Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 106819
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.106819
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.106819
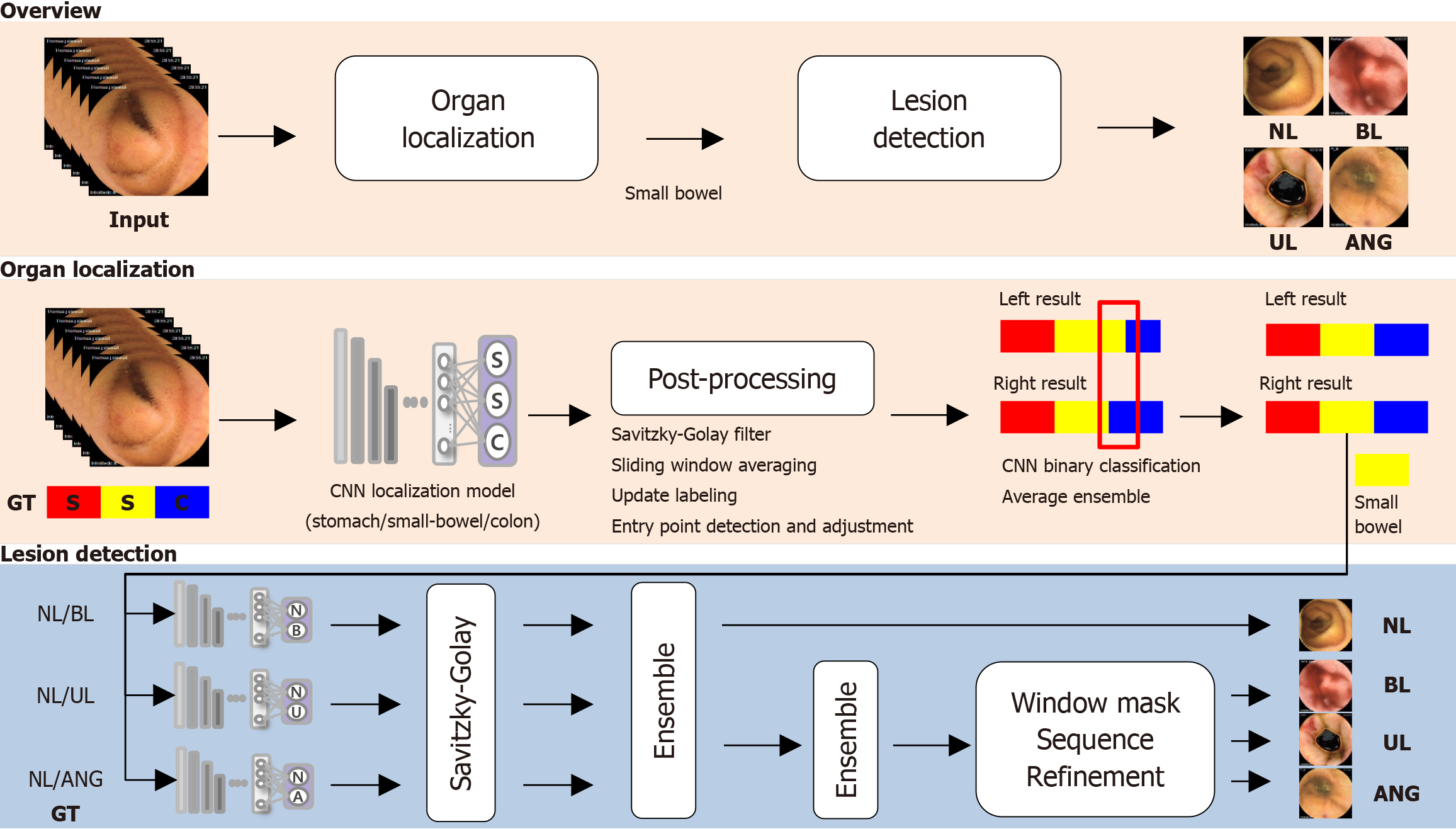
Figure 1 Overview of artificial intelligence model.
The artificial intelligence system is a two-stage process that first localizes the small bowel in capsule endoscopy videos and then detects lesions such as bleeding, erosion/ulcers, and angiodysplasia. It utilizes convolutional neural network models along with post-processing and ensemble techniques to enhance accuracy and consistency across video frames. NL: Normal mucosa (including debris, bile, and bubbles); BL: Bleeding (active bleeding or visible fresh blood); GT: Ground truth; UL: Erosions/ulcers; CNN: Convolutional neural network; ANG: Angiodysplasia
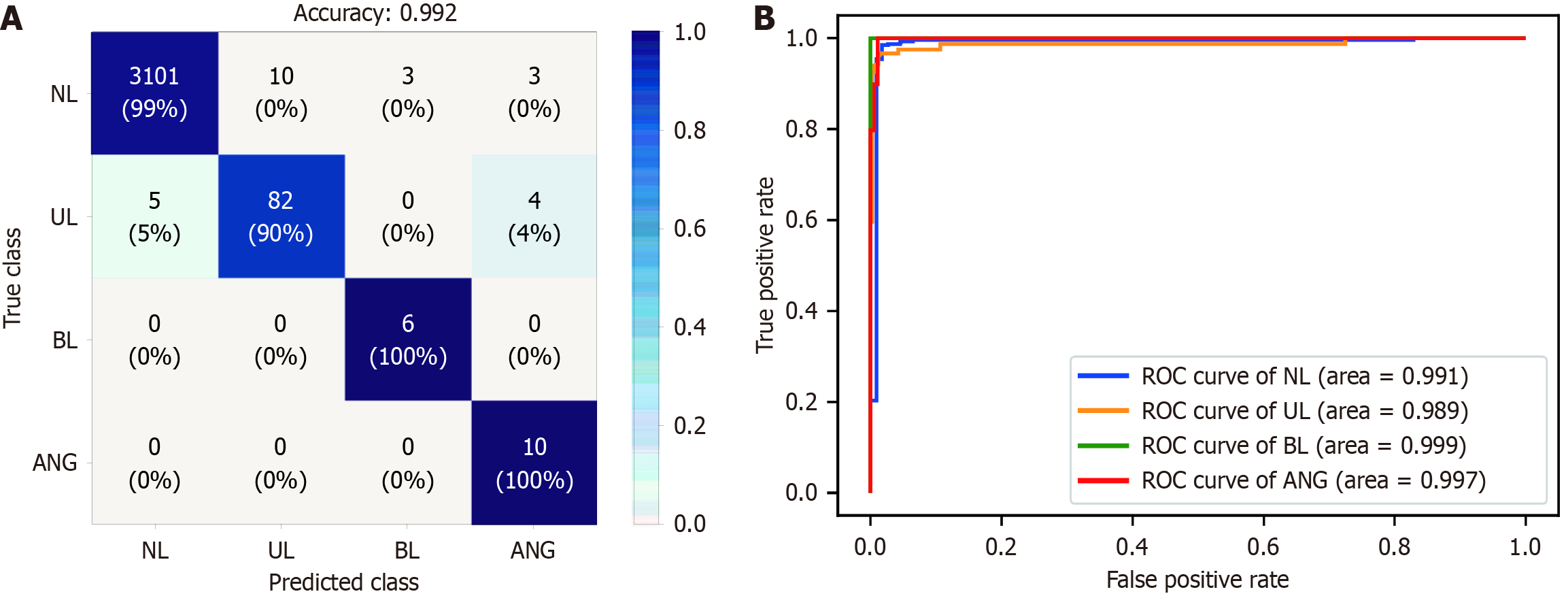
Figure 2 Performance of the artificial intelligence model for detecting small bowel abnormalities in the internal test dataset.
The model demonstrated high performance in detecting small bowel abnormalities, with an overall accuracy of 0.992 and excellent area-under-the curve scores for all classes. A: Confusion matrix; B: Receiver-operating characteristic curve. NL: Normal mucosa (including debris, bile, and bubbles); BL: Bleeding (active bleeding or visible fresh blood); GT: Ground truth; UL: Erosions/ulcers, ANG: Angiodysplasia; ROC: Receiver-operating characteristic curve.
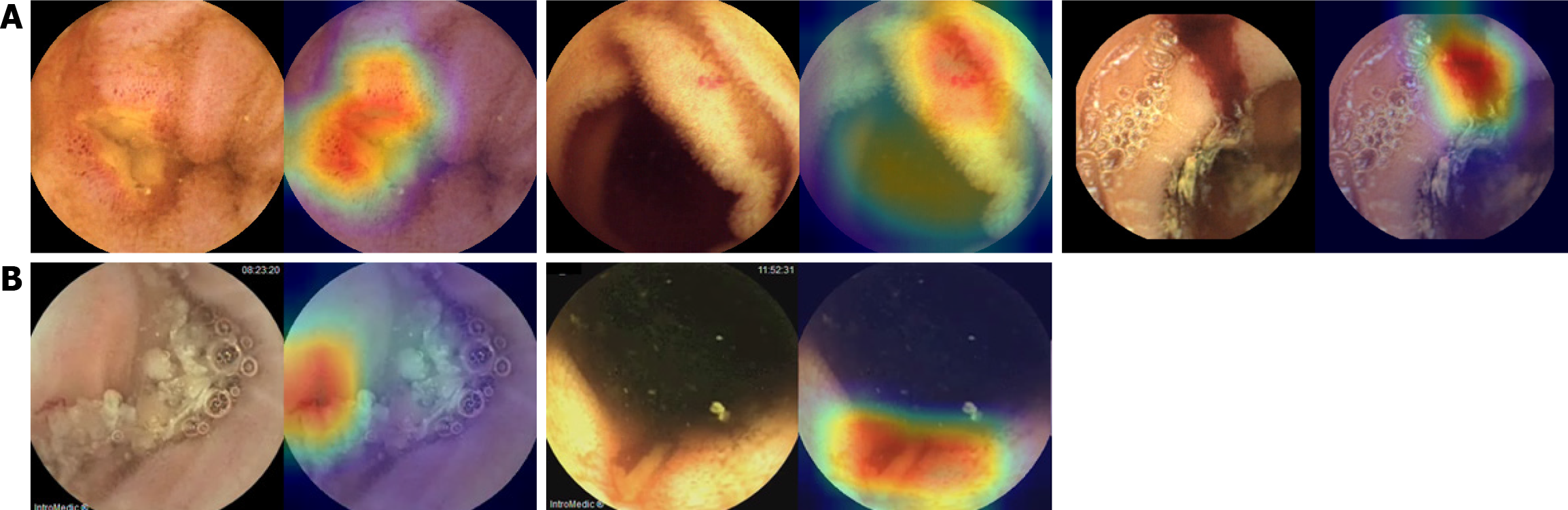
Figure 3 Representative images of small bowel abnormalities correctly detected using artificial intelligence-assisted reading in the validation data set.
A: Correct detection of erosions/ulcers (left), angiodysplasia (middle), and bleeding (right) using both artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted reading and conventional readings; B: Correct detection of angiodysplasia (left) and erosions/ulcers (right) using AI-assisted reading; however, conventional reading missed these abnormalities.
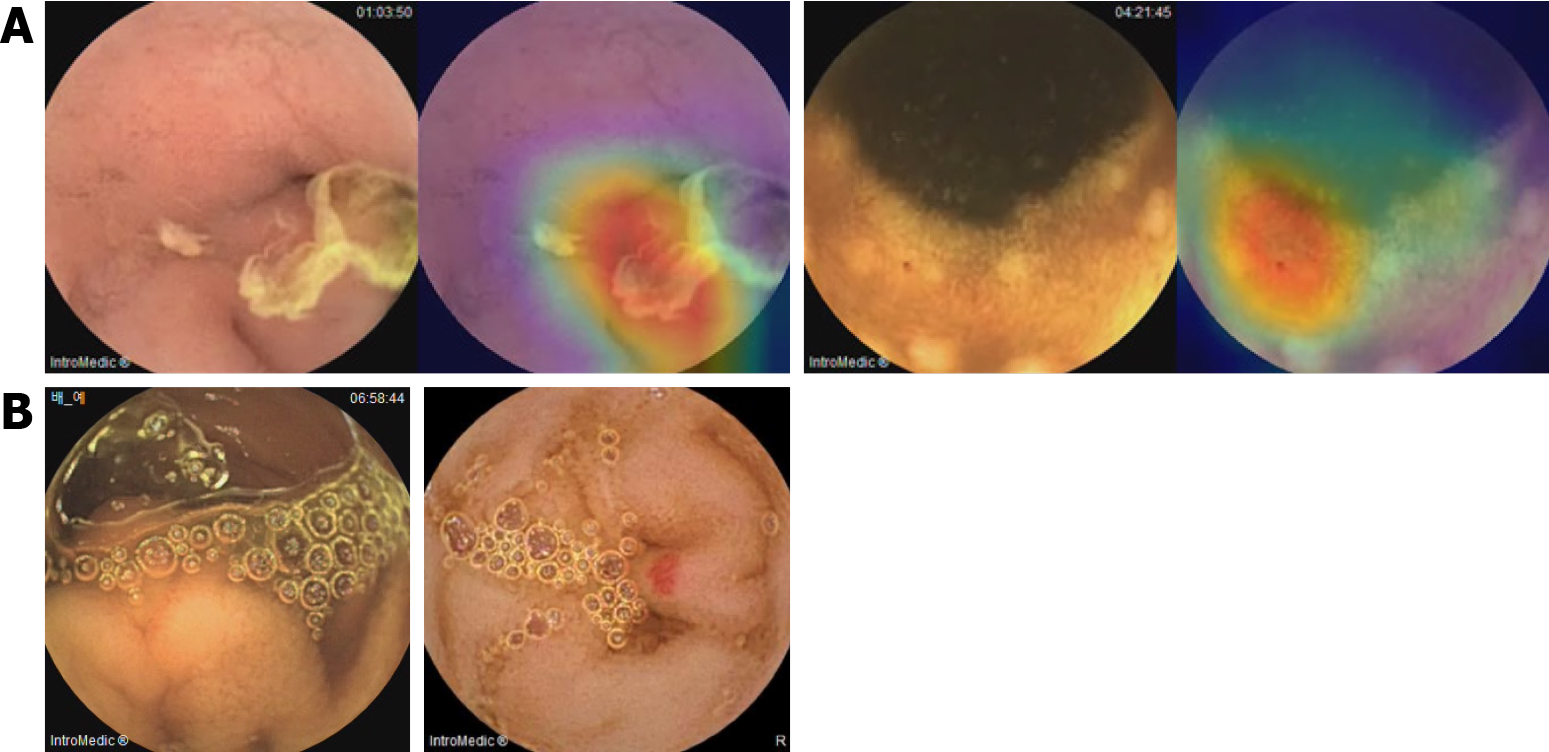
Figure 4 Representative images of incorrect recognition using artificial intelligence assisted reading on validation data set.
A: False-positive cases of erosions/ulcers (left) and angiodysplasia (right); B: False-negative cases of erosions/ulcers (left) and angiodysplasia (right).
- Citation: Kwon YS, Park TY, Kim SE, Park Y, Lee JG, Lee SP, Kim KO, Jang HJ, Yang YJ, Cho BJ. Deep learning-based localization and lesion detection in capsule endoscopy for patients with suspected small-bowel bleeding. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 106819
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/106819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.106819