Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2025; 31(9): 100221
Published online Mar 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.100221
Published online Mar 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.100221
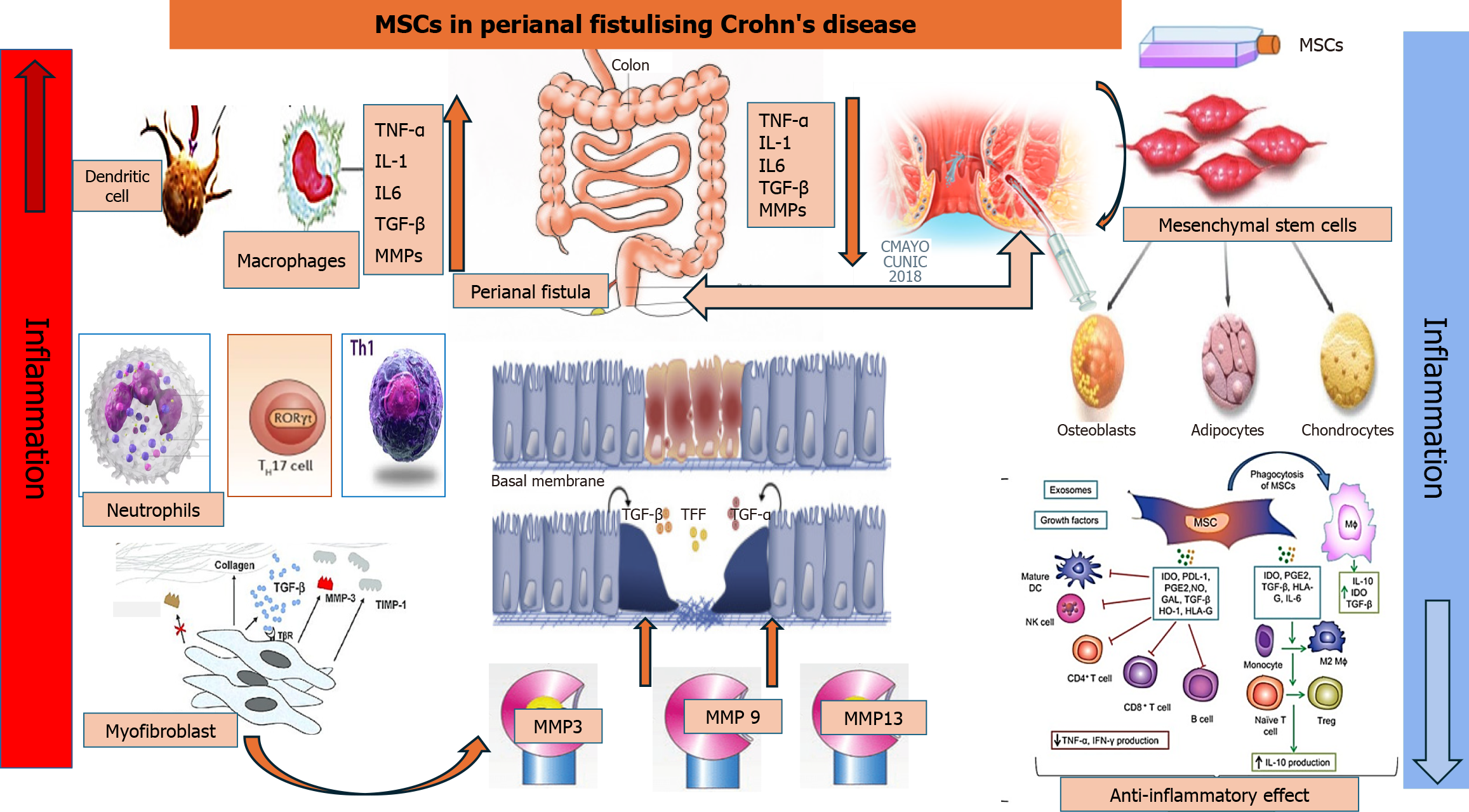
Figure 1 Mechanisms of perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease and therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cells.
Enhanced production of inflammatory cytokines by infiltrating macrophages and other inflammatory cells stimulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, resulting in activation of myofibroblasts and elevation of matrix metalloproteinases, leading to fistula formation. Injection of mesenchymal stem cells into the fistula results in suppression of the inflammatory cells and cytokines and complete resolution of perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; Th: T helper cells; TFF: Trefoil factor family; DC: Dendritic cell; NK: Natural killer; Treg: Regulatory T cell; IDO: Indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase; PDL-1: Programmed death ligand 1; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; NO: Nitrogen oxide; GAL: Gallic acid; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen.
- Citation: Bhatnagar P, Elhariri S, Burud IAS, Eid N. Perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease: Mechanisms and treatment options focusing on cellular therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(9): 100221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i9/100221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.100221