Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2025; 31(14): 104975
Published online Apr 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i14.104975
Published online Apr 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i14.104975
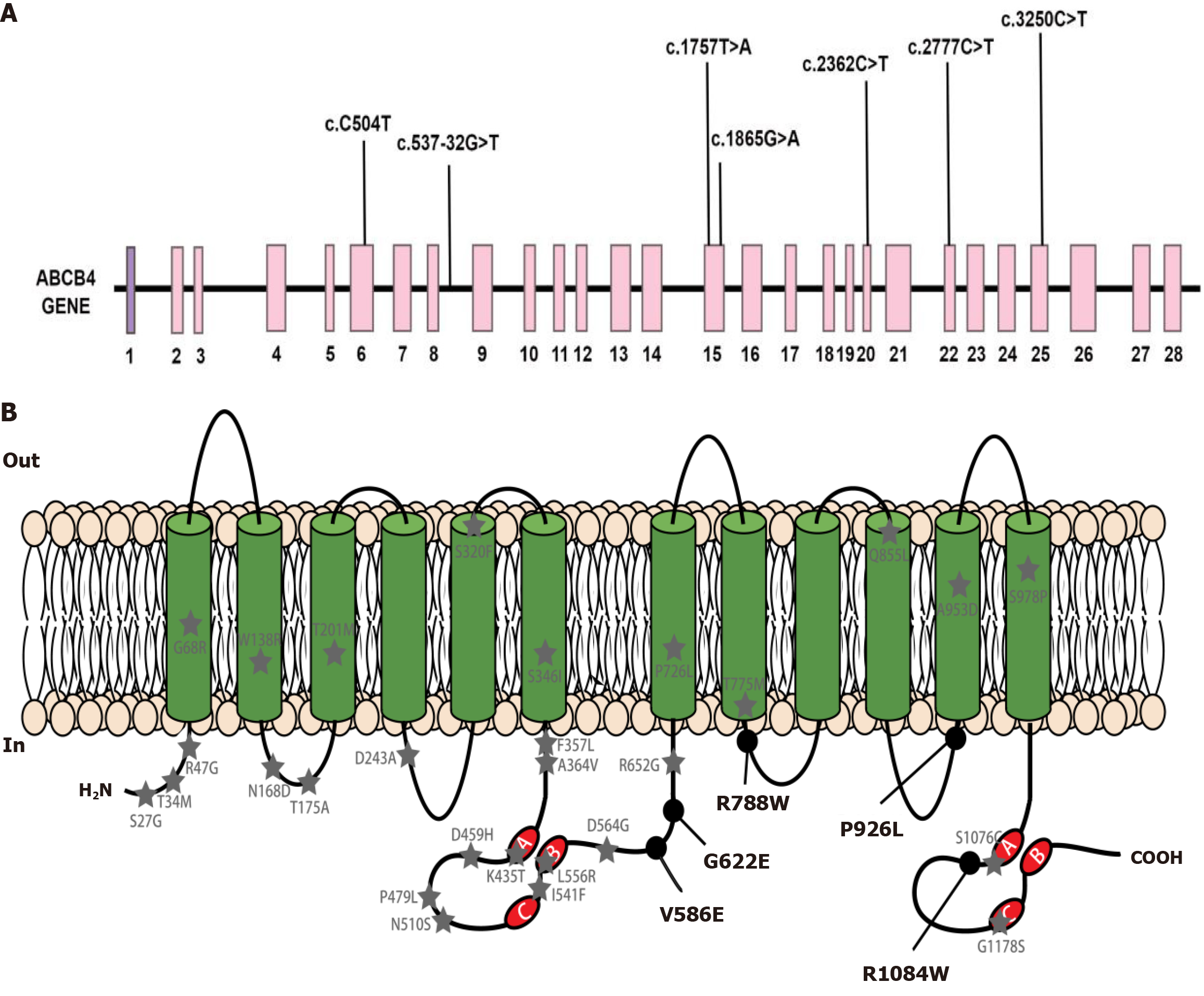
Figure 1 Schematic representation of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4.
A: ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 (ABCB4) gene structure with mutations representing exons 1 to 28. Each mutation found in our study is marked; B: The secondary structure of multidrug resistance protein 3 protein and the distribution of missense mutations found by our team. Black circle marked ABCB4 variants were detected in the patients cohort in our research. Grey pentagram marked ABCB4 variants reported in the literature; A: Walker A; B: Walker B; C: The signature motif C; COOH: Carboxyl terminus of polypeptide chain; H2N: Amino terminus of polypeptide chain; In: Inside the cell membrane; Out: Outside the cell membrane; ABCB4: ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4; MDR3: Multidrug resistance protein 3.
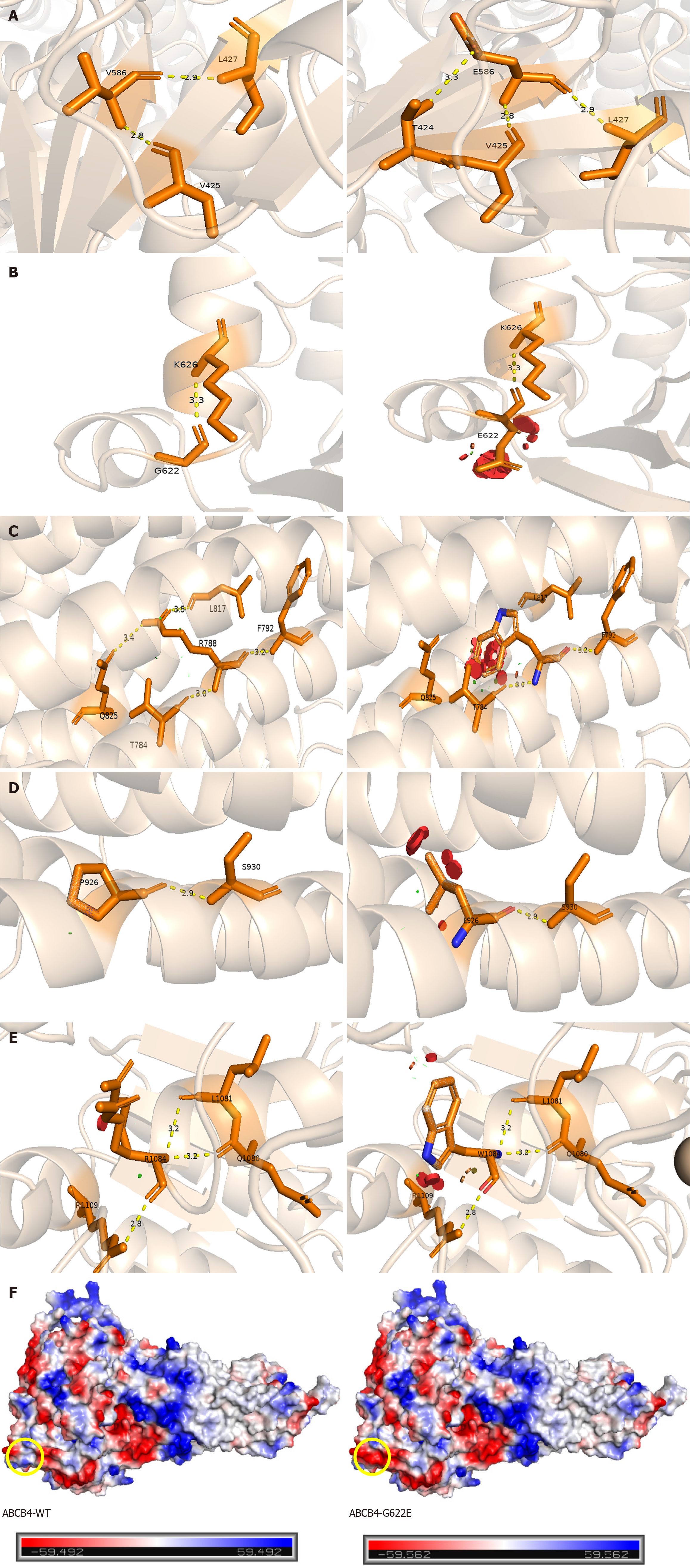
Figure 2 Structural analysis of missense variants in multidrug resistance protein 3.
Prediction of three-dimensional structure of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 (ABCB4) mutation sites by Swiss Model. A: P.V586E mutation forms new hydrogen bond with T424; B: P.G622E mutation affects steric hindrance; C: P.R788W mutation breaks hydrogen bond with Q825 and L817; D: P.P926 L mutation affects steric hindrance; E: P.R1084W mutation affects steric hindrance; F: The left image represents ABCB4-WT, while the right image illustrates the G622E variant. The yellow circle indicates that the neutral glycine is replaced by the negatively charged glutamic acid, with the red region representing negative charges, the white region indicating neutrality, and the blue region denoting positive charges. ABCB4: ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4.
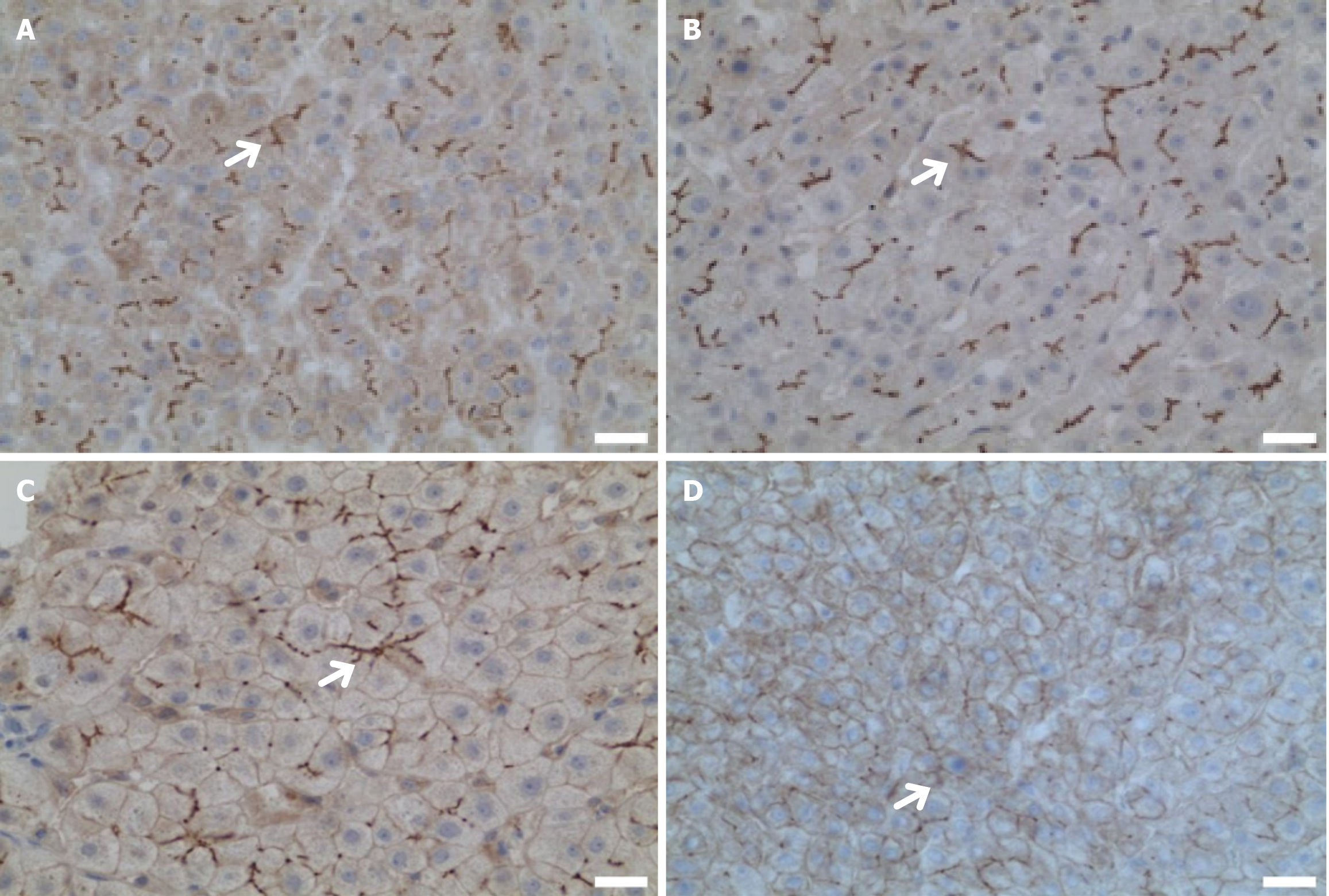
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical manifestations of the liver in a patient with ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 variants.
Except for patient 4, all other patients underwent liver biopsy. Immunohistochemical staining was performed using anti- ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 (P3II-26, Thermo, United States), with the white arrows indicating the labeling of multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3) tubules. Bars = 2.5 μm. A: MDR3 is evenly distributed in liver tissue (the white arrow indicates MDR3 is normal, case 1); B: MDR3 is evenly distributed in liver tissue (the white arrow indicates MDR3 is normal, 400 ×, case 2); C: Decreased distribution of MDR3 in liver tissue (the white arrow indicates MDR3 is decreasing, 400 ×, case 3); D: Decreased distribution of MDR3 in liver tissue (the white arrow indicates MDR3 is decreasing, 400 ×, case 5). ABCB4: ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4; MDR3: Multidrug resistance protein 3.
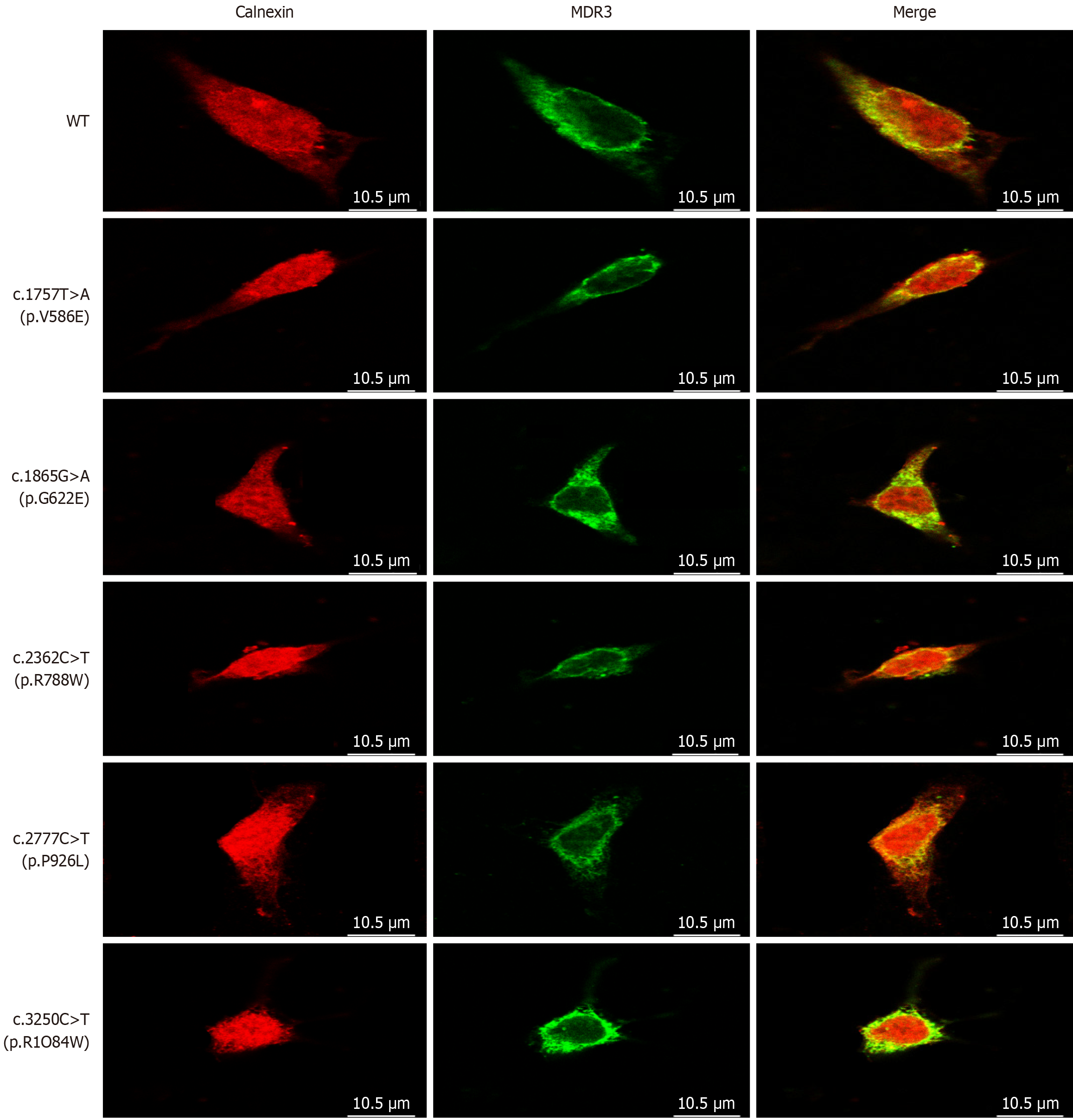
Figure 4 Confocal microscopy of cellular localization of multidrug resistance protein 3.
HEK293 cells expressing the wild-type and mutant ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 alleles were labeled with anti- multidrug resistance protein 3 (red) and anti-calnexin (green) antibodies, the yellow color indicates the coexistence of the two proteins. Followed by fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibodies, and observed using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Bars = 10.5 μm. MDR3: Multidrug resistance protein 3; WT: Wild-type.
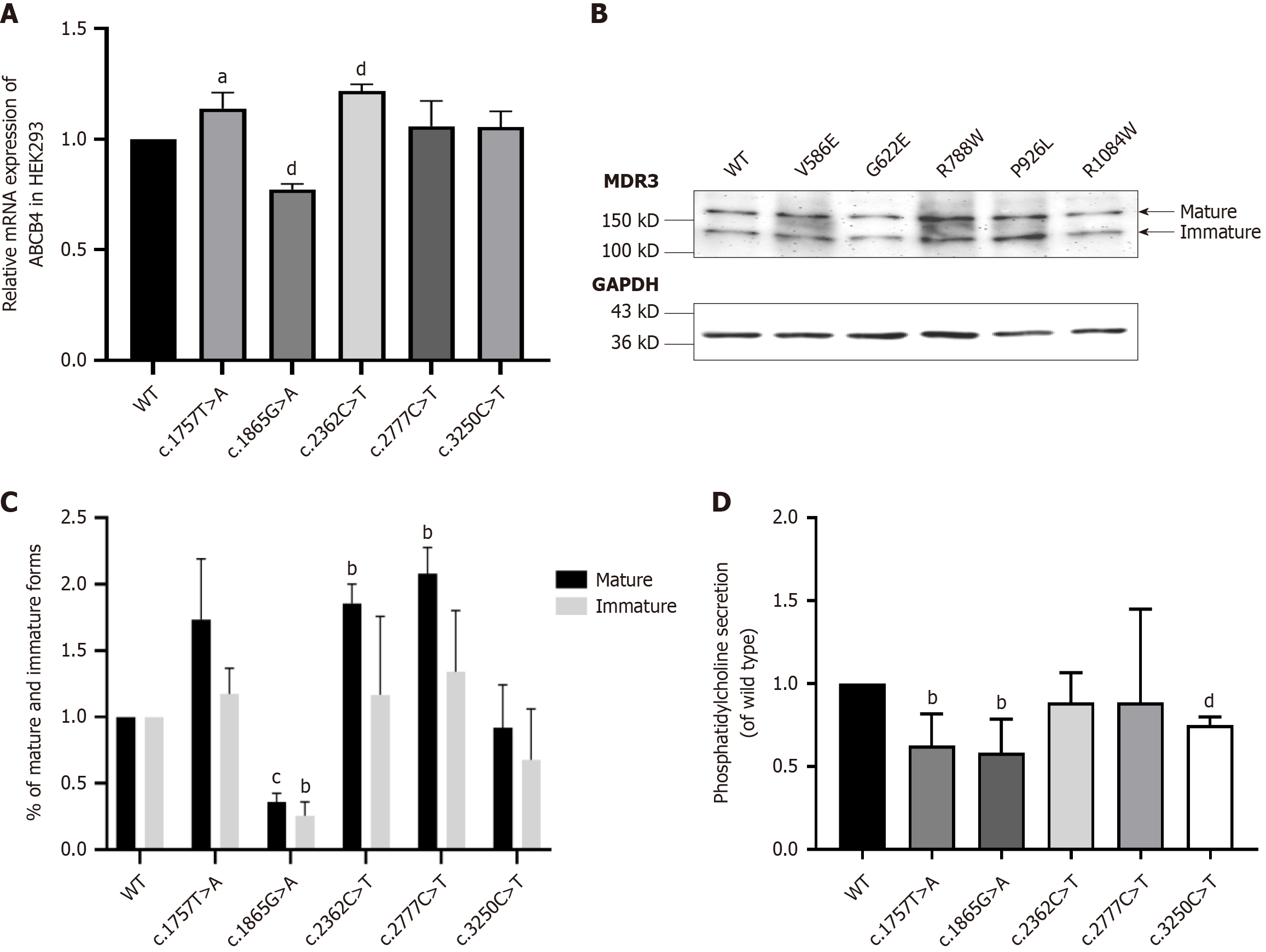
Figure 5 Expression analysis and determination of transportation capability.
A: MRNA expression analysis of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 (ABCB4)-wild-type (WT) and variants by qPCR. Using GAPDH as a reference for relative quantity analysis, Values were analyzed by GraphPad Prism 8.0. In addition, the results are the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. aP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001; B: Immunbloting of ABCB4 and variants. Representative western blot of the expression levels of the mutants with respect to ABCB4-WT. The expression and the processing of ABCB4-WT and the mutants was examined by western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from transfected HEK293 cells. ABCB4 expression was detected following SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the anti- multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3) antibody. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Molecular masses are indicated on the left (in kDa). Mature MDR3 was show in black while immature MDR3 show in white; C: Western blot analysis of ABCB4-WT and variants. The values have been normalized to ABCB4-WT. And they were measured by ImageJ and analyzed by GraphPad Prism 8.0. The dates show the means ± SD of three separate experiments. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001; D: Determination of transportation capability of MDR3 and its variants. The phosphatidylcholine levels in the supernatant of HEK293 cells were measured, which were respectively transfected with ABCB4-WT gene and mutant alleles. The secretion of phosphatidylcholine was standardized to wild type group. The data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism 8.0. And they represent the means ± SD of four independent experiments. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001. MDR3: Multidrug resistance protein 3; WT: ABCB4 wild type.
- Citation: Weng YH, Zheng YF, Yin DD, Xiong QF, Li JL, Li SX, Chen W, Yang YF. Clinical, genetic and functional perspectives on ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4 variants in five cholestasis adults. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(14): 104975
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i14/104975.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i14.104975