Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 104305
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305
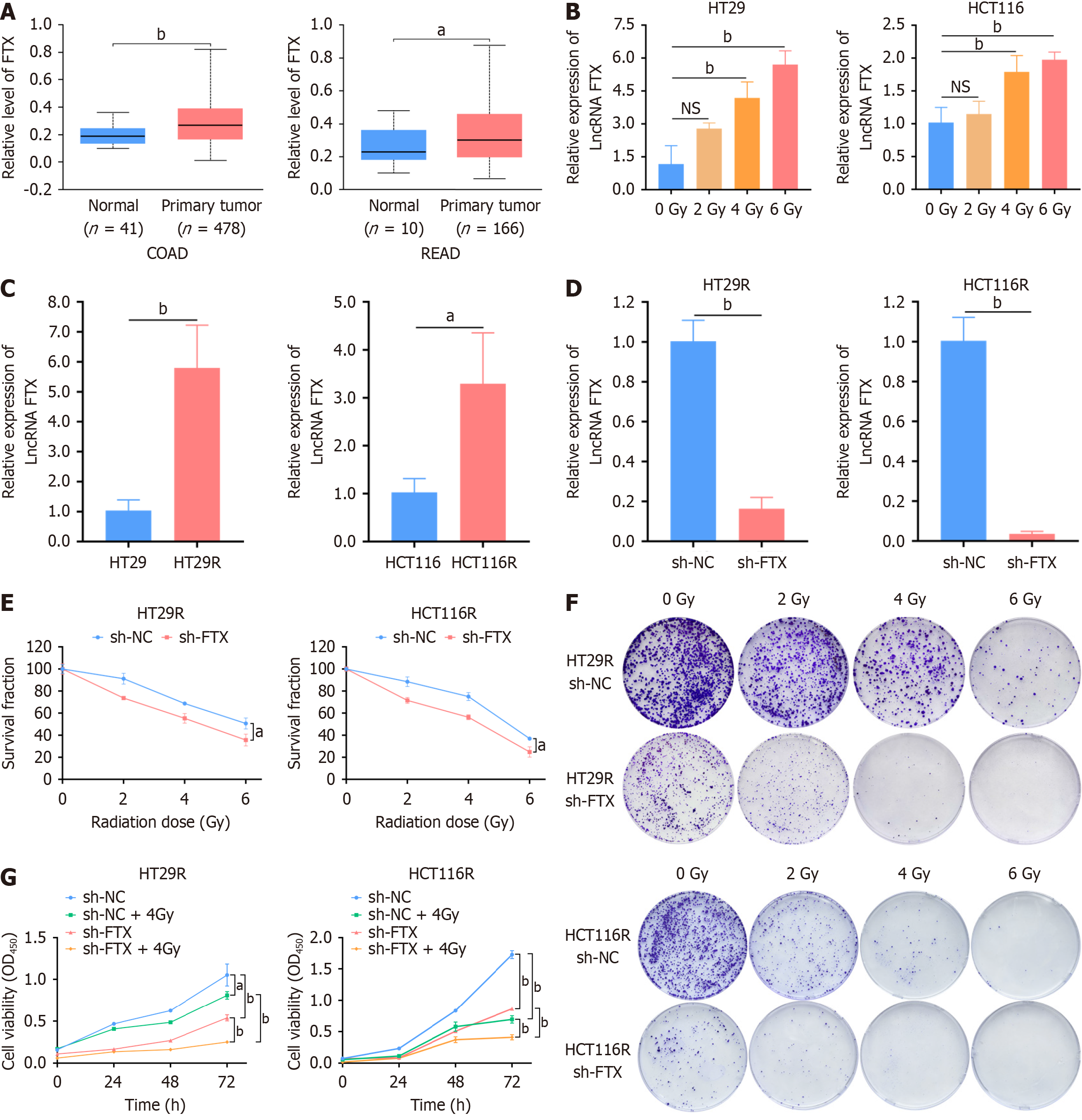
Figure 1 LncRNA FTX is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells and associated with the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer.
A: lncRNA FTX expression in colon, rectal cancer, and para-cancerous tissues; B: Relative expression of lncRNA FTX in HT29 and HCT116 cells after irradiation at different doses; C: LncRNA FTX expression was significantly higher in colorectal cancer radiotherapy-resistant cells than in the corresponding parental cells; D: Knockdown efficiency of lncRNA FTX in HT29R and HCT116R cells was validated by real-time quantitative PCR; E: Knockdown of FTX expression in HT29R and HCT116R markedly increased the sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy; F: Colony formation assay revealed that knockdown of FTX significantly increased the sensitivity of HT29R and HCT116R cells to radiotherapy; G: Cell viability was determined using CCK-8 assay after transfection of sh-FTX and sh-negative control in HT29R or HCT116R cells, which were irradiated by 4 Gy. All representative data are from three independent experiments, and the results are presented as deviation mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was conducted using the student's t-test. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
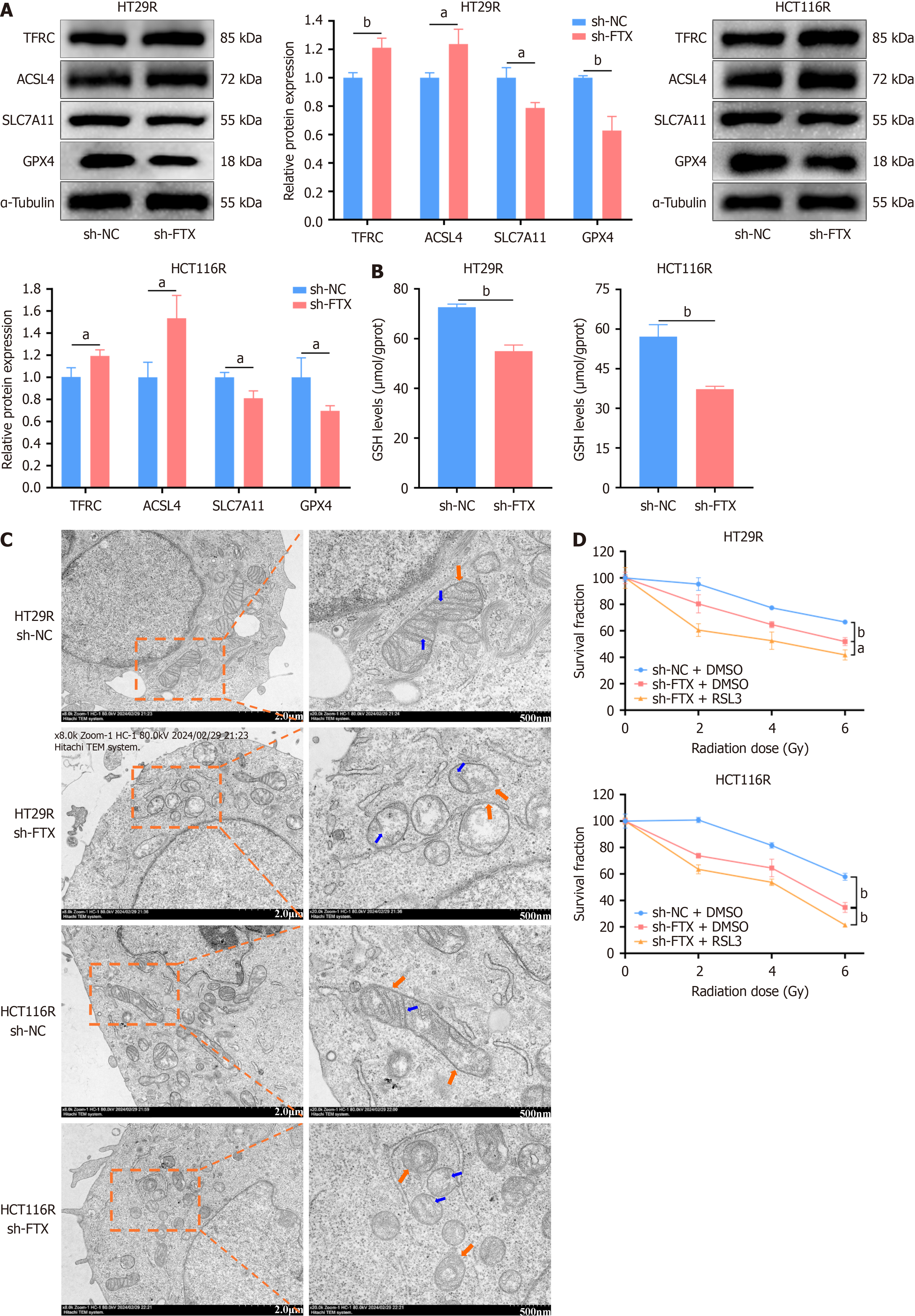
Figure 2 Downregulation of lncRNA FTX increases ferroptosis sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells.
A: Expression of ferroptosis-related proteins in HT29R, HCT116R cells after down-regulating lncRNA FTX; B: Glutathione content in HT29R and HCT116R cells after downregulating lncRNA FTX; C: Morphological changes in intracellular mitochondria in HT29R and HCT116R cells after knockdown of the lncRNA FTX were observed by electron microscopy; D: Cell viability was determined using CCK-8 assay after treatment by sh-FTX combined with RSL3 in HT29R and HCT116R cells. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
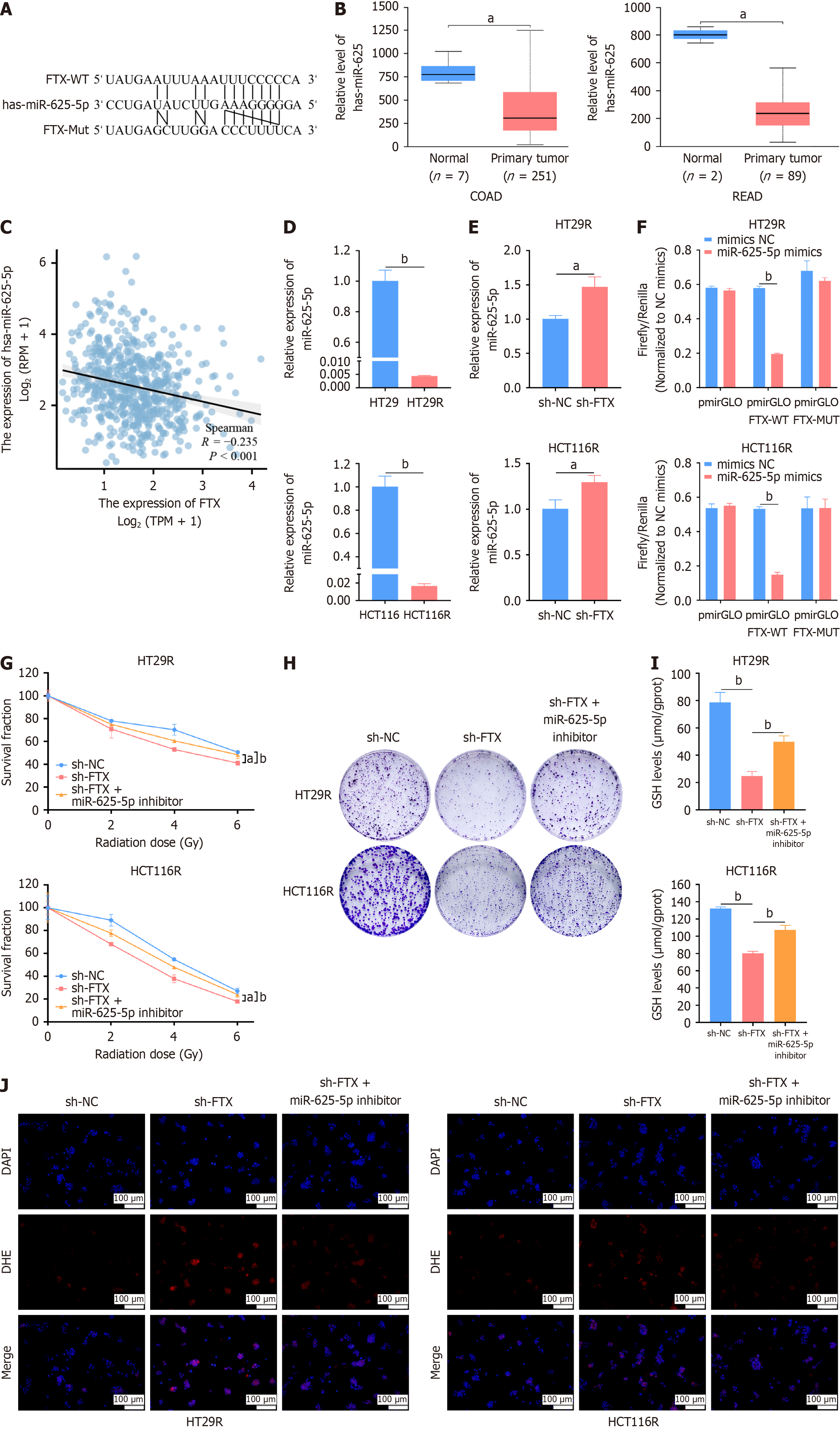
Figure 3 LncRNA FTX sequester miR-625-5p to regulate intracellular redox and radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells.
A: The potential binding site between lncRNA FTX and miR-625-5p predicted by Starbase; B: Expression of miR-625-5p in colon and rectal cancer was higher than that in paracancerous tissues; C: Pearson's correlation analysis was performed to determine the correlation between lncRNA FTX and miR-625-5p expression; D: Relative expression of miR-625-5p in HT29R and HCT116R cells; E: Relative expression of miR-625-5p in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cell lines; F: The targeting relationship between lncRNA FTX and miR-625-5p was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay; G: Transfection of miR-625-5p inhibitor reversed the inhibitory effect of FTX depletion on HT29R and HCT116R cells; H: Colony formation assay confirmed that miR-625-5p inhibitor reversed the survival effect of FTX depletion on HT29R and HCT116R cells; I: MiR-625-5p inhibitor reversed the glutathione content in HT29R and HCT116R cells caused by deletion of FTX; J: Immunofluorescence analyses suggested that miR-625-5p inhibitor altered ROS levels in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
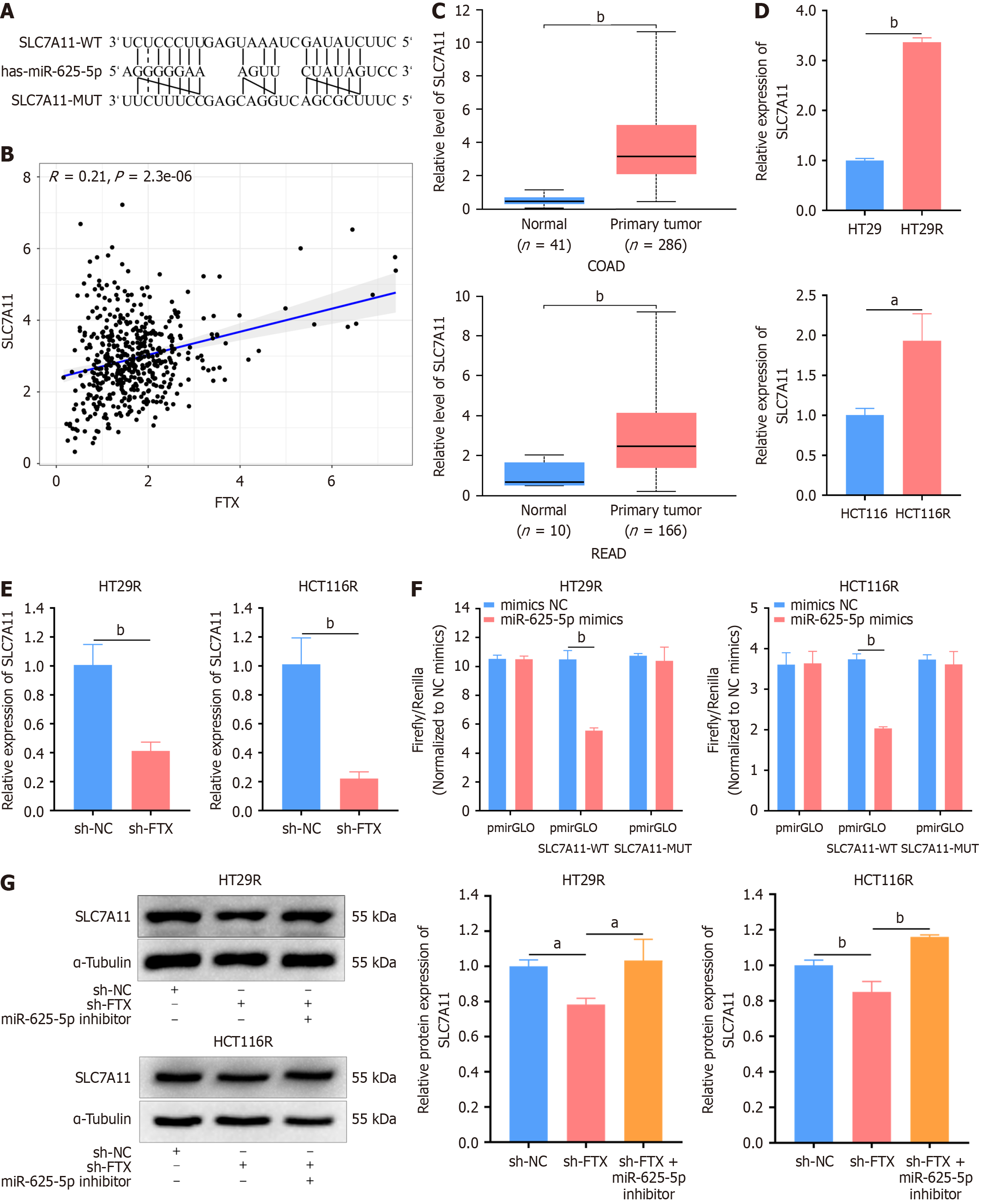
Figure 4 SLC7A11 is a direct target of lncRNA FTX/miR-625-5p signaling axis.
A: The potential binding site between SLC7A11 and miR-625-5p predicted by Starbase; B: Pearson's correlation analysis was performed to determine the correlation between SLC7A11 and lncRNA FTX expression; C: SLC7A11 expression in colon cancer, rectal cancer, and paracancerous tissues; D: Relative expression of SLC7A11 in HT29R and HCT116R cells; E: Relative expression of SLC7A11 in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cell lines; F: The targeting relationship between miR-625-5p and SLC7A11 was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay in HT29R and HCT116R cells; G: Expression levels of SLC7A11 in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells with or without transfection of miR625-5p were determined by Western blotting. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
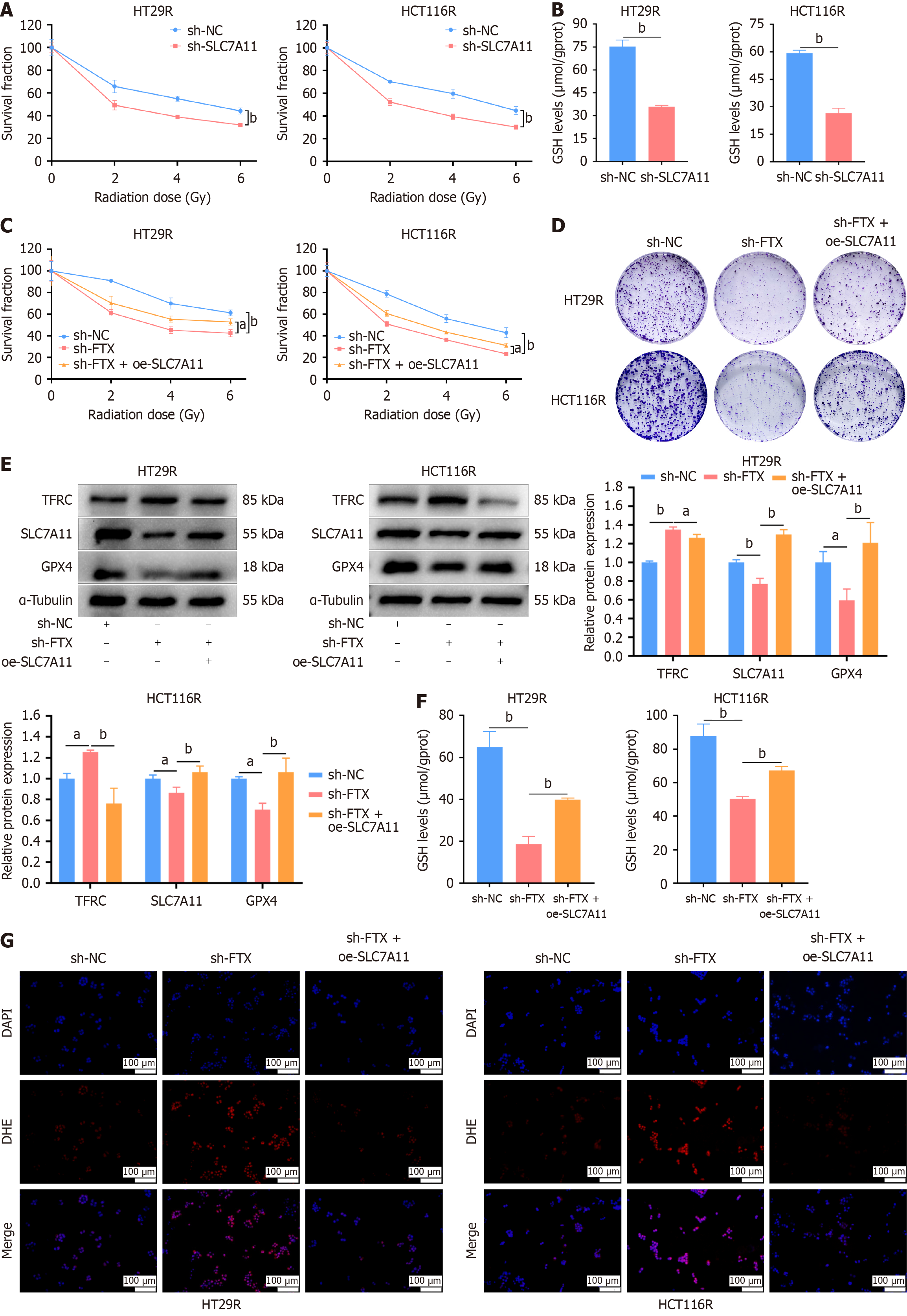
Figure 5 SLC7A11 overexpression reverses the effects of radioresistant cells knockdown lncRNA FTX in sensitivity of ferroptosis and radiotherapy.
A: Downregulation of SLC7A11 promoted radio-sensitivity in HT29R and HCT116R cells; B: Downregulation of SLC7A11 reduced glutathione (GSH) content in HT29R and HCT116R cells; C: CCK-8 assay revealed that SLC7A11 overexpression increased the tolerance of HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells to ionizing radiation; D: Colony formation assay confirmed the promoting effect of overexpression of SLC7A11 on the growth of HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTXcells; E: Western blotting analyses determined the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells after SLC7A11 over expression; F: Reversal effect GSH content in HT29R-shFTX, HCT116R-shFTX cells after overexpression of SLC7A11; G: Immunofluorescence analyses revealed overexpression of SLC7A11 and upregulated ROS levels in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
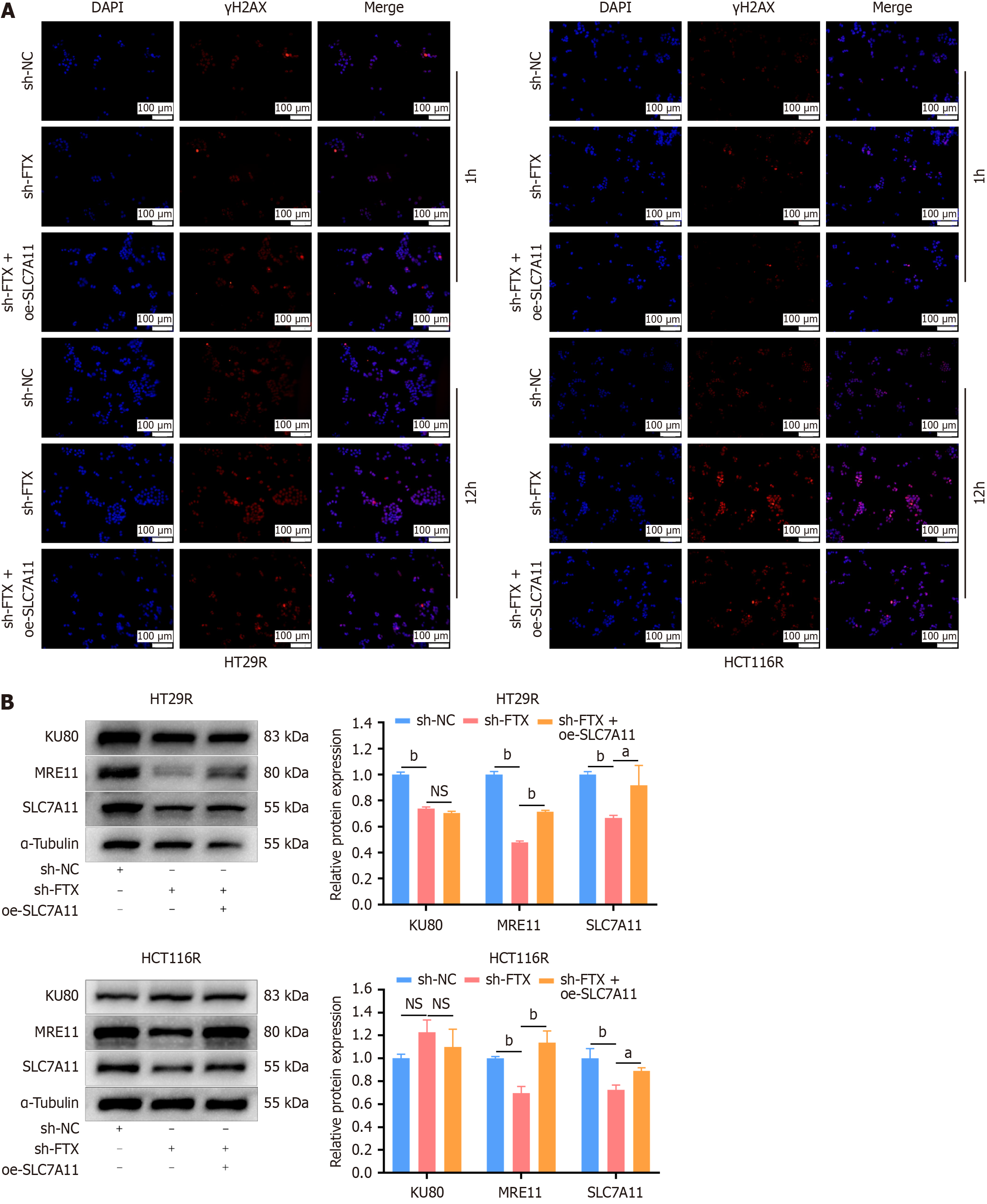
Figure 6 Overexpression of SLC7A11 promotes the repair of damaged DNA induced by ionizing radiation in colorectal cancer cells.
A: Immunofluorescence assay detected γH2AX expression in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells after overexpression of SLC7A11 at 1 or 12 hours; B: Western blotting analyses determined the expression of mismatch repair proteins in HT29R-shFTX and HCT116R-shFTX cells after SLC7A11 overexpression. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
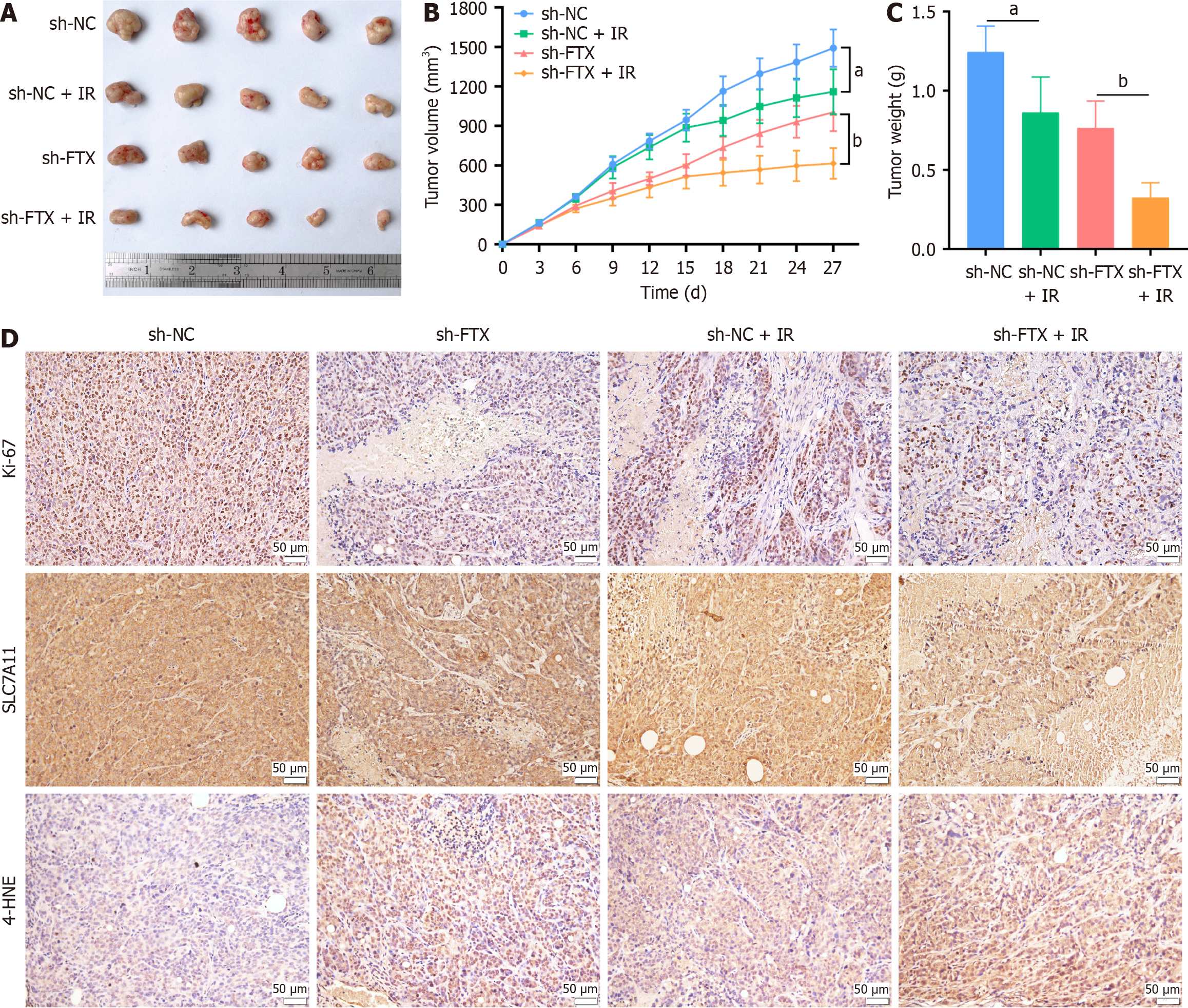
Figure 7 Inhibition of lncRNA FTX increases the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer in vivo.
A: Representative images of the tumors after receiving or not by 10 Gy irradiation, formed by HT29R-sh-FTX or control cells subcutaneous vaccination; B: Tumor volume in xenograft mice of each group at the indicated times; C: Tumor weights of xenograft mice from each group; D: Representative immunohistochemical staining images of Ki-67, SLC7A11, and 4-HNE in the subcutaneous tumor xenograft tissues. Scale bar: 50 μm. Data are expressed mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control; IR: Ionizing radiation.
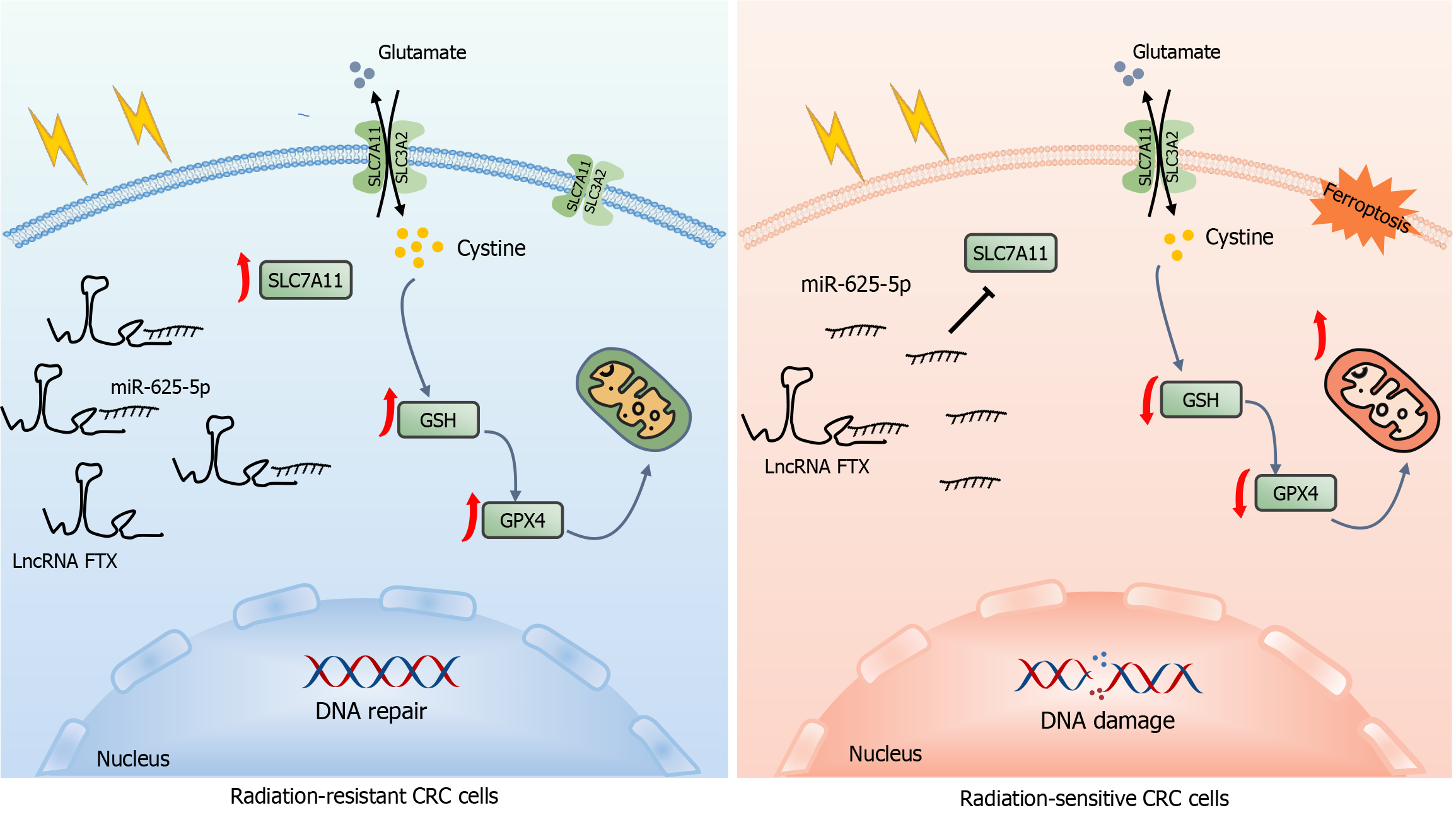
Figure 8 Molecular mechanism of lncRNA FTX in colorectal cancer radio resistance.
LncRNA FTX/miR-625-5p regulated downstream molecule SLC7A11 pathway helps cancer cells facilitates the tolerance of ferroptosis and repair of DNA damage in colorectal cancer cells, which contributes to the transformation of colorectal cancer cells into radiotherapy-resistant cells. CRC: Colorectal cancer.
- Citation: Dai Q, Qu TY, Yang JL, Leng J, Fang L, Zhu QQ, Wu KB, Wu J, Ma JJ, Yu HF. LncRNA FTX promotes colorectal cancer radioresistance through disturbing redox balance and inhibiting ferroptosis via miR-625-5p/SCL7A11 axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 104305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/104305.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305