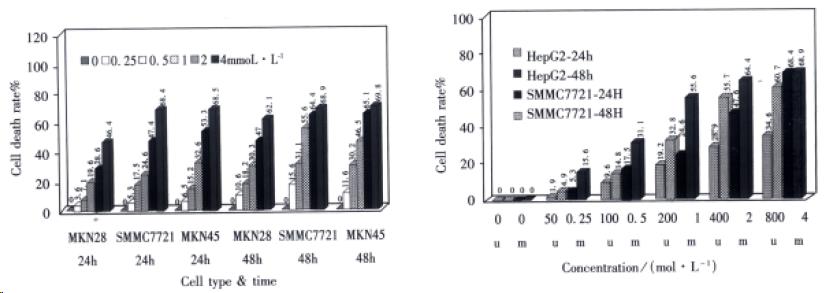
Figure 1 A: Dose-response of sulindac on growth of cell lines by MTT assay (N = 3); B: Dose-response of sulindac on growth of HCC cell lines by MTT assay (N = 3).
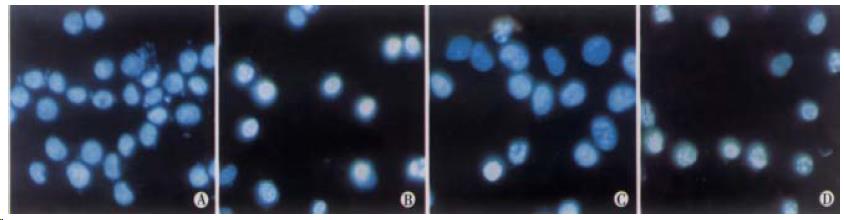
Figure 2 Morphological changes of MKN45 and HepG2.
Cells stained with Hoechst 33258 × 400. A: MKN45 cells; B: MKN45 cells treated with 2 mmol•L¯¹ sulindac for 24 h; C: HepG2 cells; D: HepG2 cells treated with 400 μmol•L¯¹ sulindac for 24 h.
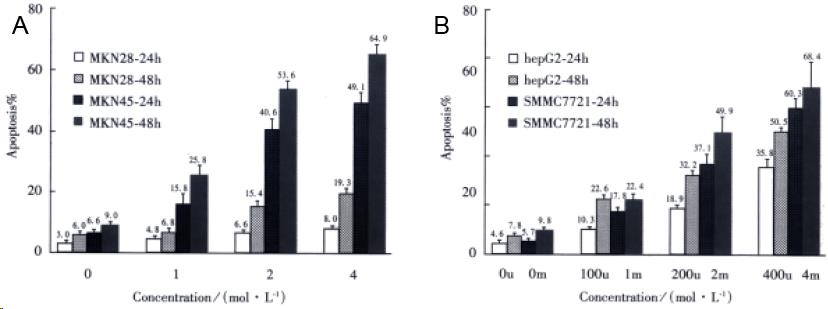
Figure 3 A: The apoptosis of gastric cancer cells induced by sul indac by Hoechst 33258 staining.
(N = 3); B: The apoptosis of 2 HCC cells induced by sulindac by Hoechst 33258 staining. (N = 3)
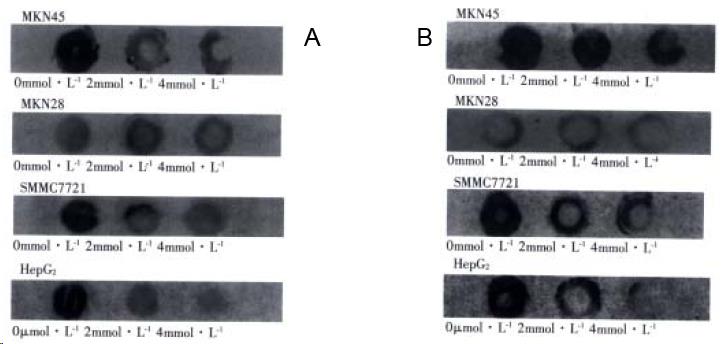
Figure 4 A: COX-2 protein levels in human gastric cancer and HCC cells with sulindac for 24 h; B: Bcl-2 protein levels in human gastric cancer cells and HCC cells with sulindac for 24 h.
- Citation: Wu YL, Sun B, Zhang XJ, Wang SN, He HY, Qiao MM, Zhong J, Xu JY. Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of Sulindac on Human gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(6): 796-800
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i6/796.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i6.796