Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2025; 31(30): 110112
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.110112
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.110112
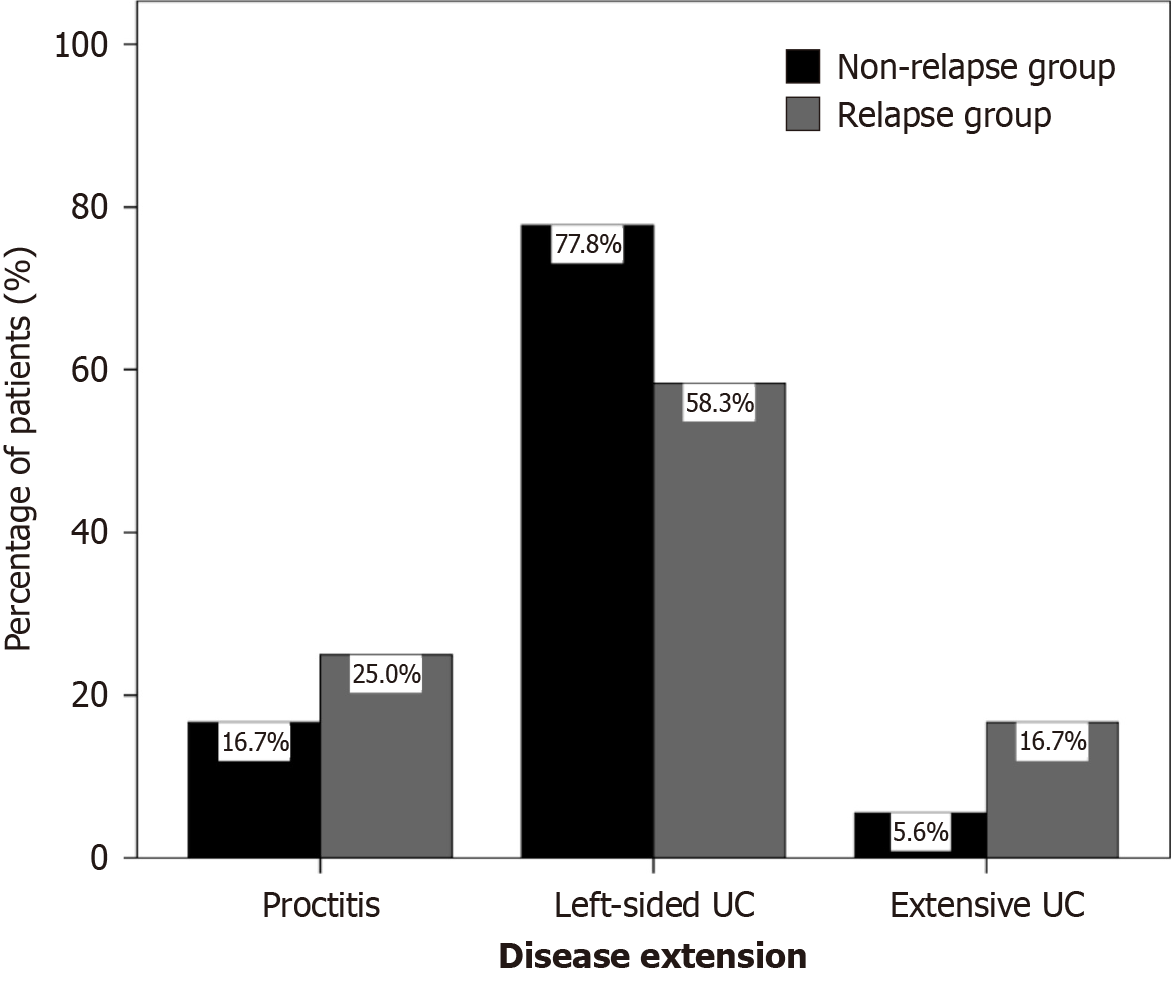
Figure 1 A clustered bar chart showing the percentage of patients with proctitis, left-sided ulcerative colitis, and extensive ulcerative colitis in both relapse and non-relapse groups.
Black bars denote participants in the non-relapse group, whereas gray bars denote those in the relapse group. UC: Ulcerative colitis.
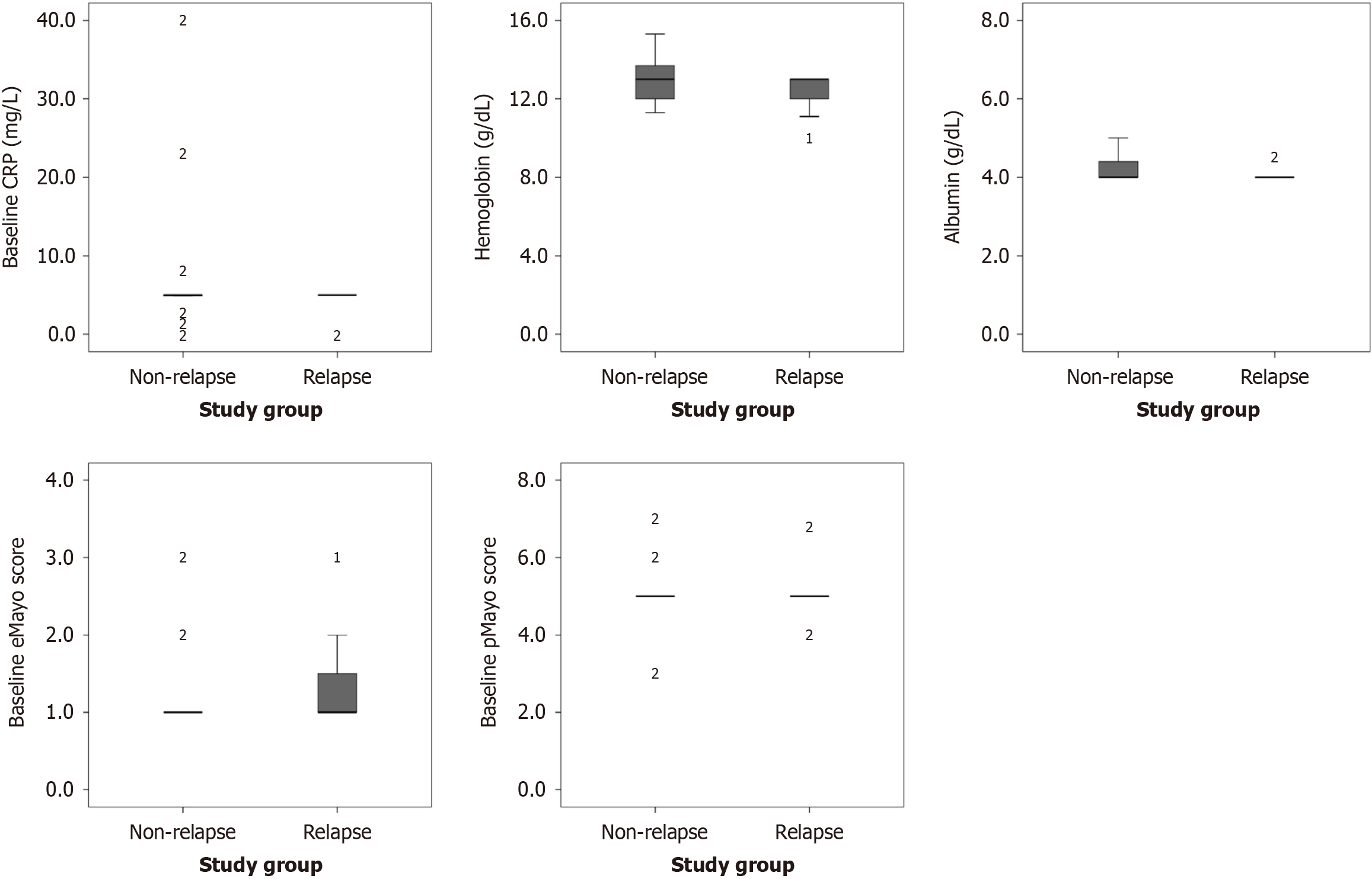
Figure 2 Boxplots comparing baseline inflammatory markers and activity scores between relapse and non-relapse groups.
The horizontal line within each box indicates the median, the box edges represent the interquartile range (IQR), and whiskers extend to 1.5 × IQR. Mild outliers (values beyond 1.5 × IQR), while extreme outliers (values beyond 3 × IQR). 1Mild outliers (values beyond 1.5 × IQR). 2Extreme outliers (values beyond 3 × IQR). CRP: C-reactive protein; eMayo: Endoscopic Mayo subscore; pMayo: Partial Mayo score.
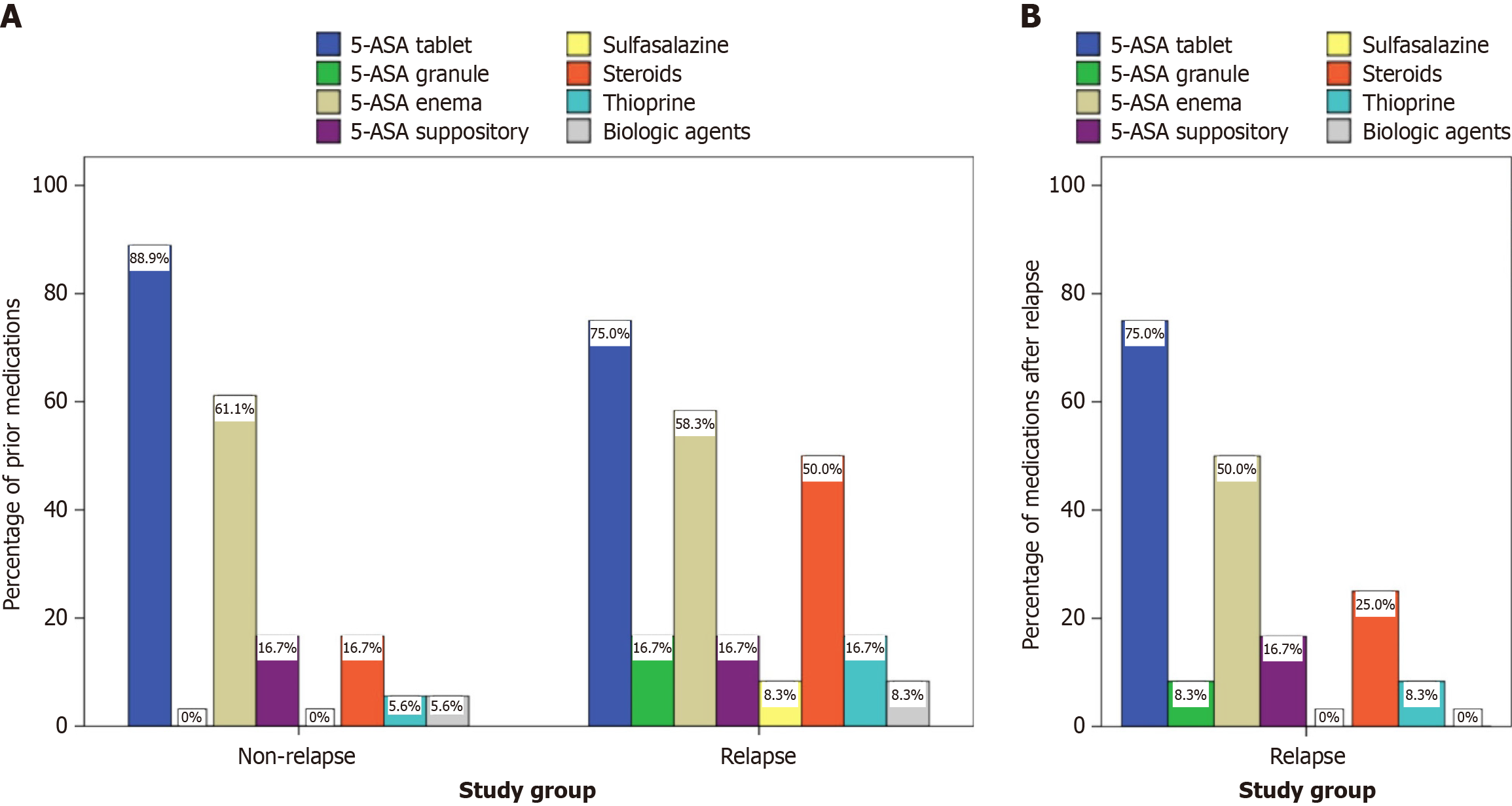
Figure 3 Two grouped bar charts side-by-side.
A: Previous treatments by relapse status; B: Treatments administered after relapse for the relapse group. Dark blue bars represent 5-aminosalicylates (5-ASA) tablets, green bars represent 5-ASA granules, beige bars represent 5-ASA enemas, purple bars represent 5-ASA suppositories, yellow bars represent sulfasalazine, red bars represent steroids, light blue bars represent thiopurines, and gray bars represent biologic agents. 5-ASA: 5-aminosalicylate.
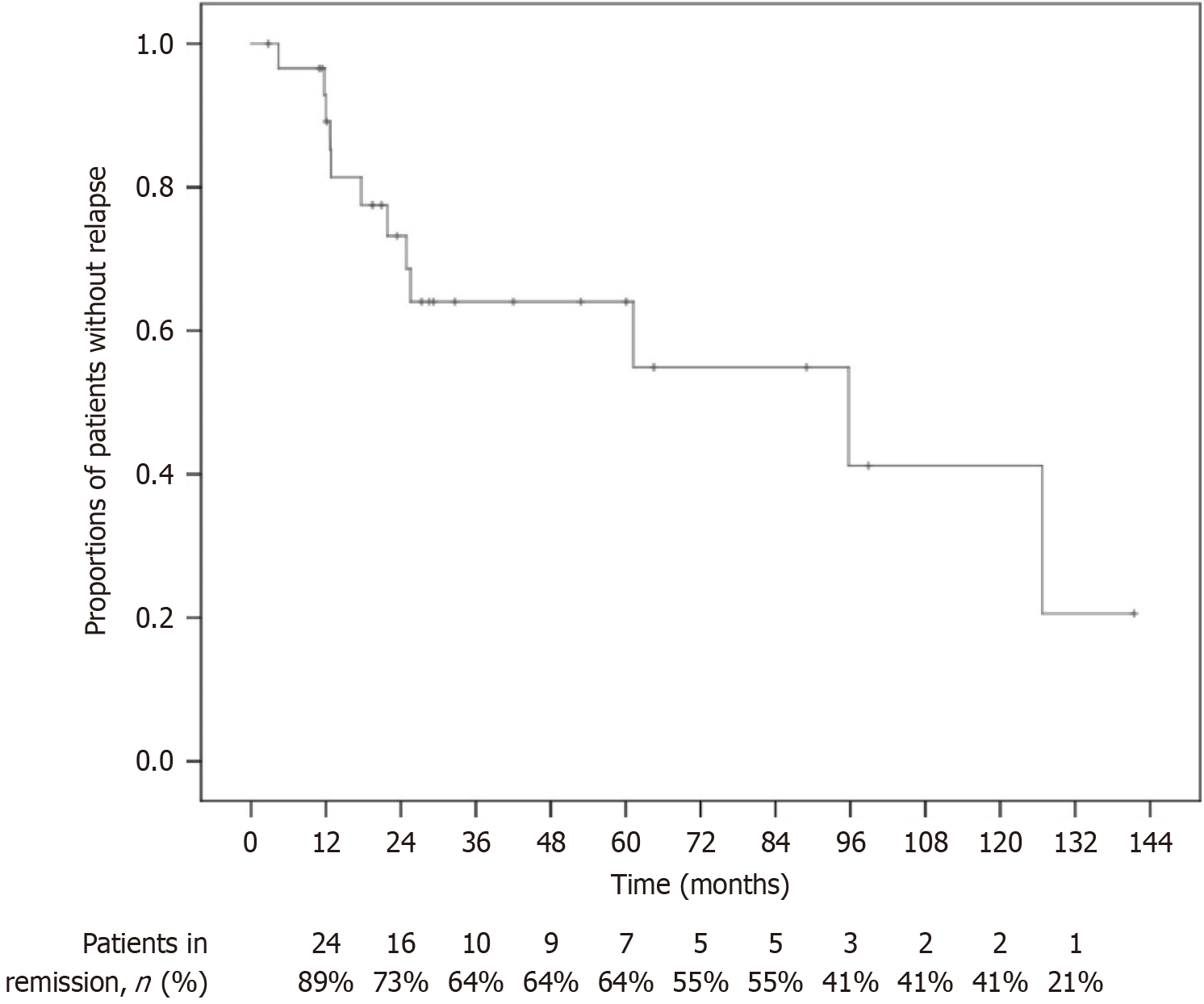
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for evaluating the trend of proportions of patients without relapse in ulcerative colitis patients who had 5-aminosalicylate withdrawal during remission.
The vertical drops in the curve represent relapse events, and the small vertical ticks indicate censored data points. The table below the X-axis shows the number and percentage of patients in remission at each time point.
- Citation: Atay A, Ergul M, Ozturk O, Acun KC, Cagir Y, Durak MB, Yuksel I. Outcomes of 5-aminosalicylates withdrawal due to non-adherence in ulcerative colitis patients: A step toward evaluating intermittent therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(30): 110112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i30/110112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.110112