Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2025; 31(19): 101913
Published online May 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i19.101913
Published online May 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i19.101913
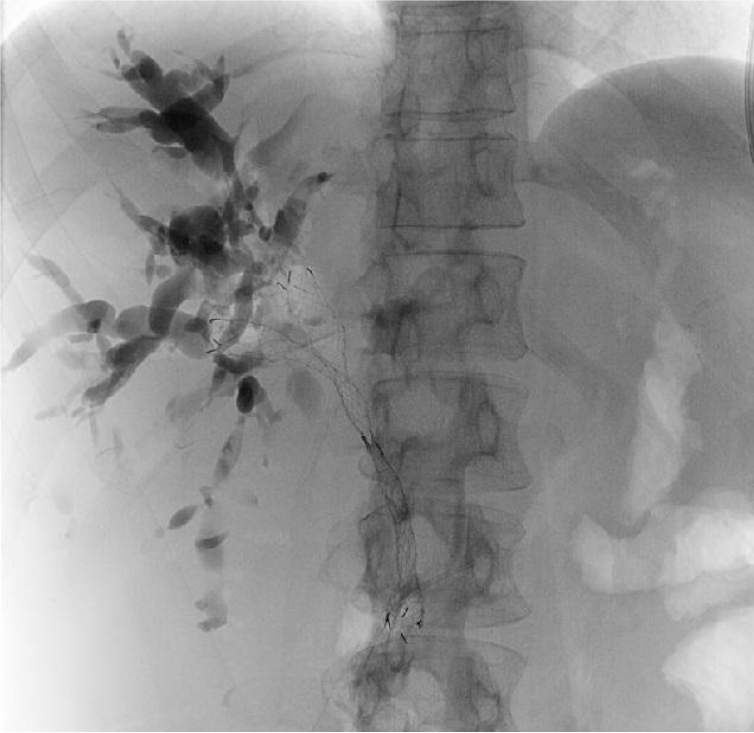
Figure 1
Sequential stent in stent bilateral drainage on X-ray view.
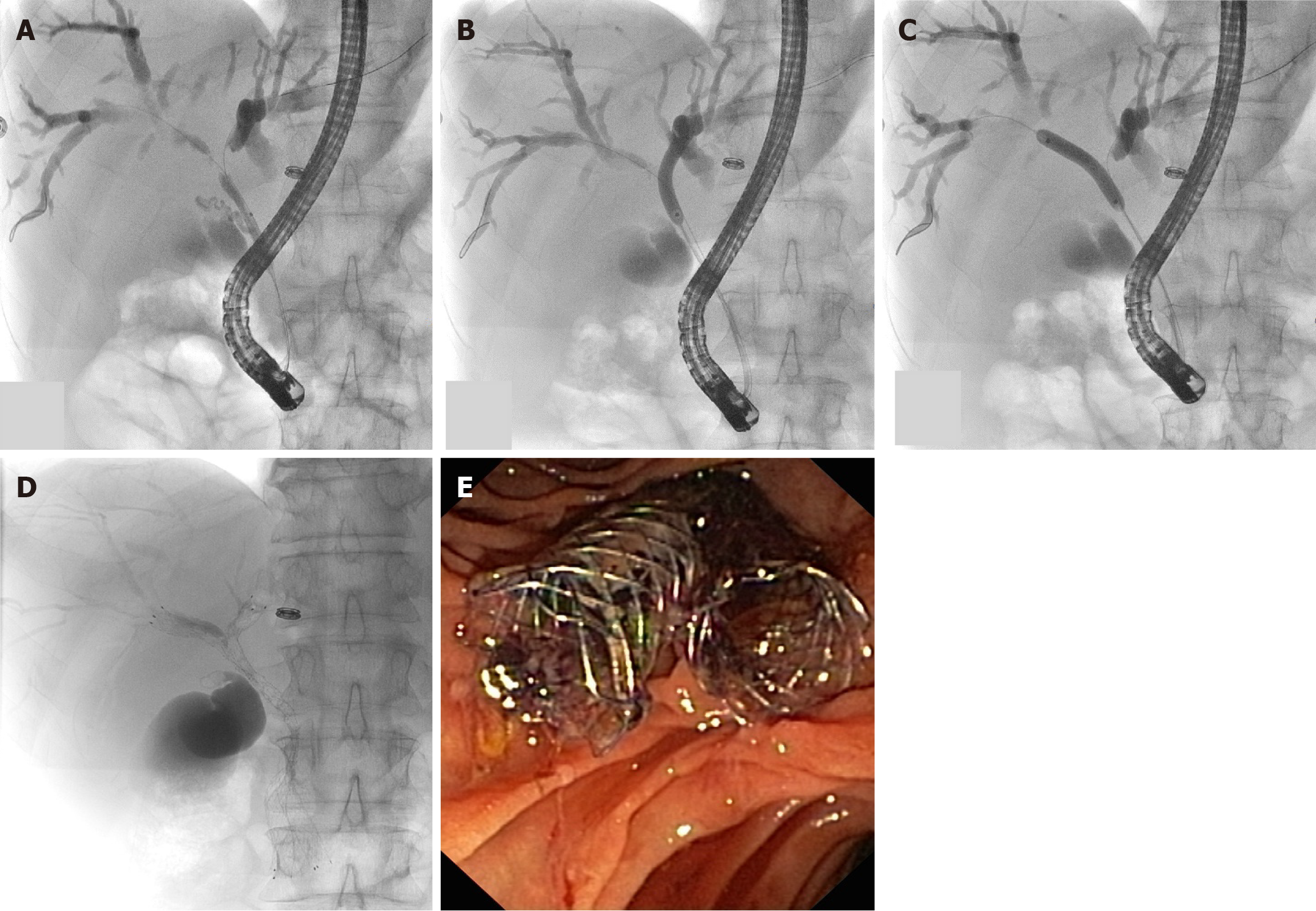
Figure 2 Sequential side by side bilateral drainage on X-ray and endoscopic view.
A: Placement of guidewires across the strictures; B: Dilation of left stricture; C: Dilation of right stricture; D: Simultaneous placement of two metallic biliary stents; E: Endoscopic view after drainage with two biliary self-expandable metallic stent well distinct in the duodenal lumen.
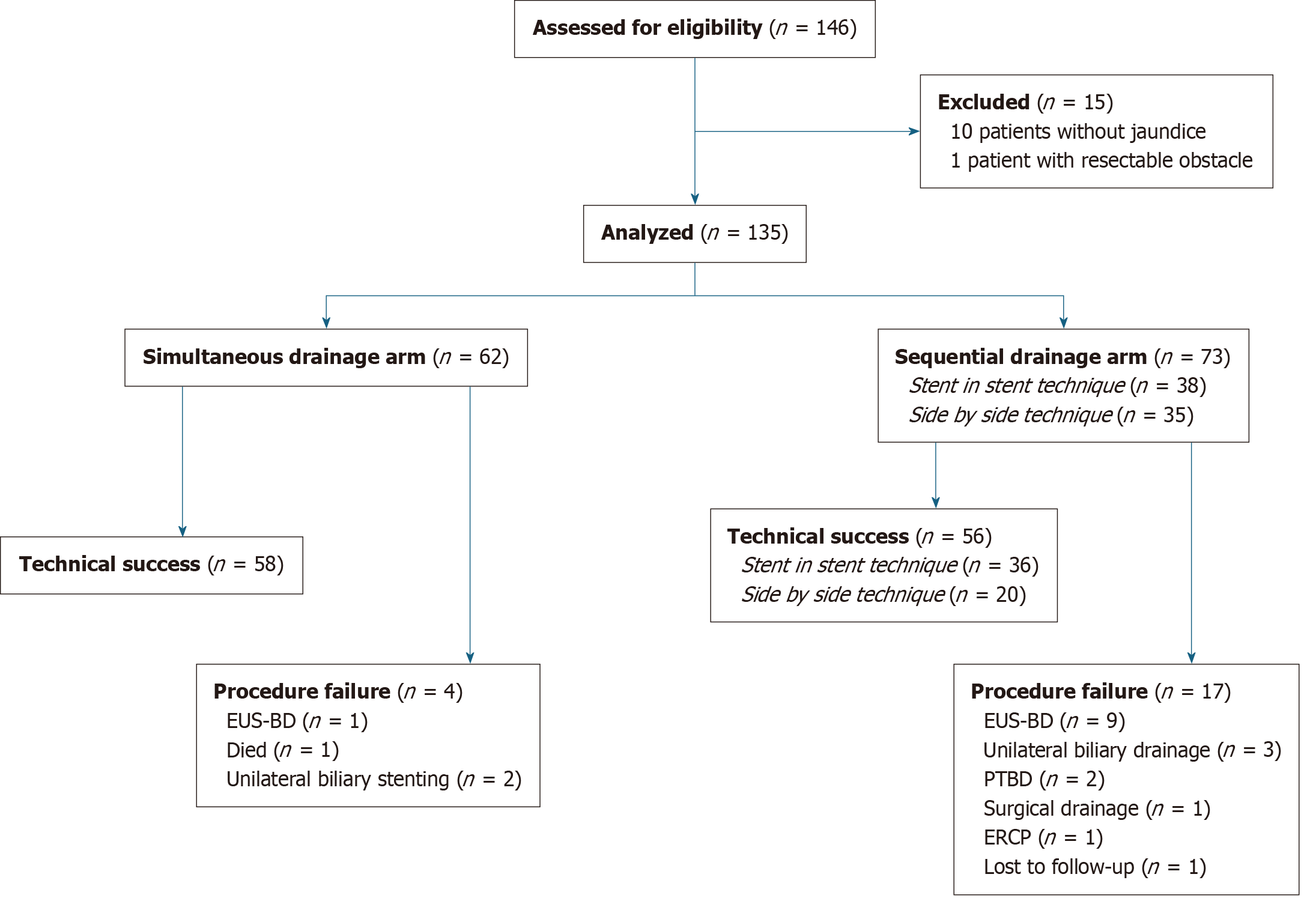
Figure 3 Flow diagram of the participants analyzed.
EUS-BD: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage; PTBD: Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
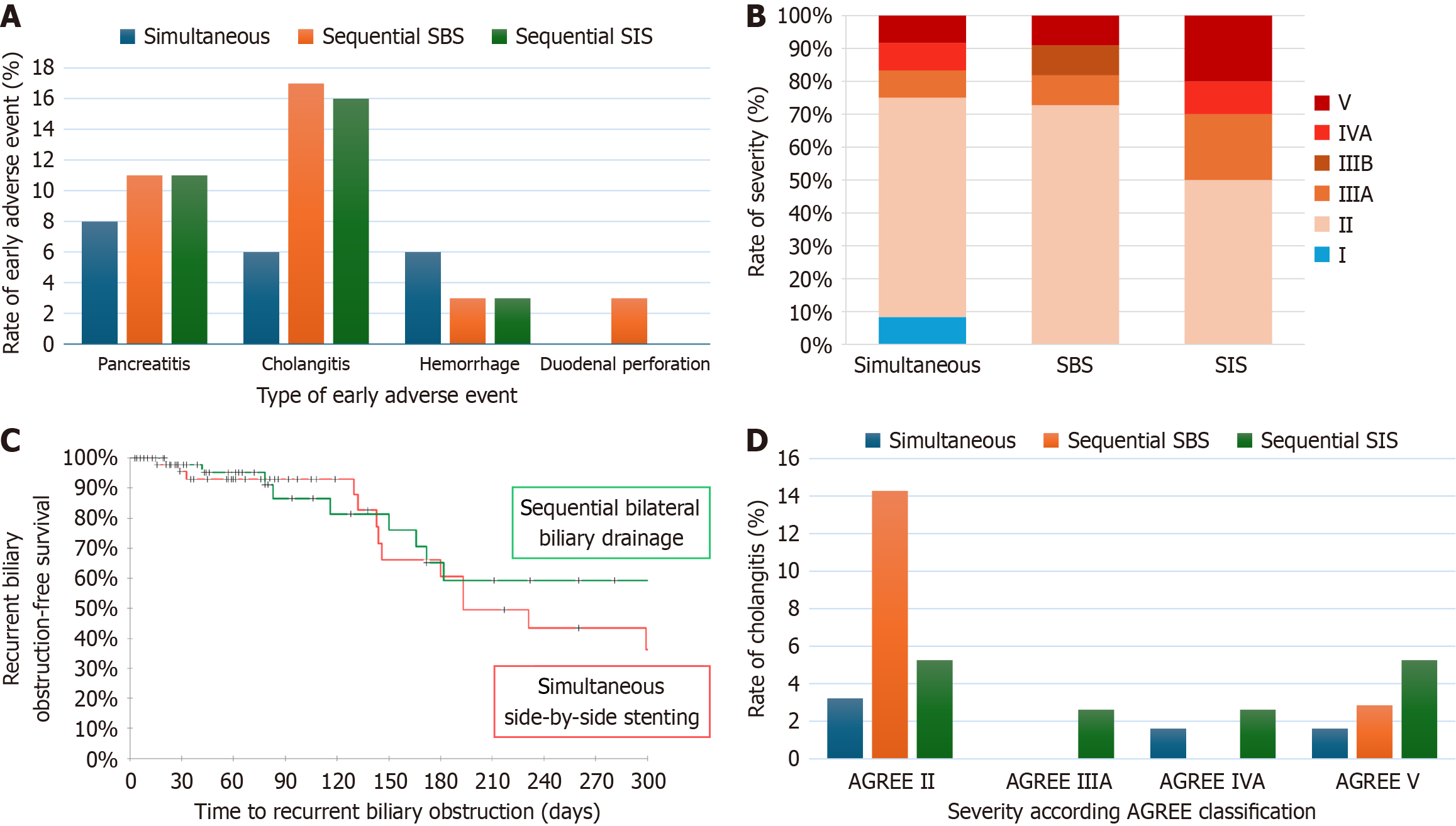
Figure 4 Adverse event and recurrent biliary obstruction outcomes.
A: Rate of early adverse events among groups; B: Repartition of severity according the Adverse Event Gastrointestinal Endoscopy classification among patients who suffered from an adverse event; C: Kaplan-Meier curves compared recurrent biliary obstruction-free survival between simultaneous and sequential groups; D: Repartition of severity according to the Adverse Event Gastrointestinal Endoscopy classification among patients with cholangitis. AGREE: Adverse Event Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; SBS: Side by side; SIS: Stent in stent.
- Citation: Guilmoteau T, Rouquette O, Buisson A, Cambier S, Abergel A, Poincloux L. Direct comparison of simultaneous and sequential endoscopic metallic bilateral stenting in malignant hilar biliary obstruction. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(19): 101913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i19/101913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i19.101913