Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2025; 31(30): 109418
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109418
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109418
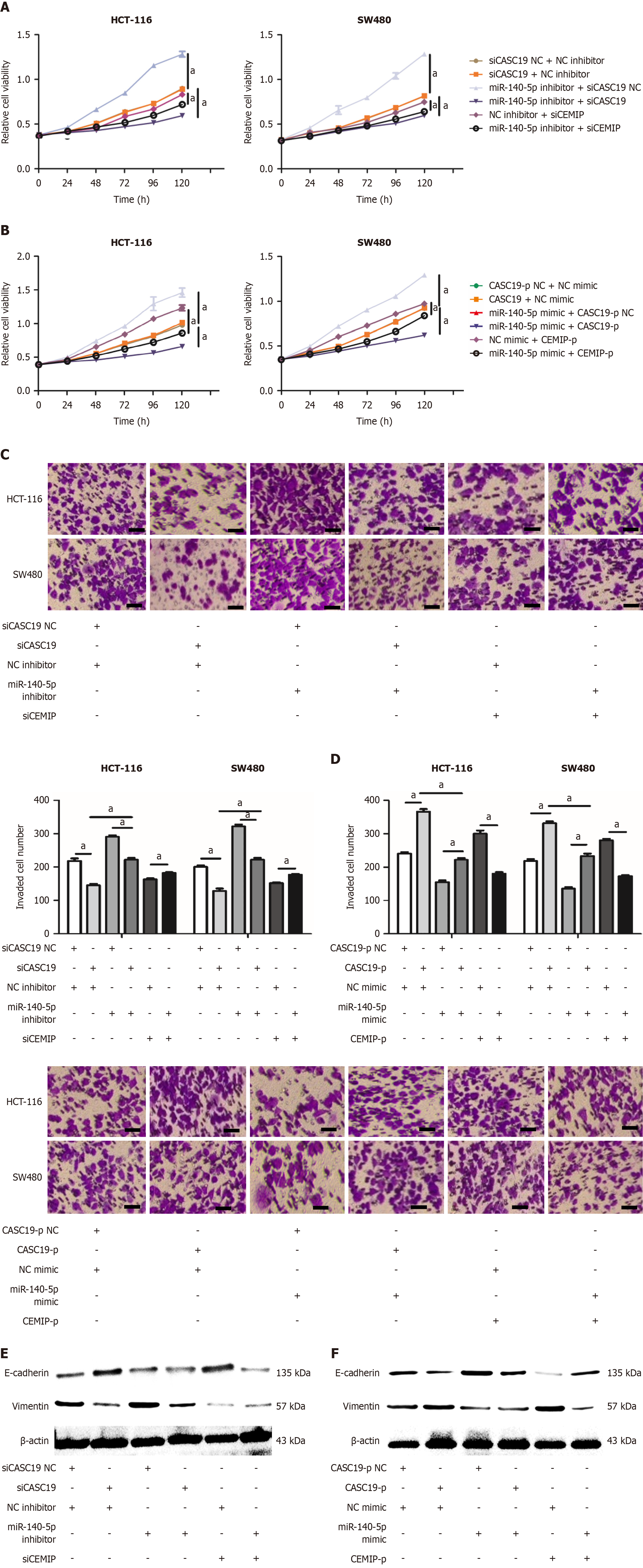
Figure 1 MiR-140-5p suppresses CASC19-induced enhancement of colorectal cancer cells proliferation and metastasis.
A and B: Growth curves of SW480 and HCT-116 cells transfected with either miR-140-5p inhibitor or si cancer susceptibility 19 (CASC19) (A), and miR-140-5p mimic or CASC19-overexpressing plasmid (CASC19-p) (B), as determined by CCK-8 assay; C and D: Transwell invasion assays of HCT-116 and SW480 cells transfected with either miR-140-5p inhibitor or siCASC19 (C) and miR-140-5p mimic or CASC19-p (D). Scale bars = 20 μm; E and F: Western blot analysis of E-cadherin and vimentin expression in CRC cells following transfection with miR-140-5p inhibitor or siCASC19 (E) and miR-140-5p mimic or CASC19-p (F). Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Wang XD, Qi F. Correction to “Functional role of long non-coding RNA CASC19/miR-140-5p/CEMIP axis in colorectal cancer progression in vitro”. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(30): 109418
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i30/109418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109418