Copyright
©The Author(s) 1998.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 1998; 4(4): 298-302
Published online Aug 15, 1998. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v4.i4.298
Published online Aug 15, 1998. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v4.i4.298
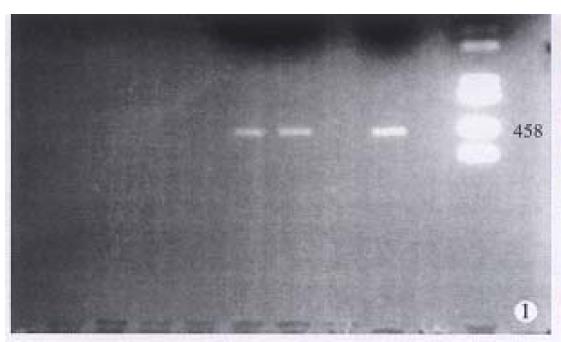
Figure 1 Detection of PCR products by agarose gel electrophoresis.
Lane A: DNA size marker (kb), Lane B: negative control, Lane C: Hela cell DNA amplified as a positive control, Lane D/E: the sample containing HPV DNA.
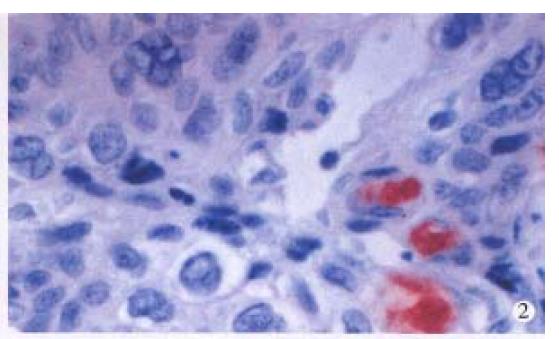
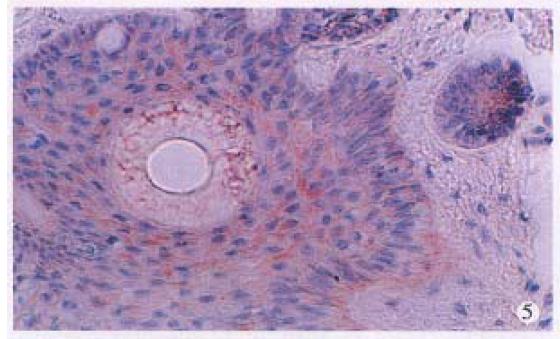
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining for HPV antigen in squamous cell carcinoma.
× 400
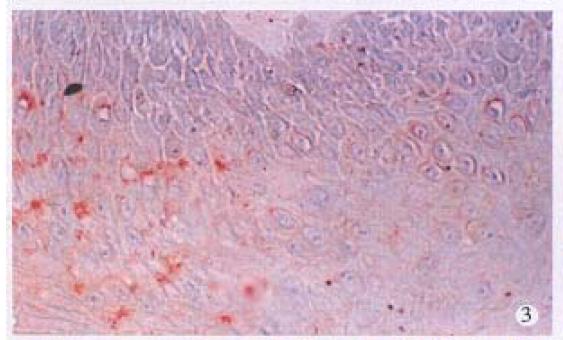
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining for HPV antigen in nonneoplastic superficial epithelium.
× 400
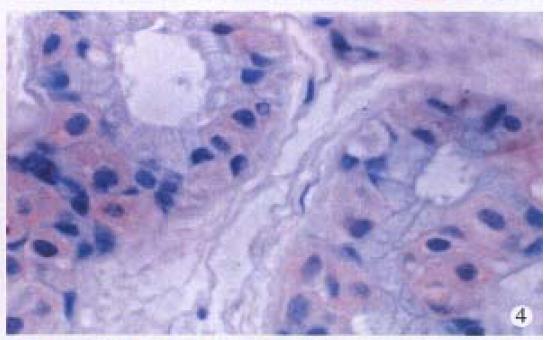
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining for HPV antigen in sweat gland.
× 400
Figure 5 Immunohistochemical staining for HPV antigen in hair follicles.
× 400
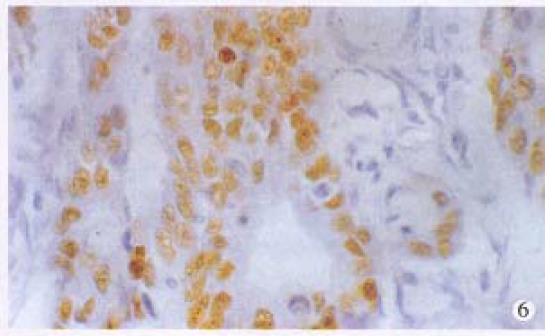
Figure 6 Immunohistochemical staining for p53 in anal adenocarcinoma.
× 400
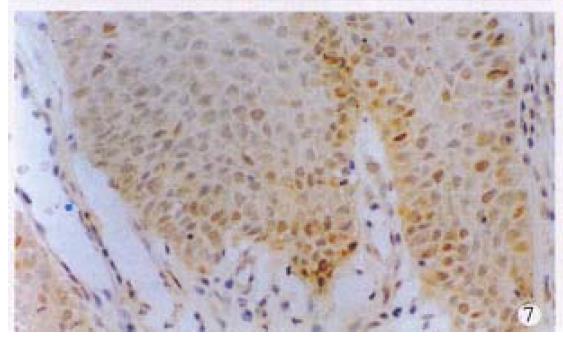
Figure 7 Immunohistochemical staining for p53 in condyloma acuminatum.
× 200
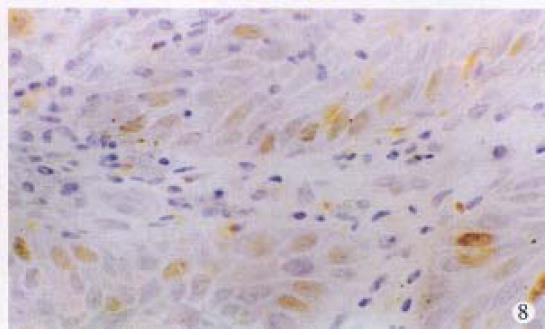
Figure 8 Immunohistochemical staining for p53 in morphologically normal epithelium invaded by anal adenocarcinoma (left above).
× 400
- Citation: Lai MD, Luo MJ, Yao JE, Chen PH. Anal cancer in Chinese: human papillomavirus infection and altered expression of p53. World J Gastroenterol 1998; 4(4): 298-302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v4/i4/298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v4.i4.298