Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2024; 30(9): 1121-1131
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1121
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1121
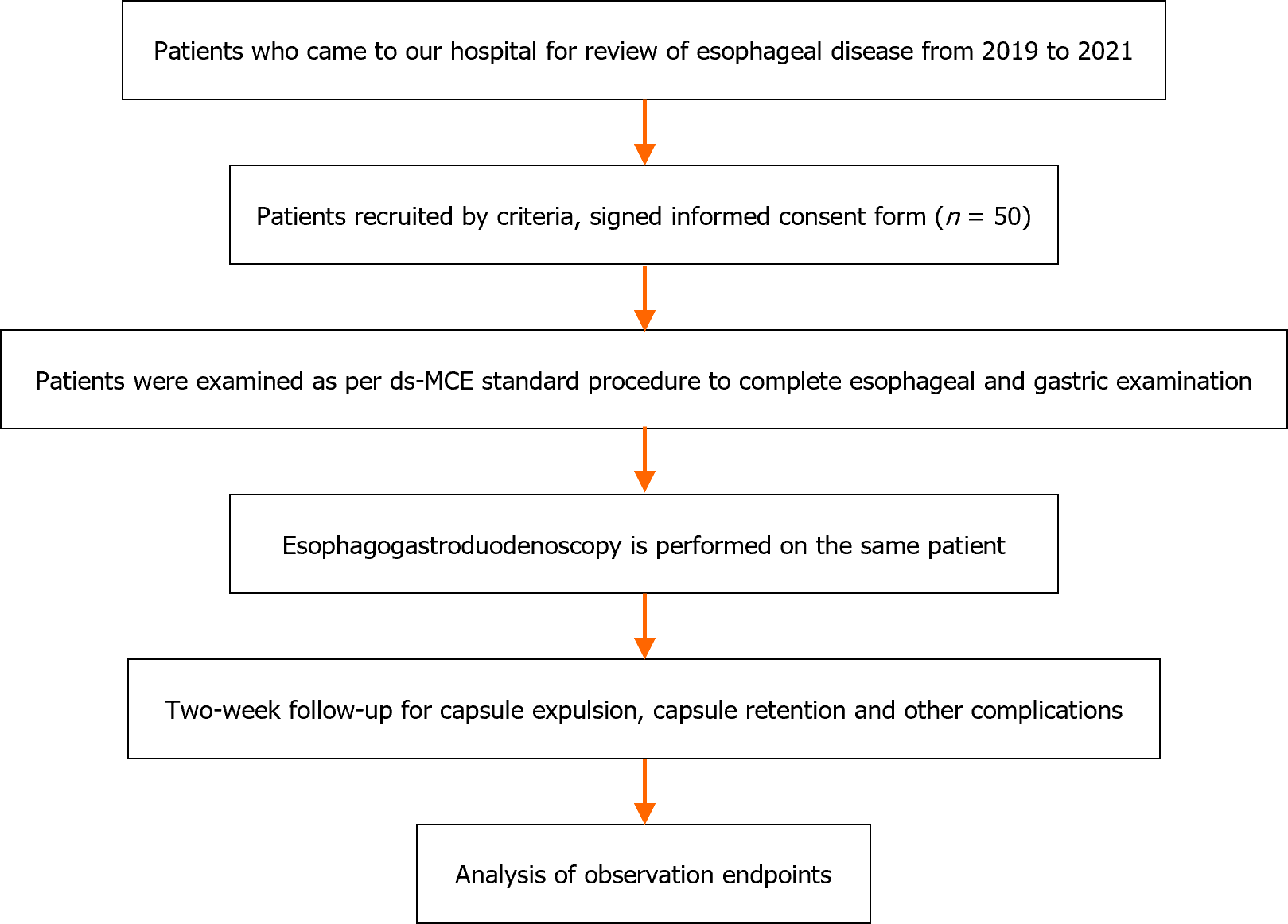
Figure 1 The procedure for this study.
ds-MCE: Detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy.
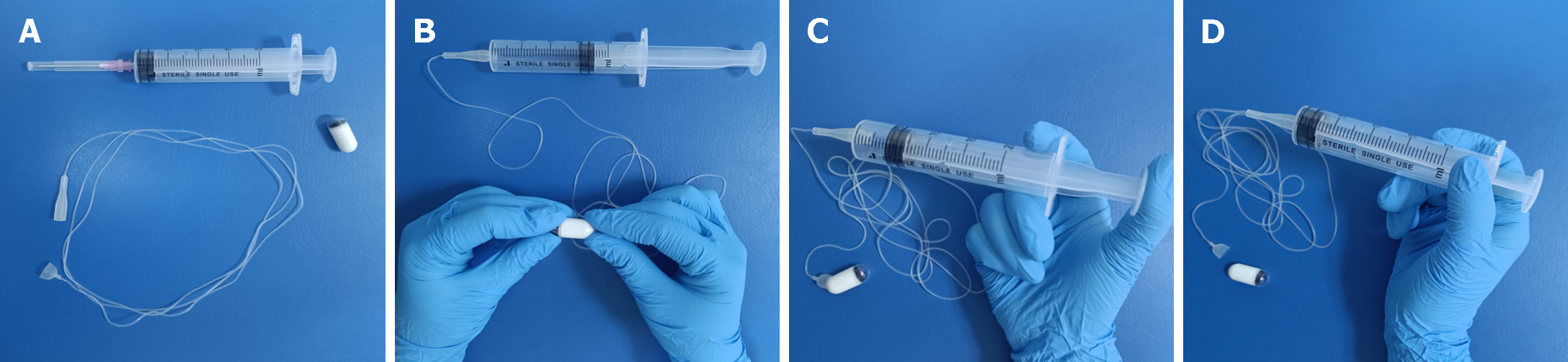
Figure 2 The operational procedure of detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy.
A: A single-use capsule endoscope and detachable string; B: The detachable string is connected to one end of the capsule and the other end is attached to a syringe; C: Air is injected into the hollow string through the syringe; D: Separating the capsule from the string.
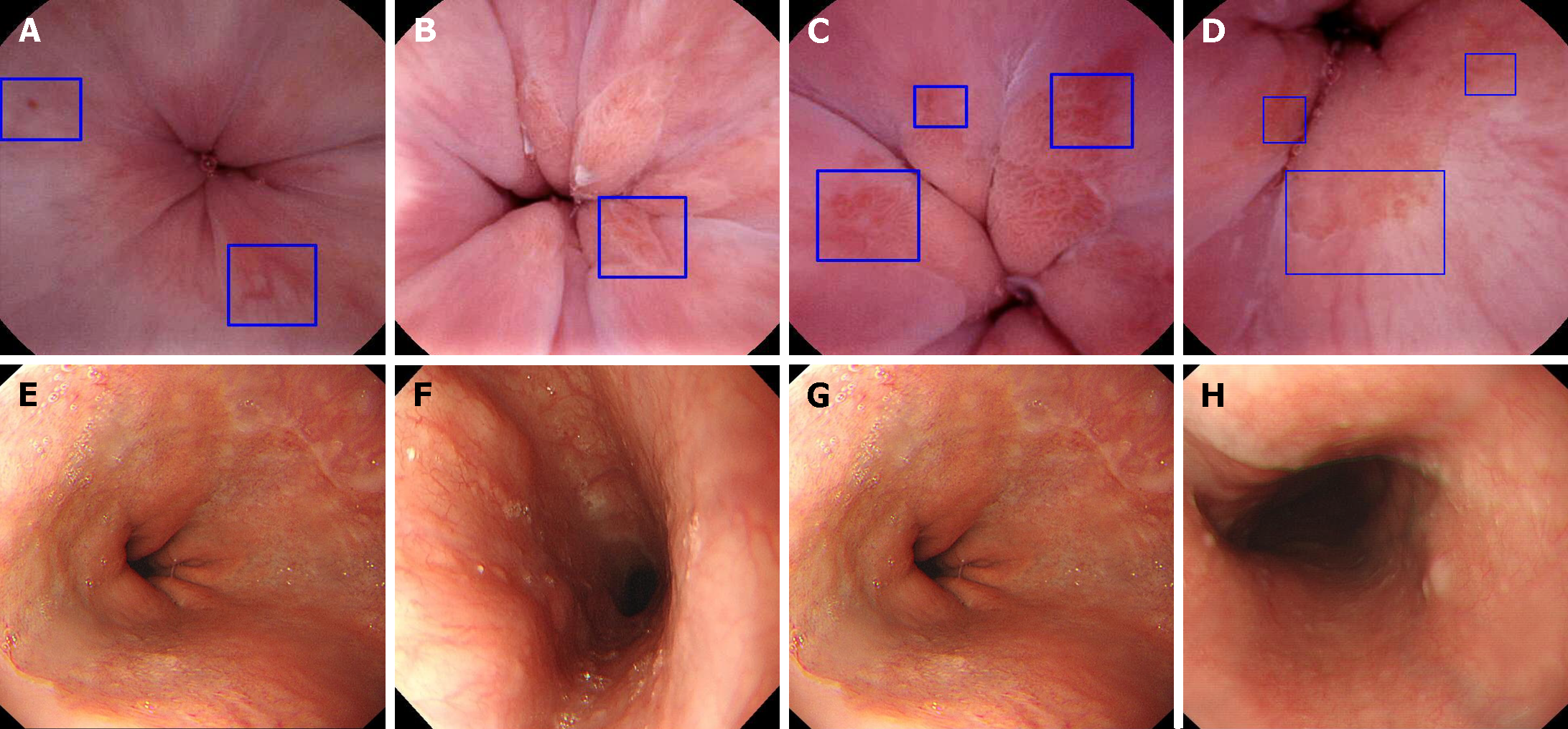
Figure 3 Representative diseases observed on detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy and esophagogastroduode
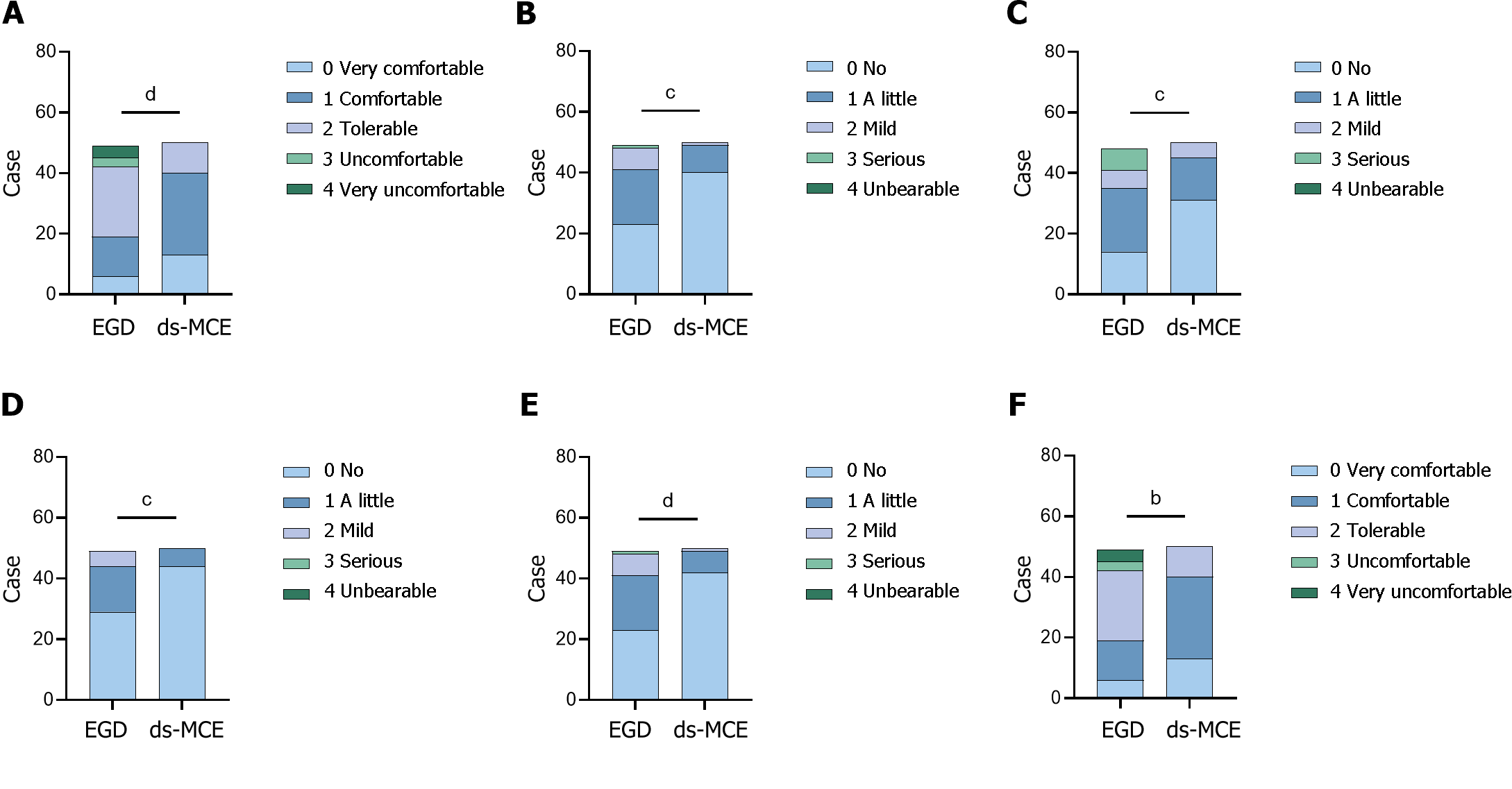
Figure 4 Perception analysis of subjects undergoing esophagogastroduodenoscopy and detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy examination.
A: Comfort level; B: Pain during the examination; C: Discomfort during the examination; D: Pain after the examination; E: Discomfort after the examination; F: Convenience of inspection. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. ds-MCE: Detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy; EGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
- Citation: Yang YL, Qin HW, Chen ZY, Fan HN, Yu Y, Da W, Zhu JS, Zhang J. Detachable string magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy for the noninvasive diagnosis of esophageal diseases: A prospective, blind clinical study. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(9): 1121-1131
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i9/1121.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1121