Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2025; 31(6): 102090
Published online Feb 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.102090
Published online Feb 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.102090
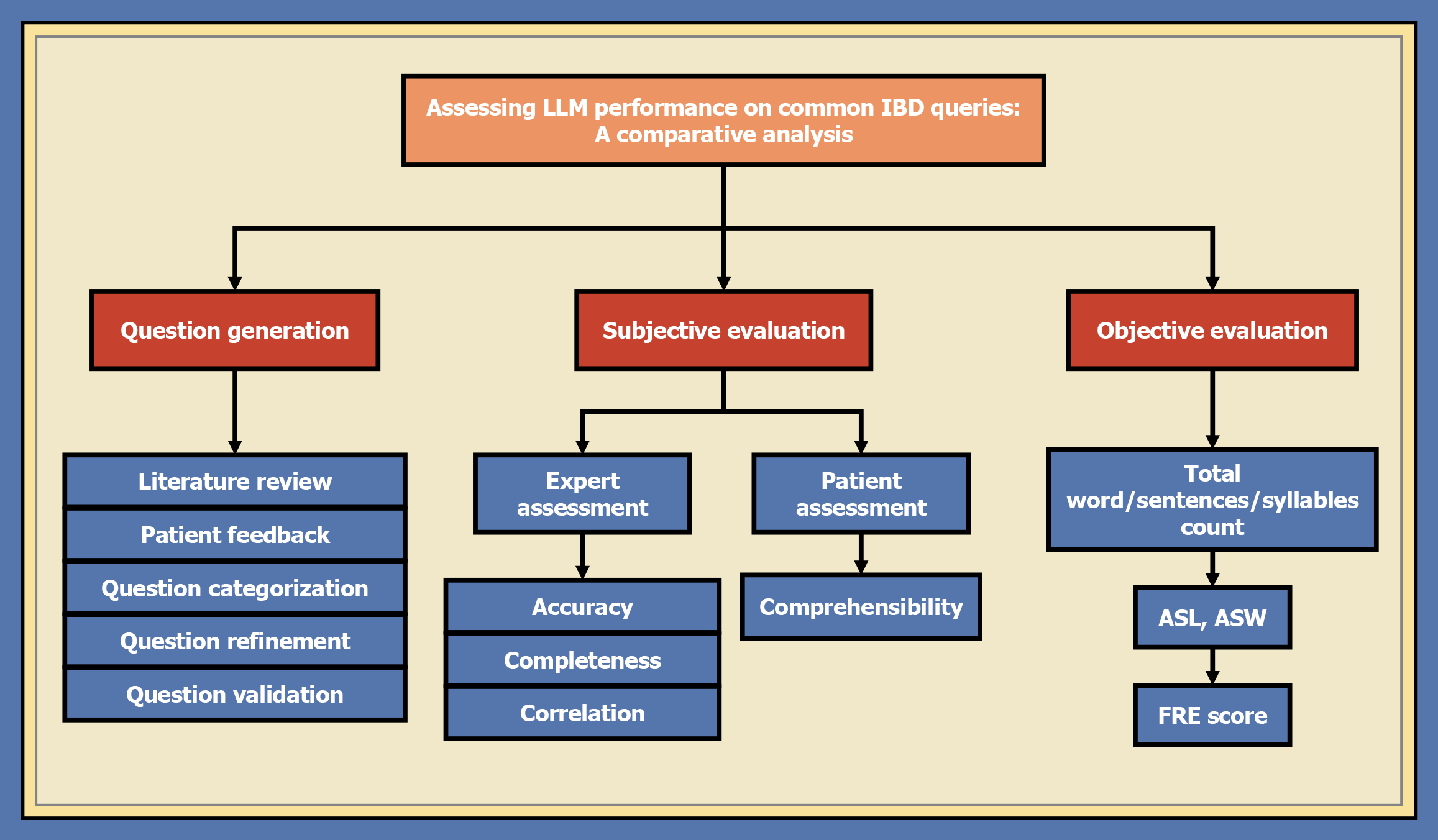
Figure 1 Clinical research framework: Evaluating large language models’ answers to inflammatory bowel disease queries.
LLM: Large language model; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; ASL: Average number of words per sentence; ASW: Average number of syllables per word; FRE: Flesch Reading Ease.
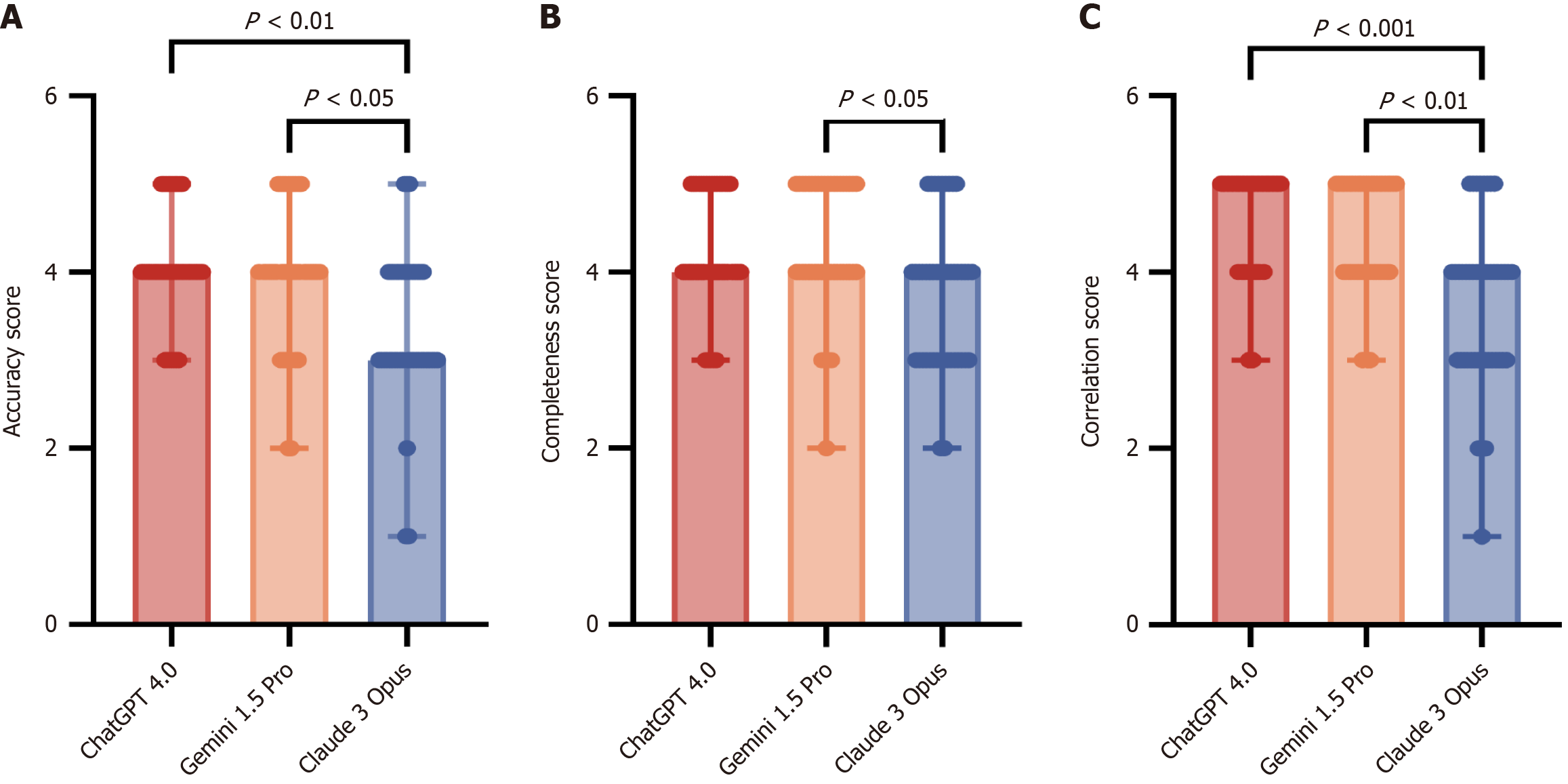
Figure 2 Comparison of medical expert evaluation scores for the answers to the 15 questions on inflammatory bowel disease using different large language models.
A: Accuracy median scores of the answers; B: Completeness median scores of the answers; C: Correlation median scores of the answers. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease.
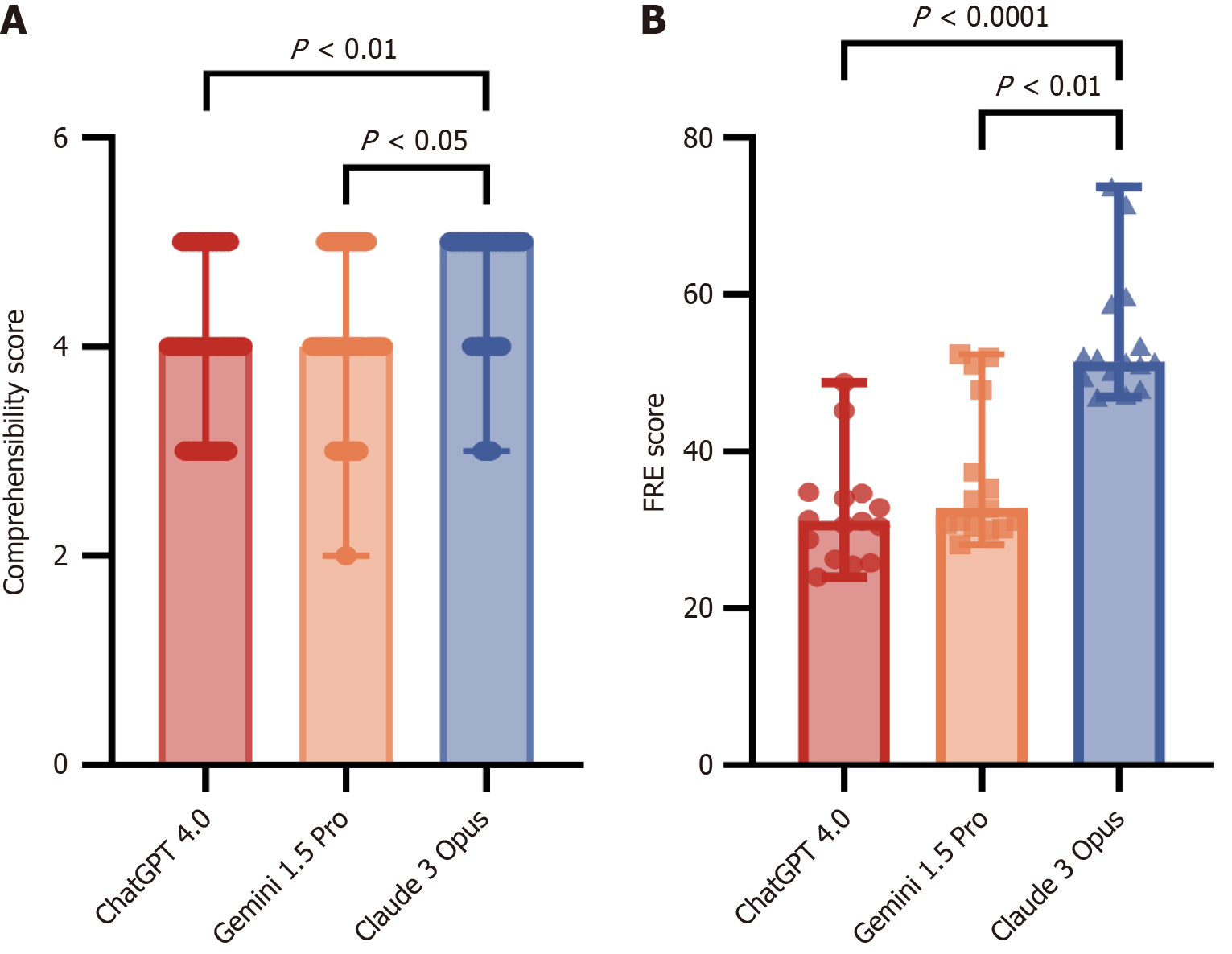
Figure 3 Different scores for the answers to the 15 questions on inflammatory bowel disease using different large language models.
A: Comparison of patient evaluation scores; B: Flesch Reading Ease scores. FRE: Flesch Reading Ease scores.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Wan XH, Kong QZ, Liu H, Liu J, Guo J, Yang XY, Zuo XL, Li YQ. Evaluating large language models as patient education tools for inflammatory bowel disease: A comparative study. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(6): 102090
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i6/102090.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.102090