Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2025; 31(17): 105411
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411
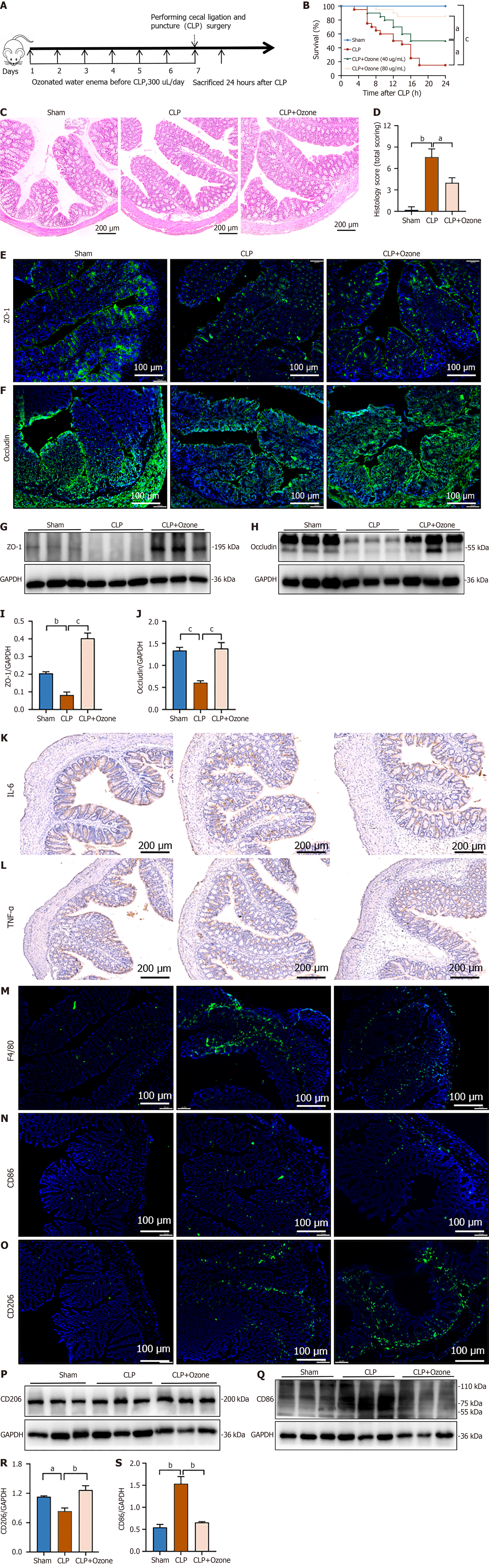
Figure 1 Ozone-rich water mitigates sepsis-induced intestinal injury diagram of the mouse model.
A: Diagram of the mouse model; B: Survival of mice shown by Kaplan-Meier curves; C and D: Hematoxylin-eosin staining and histopathological score; E and F: Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and occludin levels shown by immunofluorescent staining; G-J: Western blotting of occludin and ZO-1 normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH); K and L: Immunohistochemistry of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in the colon; M: F4/80 levels shown by immunofluorescence staining; N and O: Immunofluorescence staining of cluster of differentiation (CD) 86 and CD206; P-S: Western blotting of CD206 and CD86, normalized to GAPDH. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; IL-6: Interleukin-6; CD: Cluster of differentiation; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1.
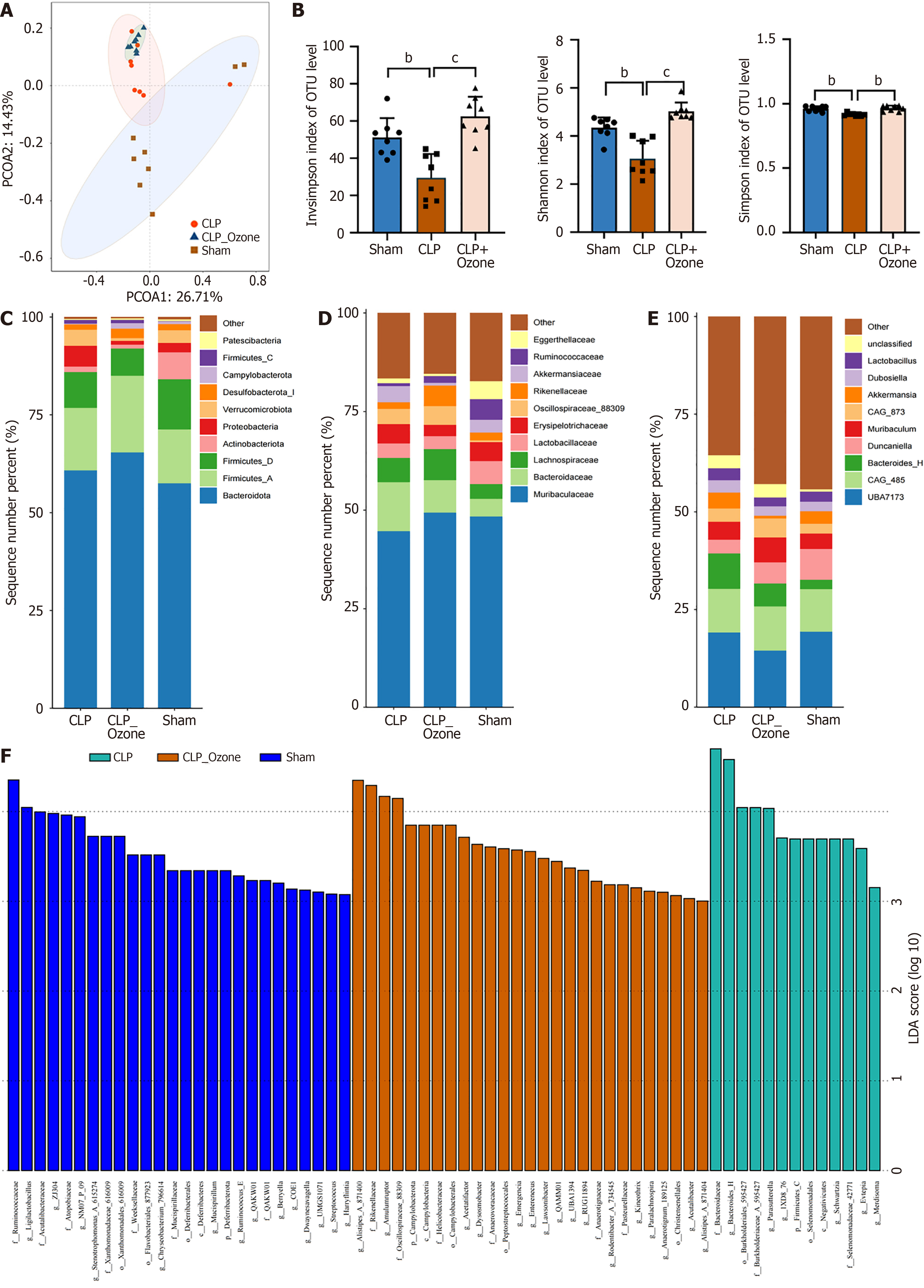
Figure 2 Ozone-rich water alleviates intestinal flora disorders induced by sepsis.
A: Principal co-ordinates analysis of 16S rRNA sequencing data; B: Analysis of alpha diversity; C: Abundance of phyla; D: Abundance of families; E: Abundance of genera; F: Linear discriminant analysis effect size analysis. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; PCoA: Principal co-ordinates analysis; OTU: Operational taxonomic unit; LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
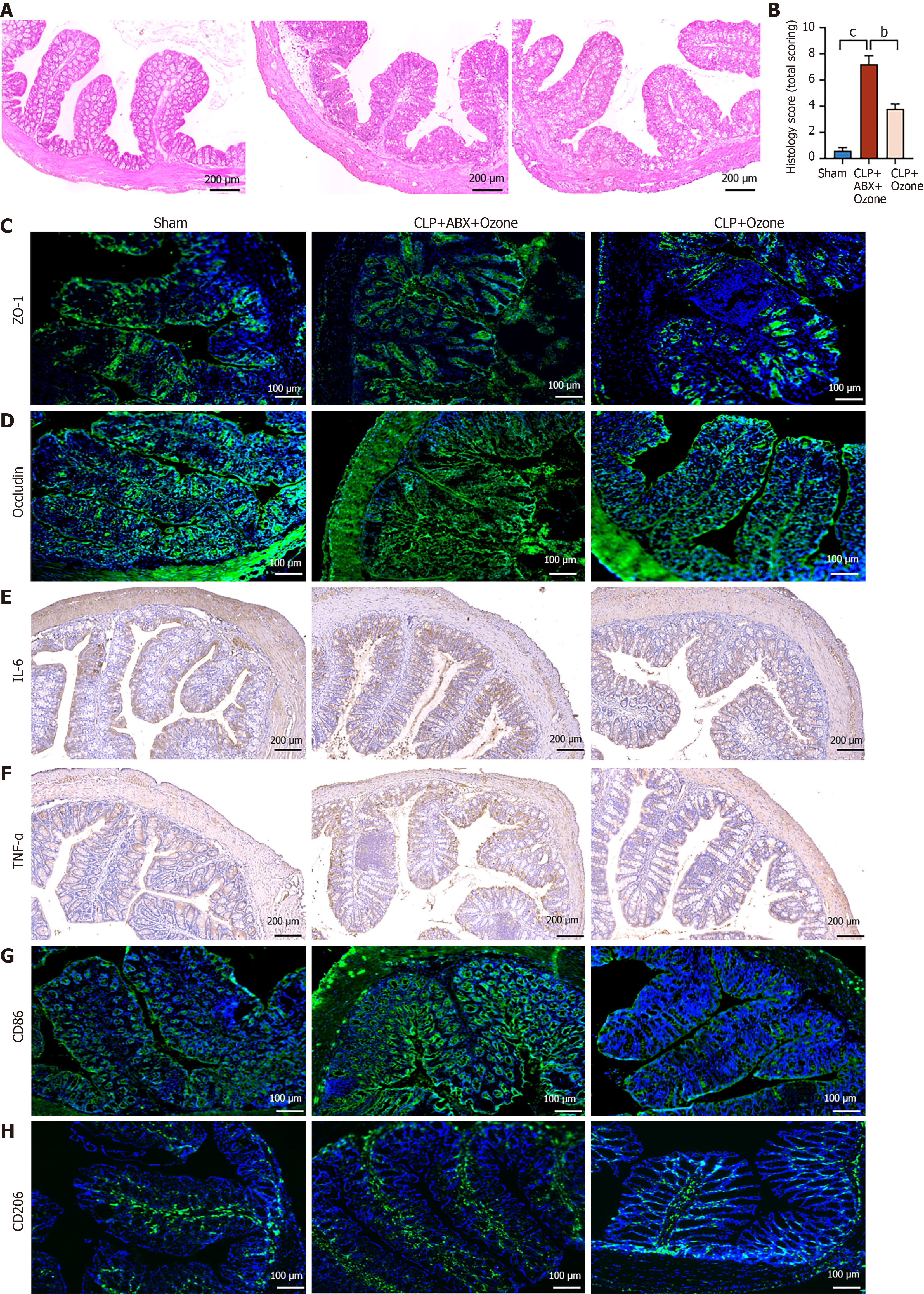
Figure 3 Ozone-rich water alleviation of sepsis-induced intestinal injury is dependent on the intestinal flora.
A and B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining; C and D: Zonula occludens-1 and occludin levels, shown by immunofluorescence staining; E and F: Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in the colon, shown by immunohistochemistry; G and H: Immunofluorescence staining of cluster of differentiation (CD) 86 and CD206. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; IL-6: Interleukin-6; CD: Cluster of differentiation; ABX: Antibiotics; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1.
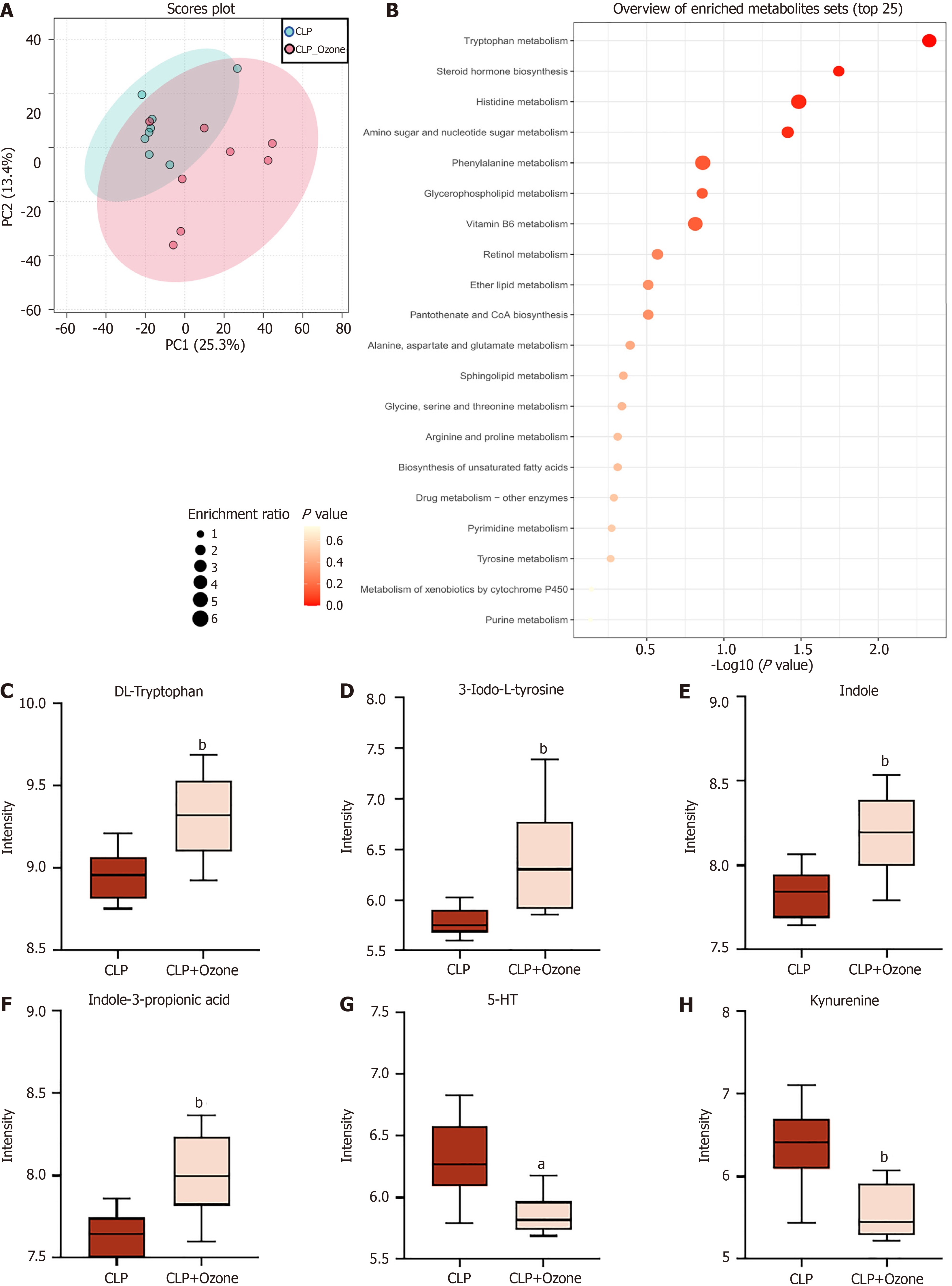
Figure 4 Ozone-rich water regulates tryptophan metabolism in the intestinal flora.
A: Principal component analysis scatter plots; B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis; C-H: Relative expression of DL-tryptophan (C); 3-Iodo-L-tyrosine (D); Indol (E); Indole-3-propionic acid (F); 5-hydroxytryptamine (G); Kynurenine (H). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; PC: Principal component; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine.
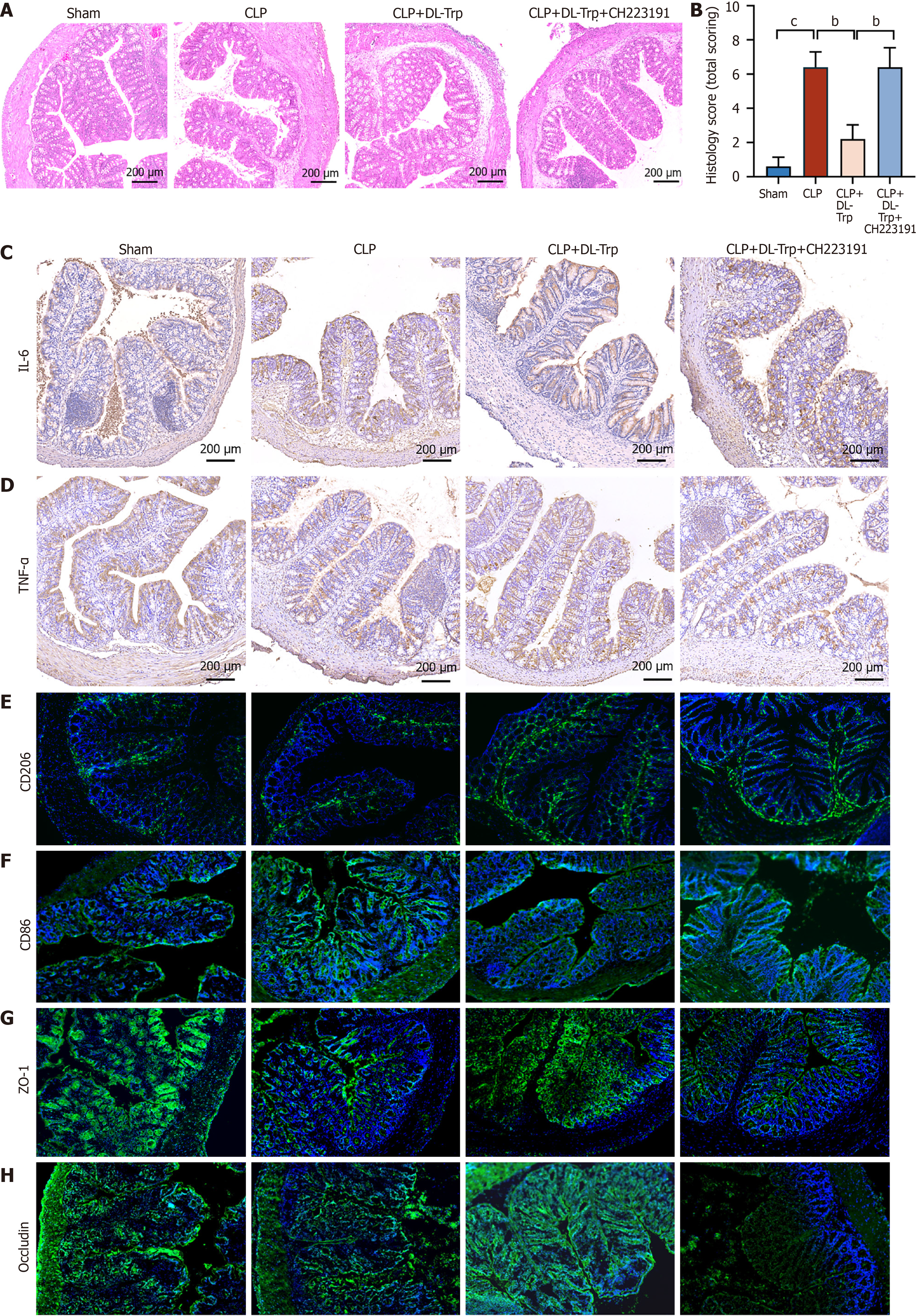
Figure 5 Tryptophan metabolism of the intestinal flora-DL-tryptophan activates aryl hydrocarbon receptor to mitigate sepsis-induced intestinal injury.
A and B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining; C and D: Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in the colon, shown by immunohistochemistry; E-H: Immunofluorescence staining of cluster of differentiation (CD) 206, CD86, zonula occludens-1, and occluding. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; DL-Trp: DL-tryptophan; IL-6: Interleukin-6; CD: Cluster of differentiation; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1.
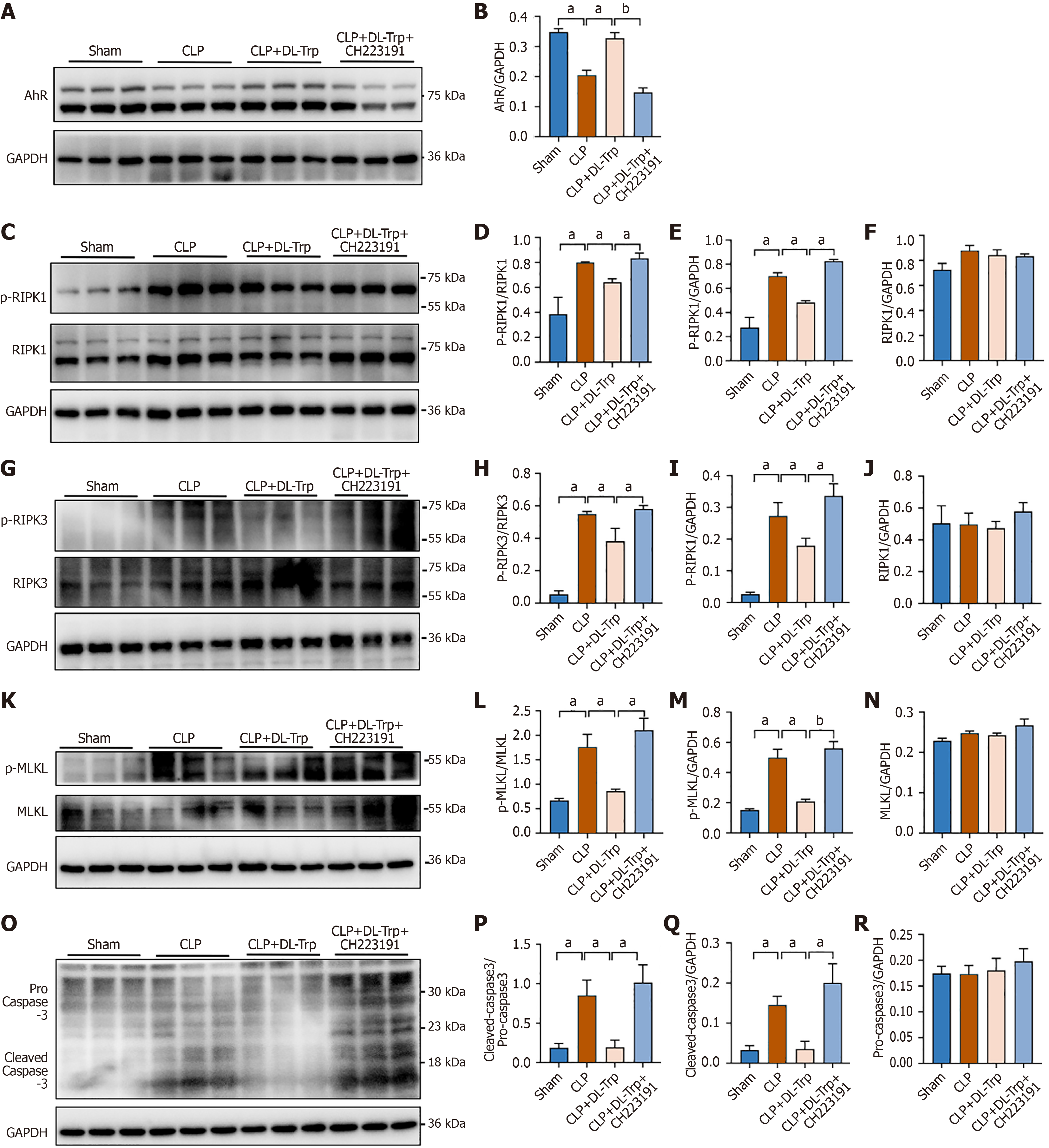
Figure 6 DL-tryptophan water inhibits necroptosis to mitigate sepsis-induced intestinal injury via aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
A and B: Western blotting of aryl hydrocarbon receptor; C-F: Western blotting of phospho-receptor-interacting protein kinase (p-RIPK) 1, receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK) 1; G-J: Western blotting of pRIPK3, RIPK3; K-N: Western blotting of phospho-mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; O-R: Western blotting of pro-caspase-3, and cleaved caspse-3 normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; DL-Trp: DL-tryptophan; AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; p-RIPK: Phospho-receptor-interacting protein kinase; RIPK: Receptor-interacting protein kinase; MLKL: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; p-MLKL: Phospho-mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein.
- Citation: Wang Q, Liu CZ, Li BT, Yu XQ, Zhang JY, Wang ZT, Liao LJ, Liu XD. Ozone controls the metabolism of tryptophan protecting against sepsis-induced intestinal damage by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(17): 105411
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i17/105411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411