Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2025; 31(4): 100401
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100401
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100401
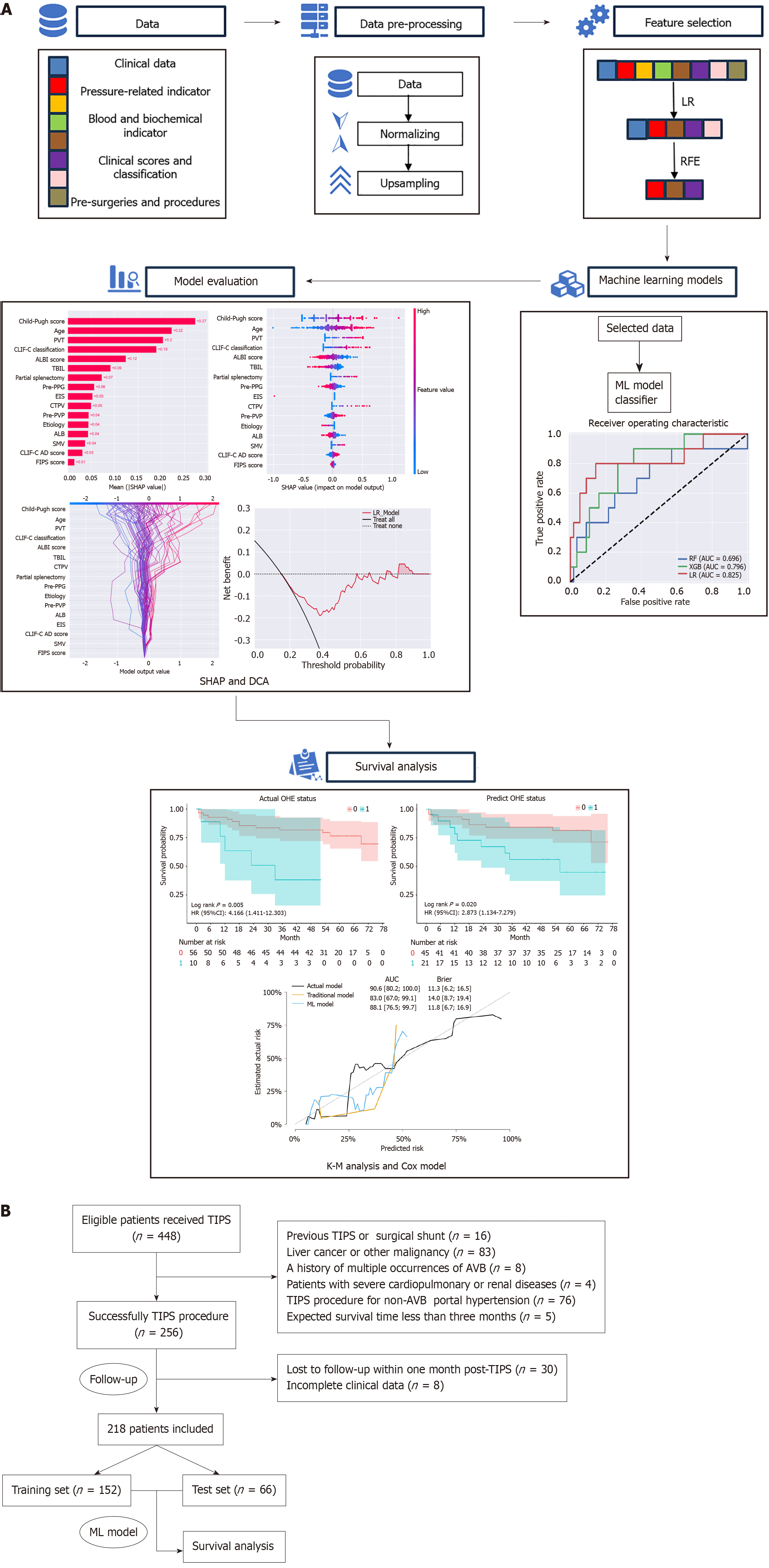
Figure 1 Study design.
A: Development and validation of the overt hepatic encephalopathy prediction model; B: Flowchart of patient enrollment and grouping. LR: Logistic regression; RFE: Recursive feature elimination; K-M: Kaplan-Meier; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations; DCA: Decision curve analysis; AVB: Acute variceal bleeding; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; ML: Machine learning.
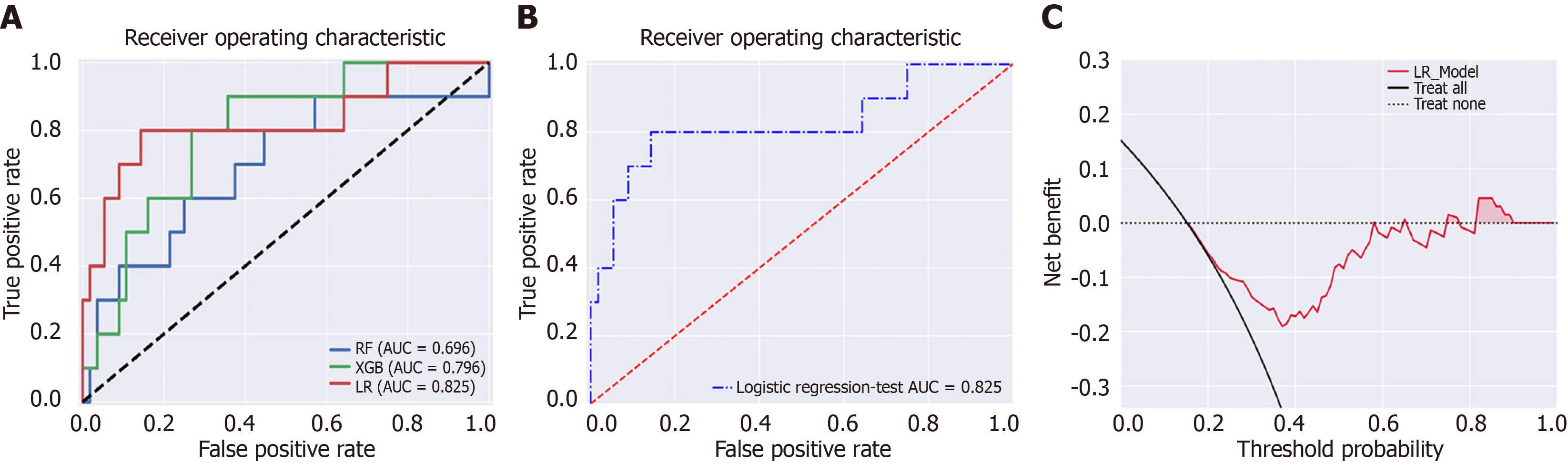
Figure 2 Comparison of various machine learning models in a classification task and decision curve analysis for the logistic regression model.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for random forest, extreme gradient boosting, and logistic regression (LR); B: ROC curve for the LR model, presented individually with an area under the curve value of 0.825; C: Decision curve analysis for the LR model, illustrating the net benefit at various threshold probabilities in comparison to the “treat all” and “treat none” strategies. AUC: Area under the curve; XGB: Extreme gradient boosting; LR: Logistic regression.
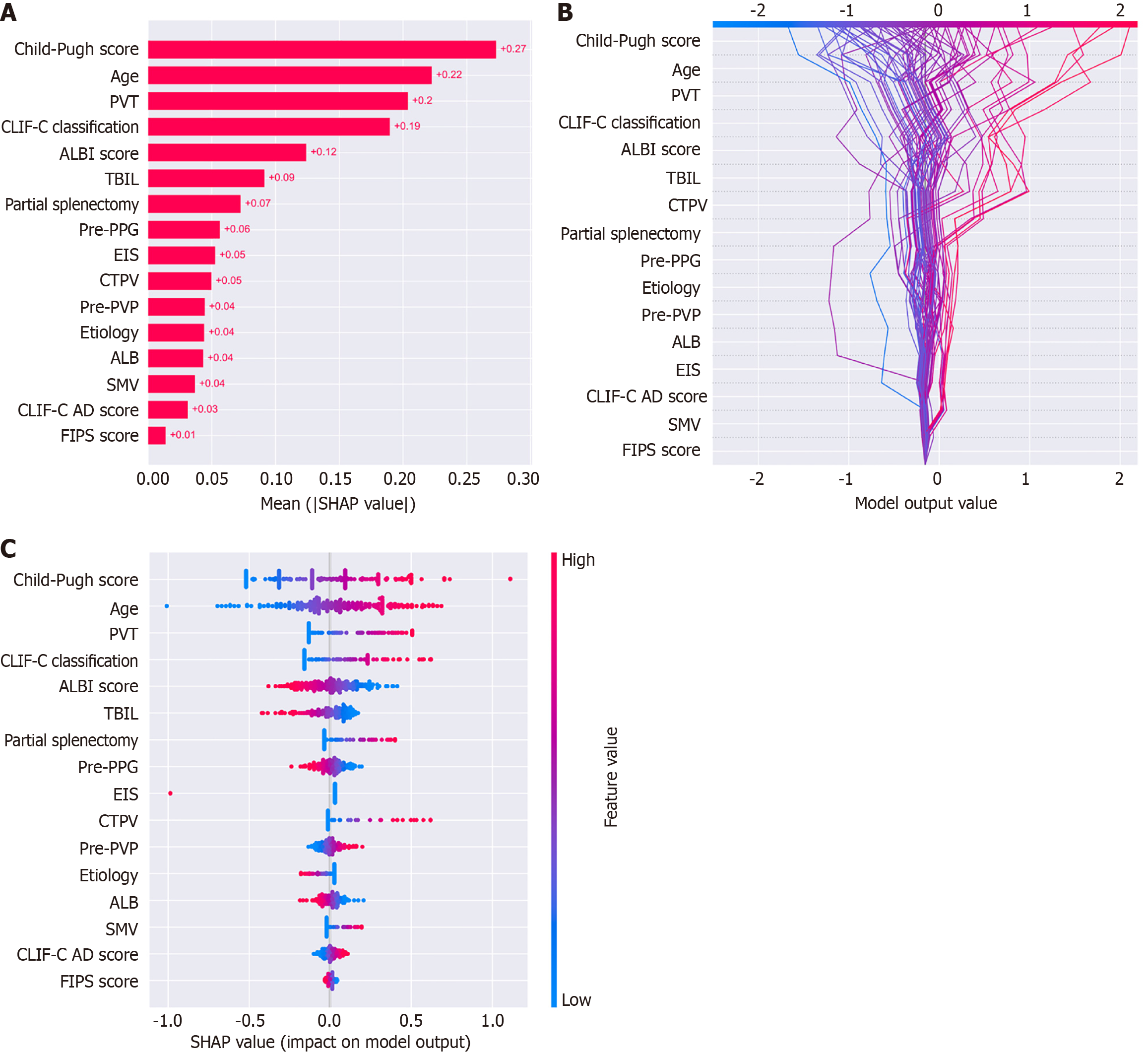
Figure 3 Analysis of feature importance using SHapley Additive exPlanations values in the logistic regression model.
A: Bar chart displaying the mean SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) values, which indicate the average impact of each feature on the model output; B: Beeswarm plot showing the distribution of SHAP values for individual predictions; C: Summary plot combining SHAP values and feature importance, with feature values represented by color (blue for low and red for high). PVT: Portal vein thrombosis; CLIF-C: Chronic liver failure consortium; ALBI: Albumin-bilirubin; TBIL: Total bilirubin; PPG: Portal pressure gradient; EIS: Endoscopic injection sclerotherapy; CTPV: Cavernous transformation of the portal vein; PVP: Portal venous pressure; ALB: Albumin; SMV: Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis; CLIF-C AD: Chronic liver failure consortium acute decompensation; FIPS: Fibrosis-4 index for liver fibrosis; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations.
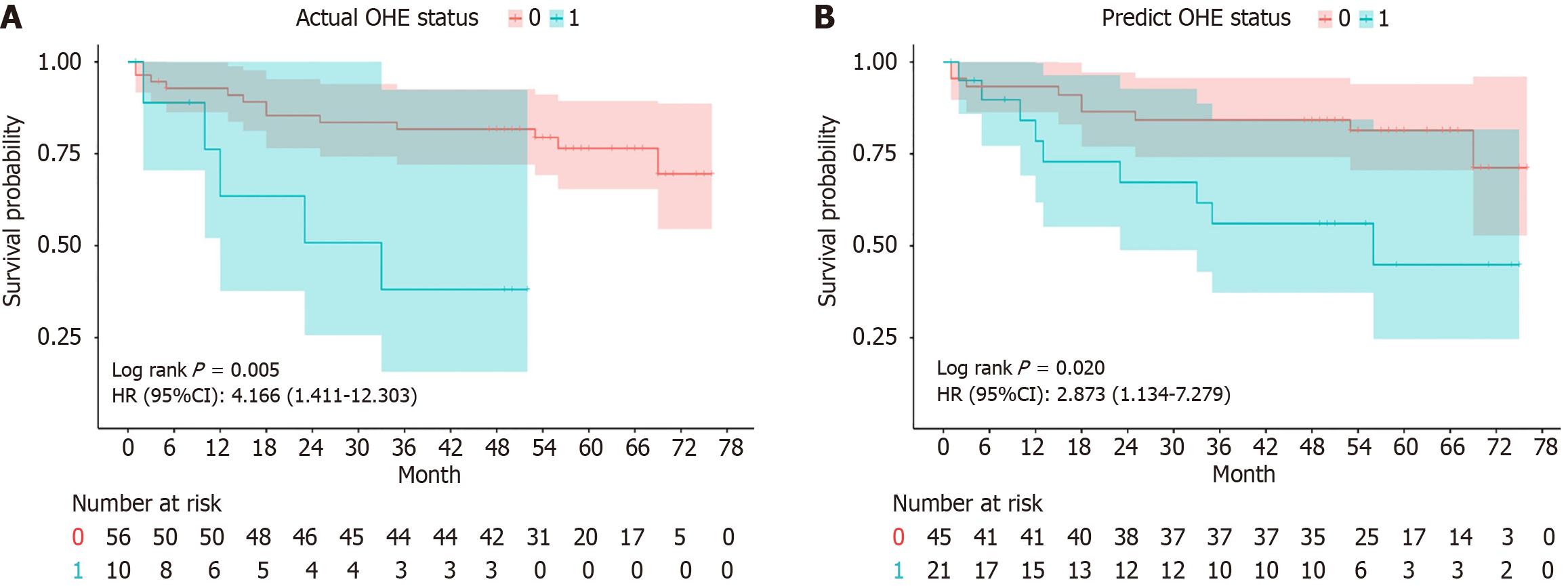
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier survival curves comparing different overt hepatic encephalopathy status groups.
A: Survival analysis based on actual overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) status; B: Survival analysis based on predicted OHE status. CI: Confidence interval; HR Hazard ratio; OHE: Overt hepatic encephalopathy.
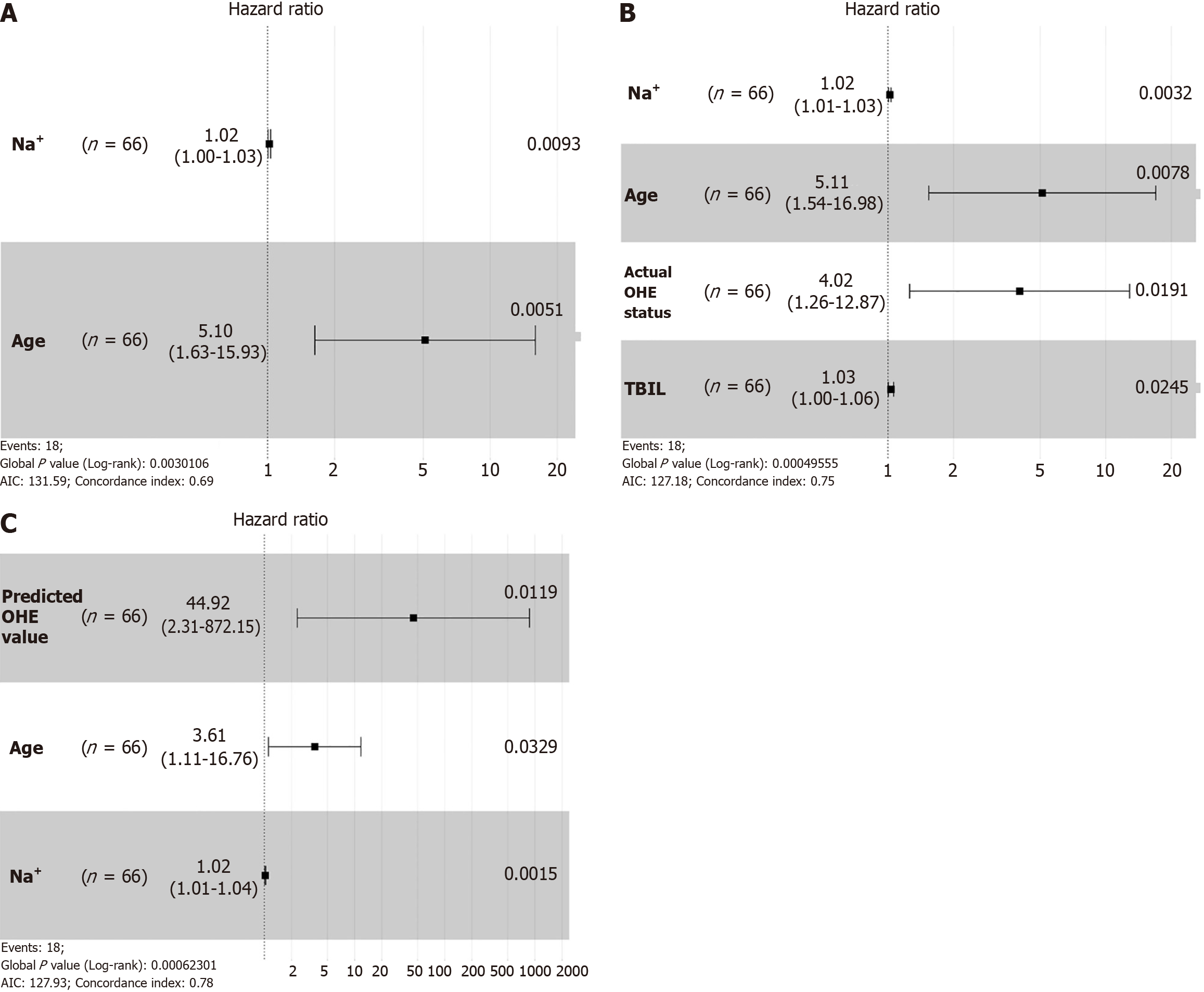
Figure 5 Multivariate Cox regression analyses of overall survival.
A: Cox regression model established with preoperative data; B: Cox regression model established with preoperative data and actual overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) status; C: Cox regression model established with preoperative data and predicted OHE value. Na+: Sodion; AIC: Akaike information criterion; TBIL: Total bilirubin; OHE: Overt hepatic encephalopathy.
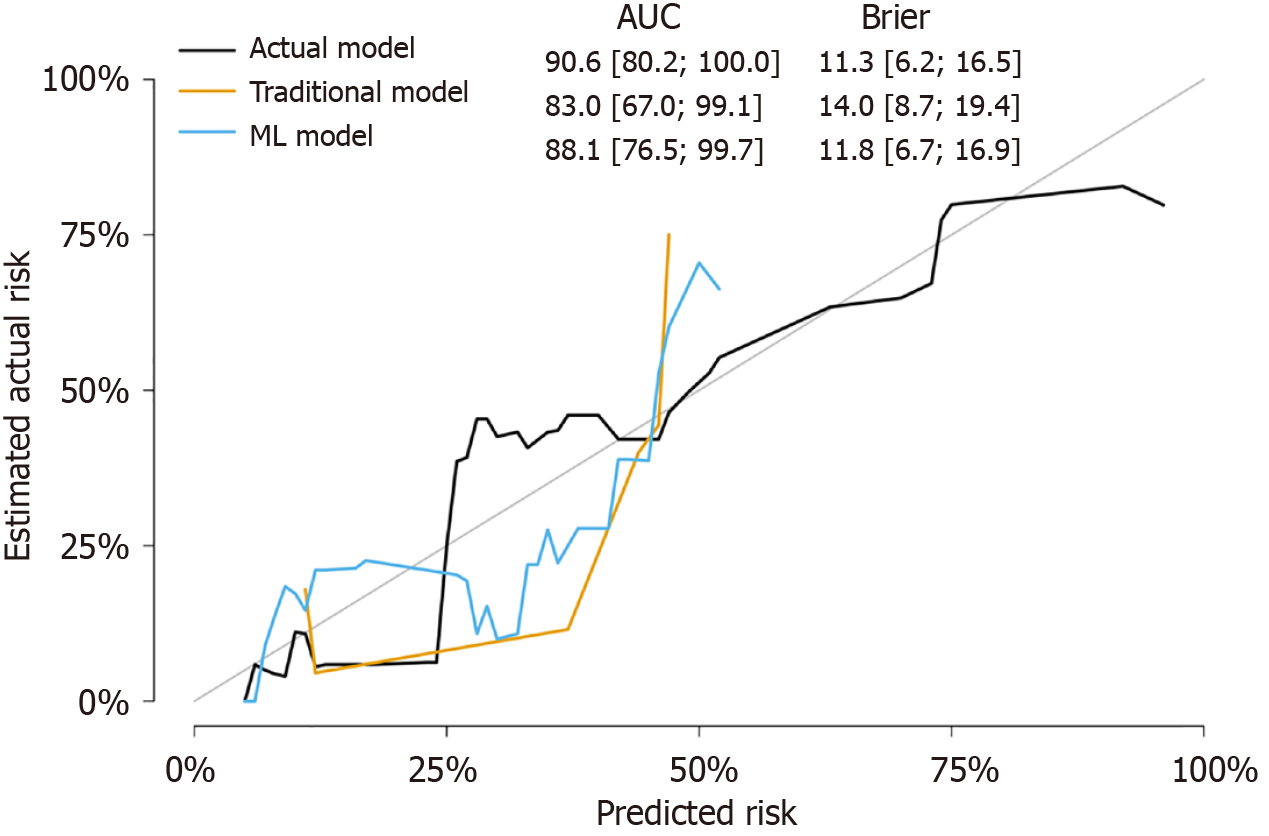
Figure 6 Calibration plot comparing the predicted risk to the actual risk for three different models: actual model (black line), traditional model (yellow line), and machine learning model (blue line).
The performance metrics include the area under the curve and Brier score for each model. AUC: Area under the curve; ML: Machine learning.
- Citation: Liu DJ, Jia LX, Zeng FX, Zeng WX, Qin GG, Peng QF, Tan Q, Zeng H, Ou ZY, Kun LZ, Zhao JB, Chen WG. Machine learning prediction of hepatic encephalopathy for long-term survival after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in acute variceal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(4): 100401
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i4/100401.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100401