Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2025; 31(2): 100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
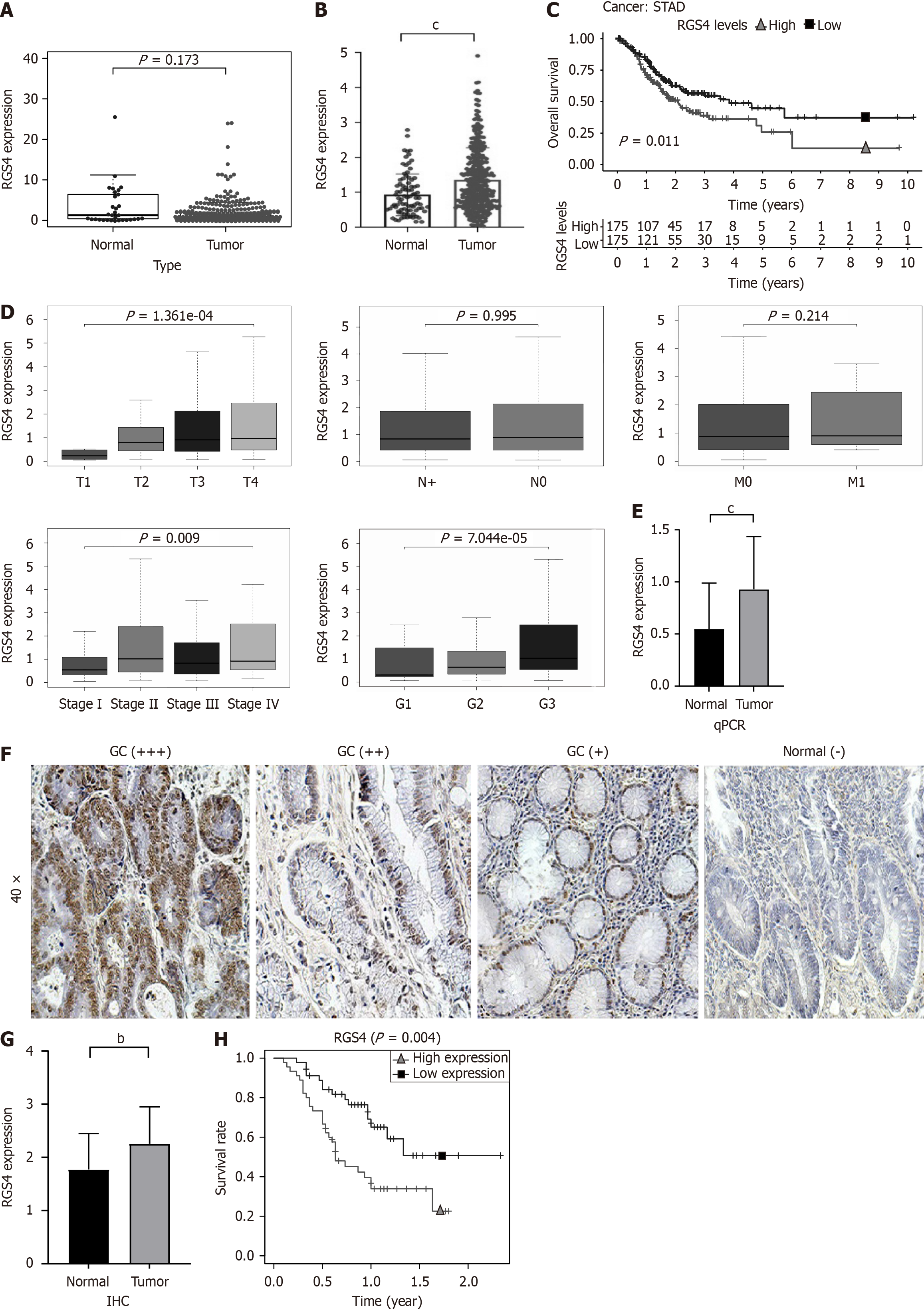
Figure 1 High expression of regulator of G protein signaling 4 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer.
A: Differential expression of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in The Cancer Genome Atlas Stomach Cancer dataset (TCGA-STAD); B: Differential expression of RGS4 in the integrated analysis of TCGA-STAD and the Genotype-Tissue Expression dataset; C: High expression of RGS4 was associated with lower overall survival in TCGA-STAD dataset; D: The correlation between RGS4 and T stage, N stage, M stage, tumor-node-metastasis stage and tumor grade of gastric cancer (GC); E: Differential expression of RGS4 in GC and para-carcinoma normal tissues of our center’s patients; F: Representative immunohistochemistry images showing the expression of RGS4 in GC and para-carcinoma normal tissues (strong staining: +++; moderate staining: ++; weak staining: +; negative staining: -); G: Differences in protein expression levels of RGS4 between GC and para-carcinoma normal tissues; H: High expression of RGS4 was associated with lower overall survival in GC patients in our center. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4; GC: Gastric cancer.
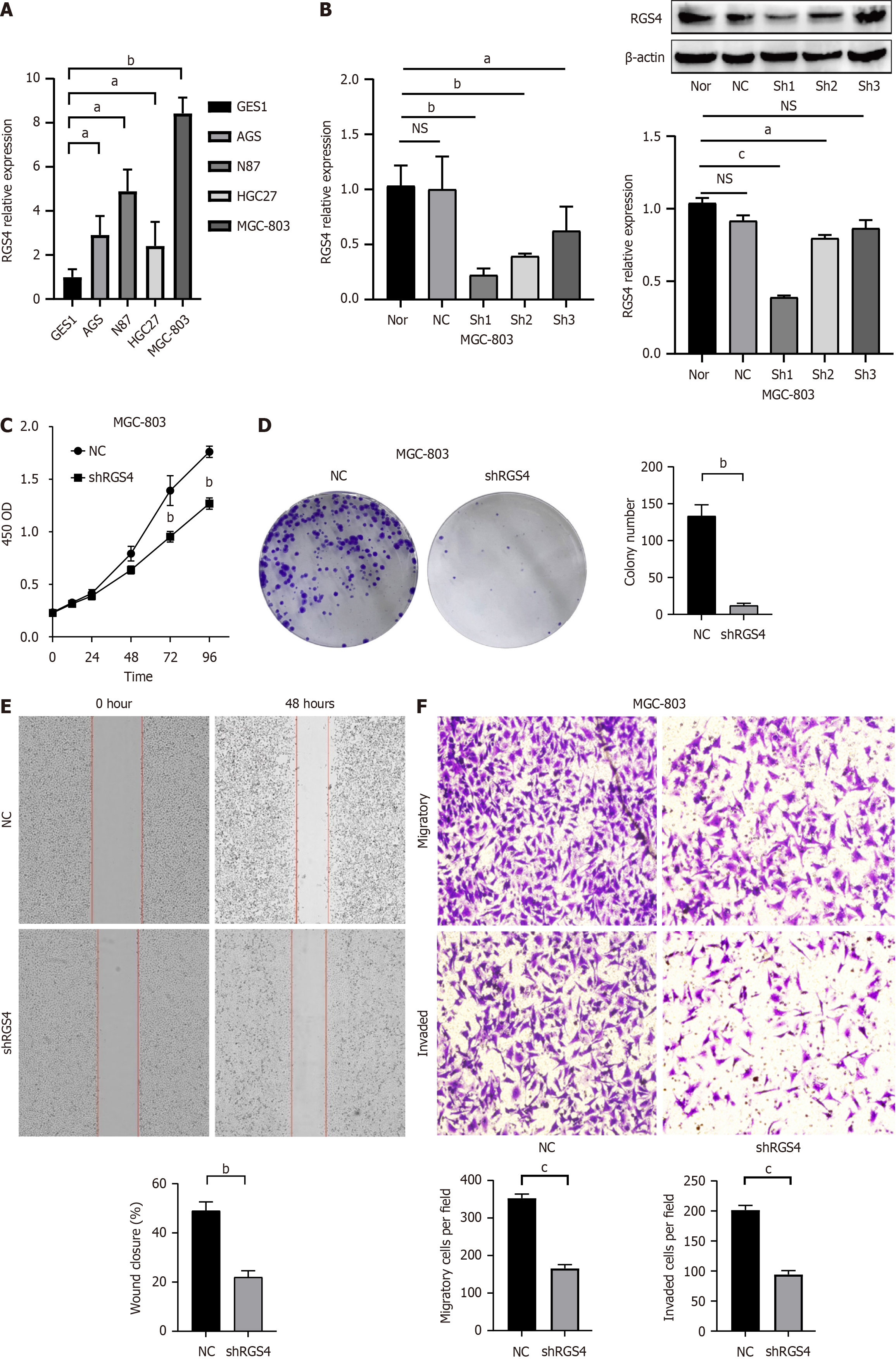
Figure 2 Regulator of G protein signaling 4 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro.
A: The expression levels of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in different gastric cancer (GC) cell lines were detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; B: The interference efficiency of the lentiviral human RGS4-targeting short hairpin RNA was validated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (left) and western blot (right) analysis; C: The proliferation of MGC-803 cells with RGS4 knockdown was determined by cell counting kit-8 assays; D: The effects of RGS4 knockdown on the colony formation of MGC-803 cells; E: The migration ability of MGC-803 cells was measured by wound healing; F: The invasion of MGC-803 cells with RGS4 knockdown was determined by transwell assays. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, NS: No significance. RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4.
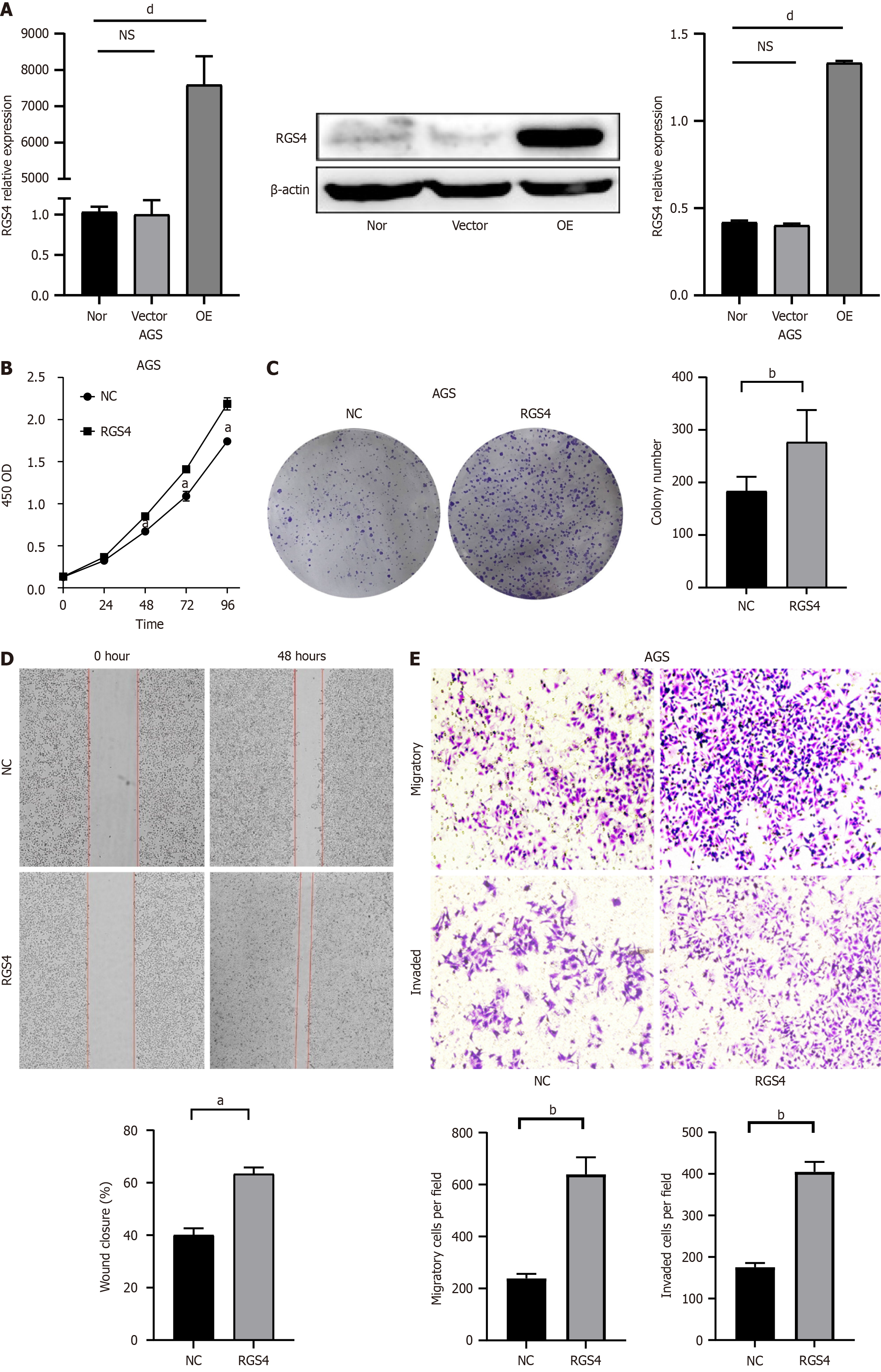
Figure 3 Overexpression of regulator of G protein signaling 4 promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro.
A: The interference efficiency of the lentiviral carrying regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) was validated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (left) and western blot (right) analysis (overexpressing RGS4); B: The proliferation of AGS cells with RGS4 overexpression was determined by cell counting kit-8 assays; C: The effects of RGS4 overexpression on the colony formation of AGS cells; D: The migration ability of AGS cells was measured by wound healing; E: The invasion of AGS cells with RGS4 overexpression was determined by transwell assays. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001, NS: No significance. RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4.
Figure 4 The expression level of regulator of G protein signaling 4 affected the focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells.
A: Gene Set Enrichment Analysis results showed the relevant pathways that regulator of G protein signaling 4 may affected in The Cancer Genome Atlas Stomach Cancer dataset; B-E: The expression levels of focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway and epithelial mesenchymal transition related protein of MGC-803 cells and AGS cells were determined by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as a loading control. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B.
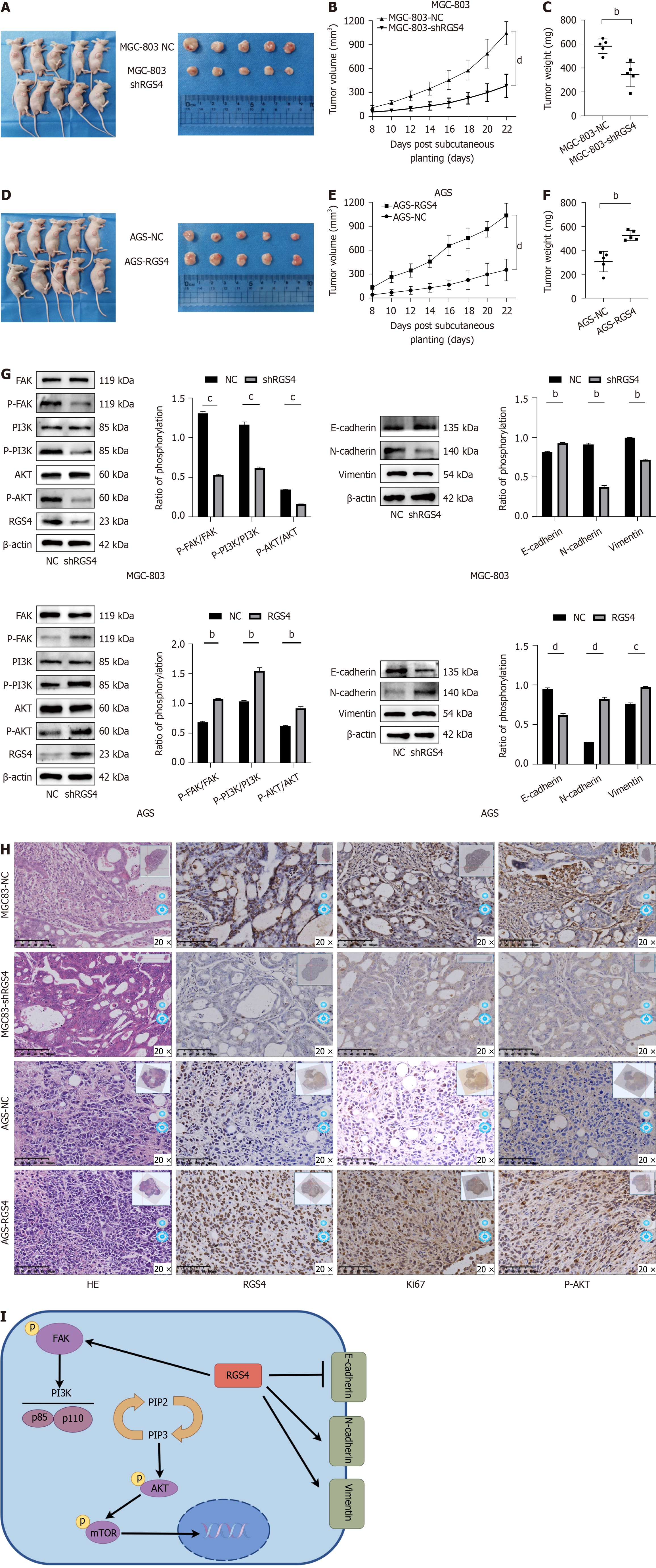
Figure 5 Knocking down regulator of G protein signaling 4 in gastric cancer cells inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
A-F: Tumors from MGC-803 cells with regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) knockdown and AGS cells with RGS4 overexpression and their controls (n = 5/groups) (A and D), tumor growth curves (B and E), tumor weight of each group (C and F); G: The expression of focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial mesenchymal transition related proteins in MGC-803 cells and AGS cells in vivo were validated by western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control; H: The expression of RGS4, Ki67 and p-AKT in these xenografts via immunohistochemistry staining; I: Schematic diagram of the mechanism of RGS4 promoting gastric cancer progression. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4; PIP: Prolactin-induced protein; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Chen PY, Wang PY, Liu B, Jia YP, Zhang ZX, Liu X, Wang DH, Yan YJ, Fu WH, Zhu F. RGS4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through the focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(2): 100898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i2/100898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898