Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2024; 30(8): 817-832
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.817
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.817
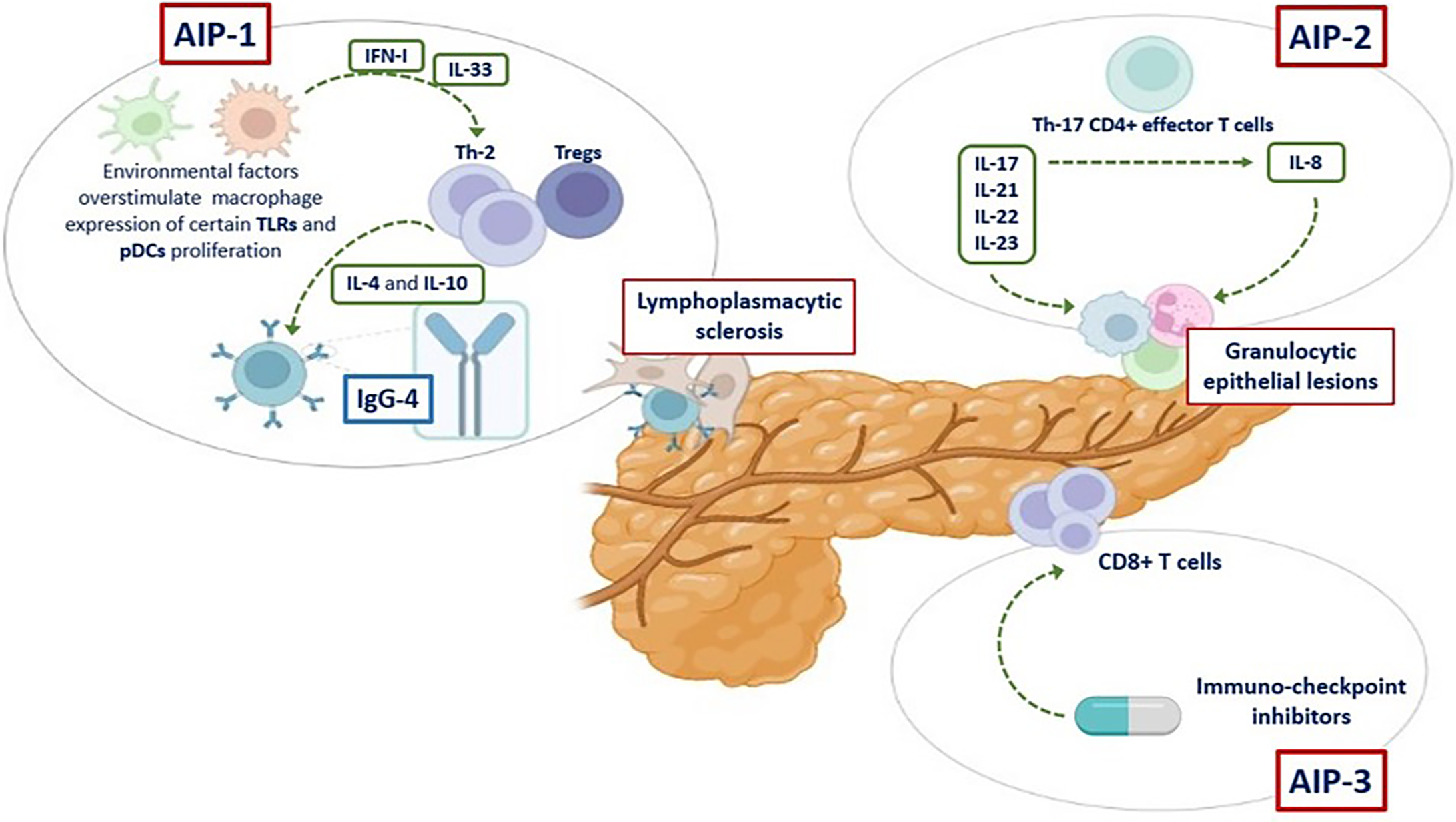
Figure 1 Ethiopathology of different types of autoimmune pancreatitis.
Ethiopathological mechanisms of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis, type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis, and type 3 autoimmune pancreatitis. AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukine; TLRs: Toll-like receptors; pDCs: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells; IgG4: Immunoglobulin G4; AIP-1: Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis; AIP-2: Type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis; AIP-4: Type 3 autoimmune pancreatitis.
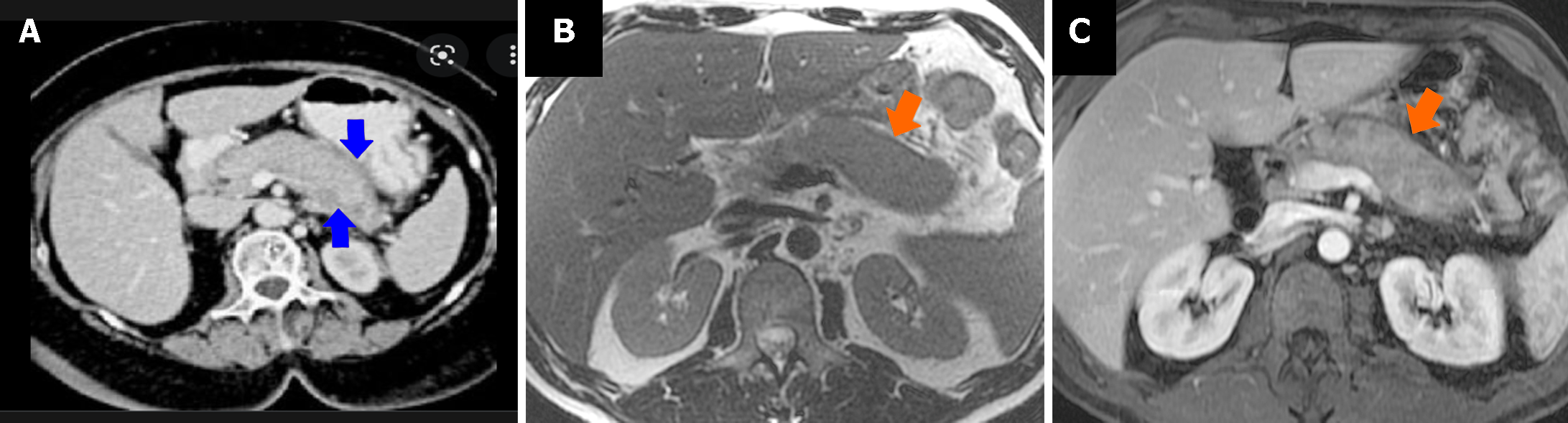
Figure 2 Radiological appearance of autoimmune pancreatitis-part 1.
A: Unenhanced computed tomography scan appearance of a diffuse autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP): Sausage-like swelling of the parenchyma, with straight margins, and consequent loss of the typical lobular structure. A hypodense fibrotic capsule-like rim demarcates the swollen pancreas (blue arrow); B: Unenhanced T1 weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance of a diffuse AIP: Sausage-like swelling of the parenchyma, with straight margins, and rectangular shape of the tail (cut-tail sign) (orange arrow); C: Arterial phase of the contrast-enhanced T1 weighted MRI: Homogeneous reduced enhancement of the pancreatic parenchyma, with a more hypointense fibrotic capsule-like rim that demarcates the swollen pancreas (orange arrow).
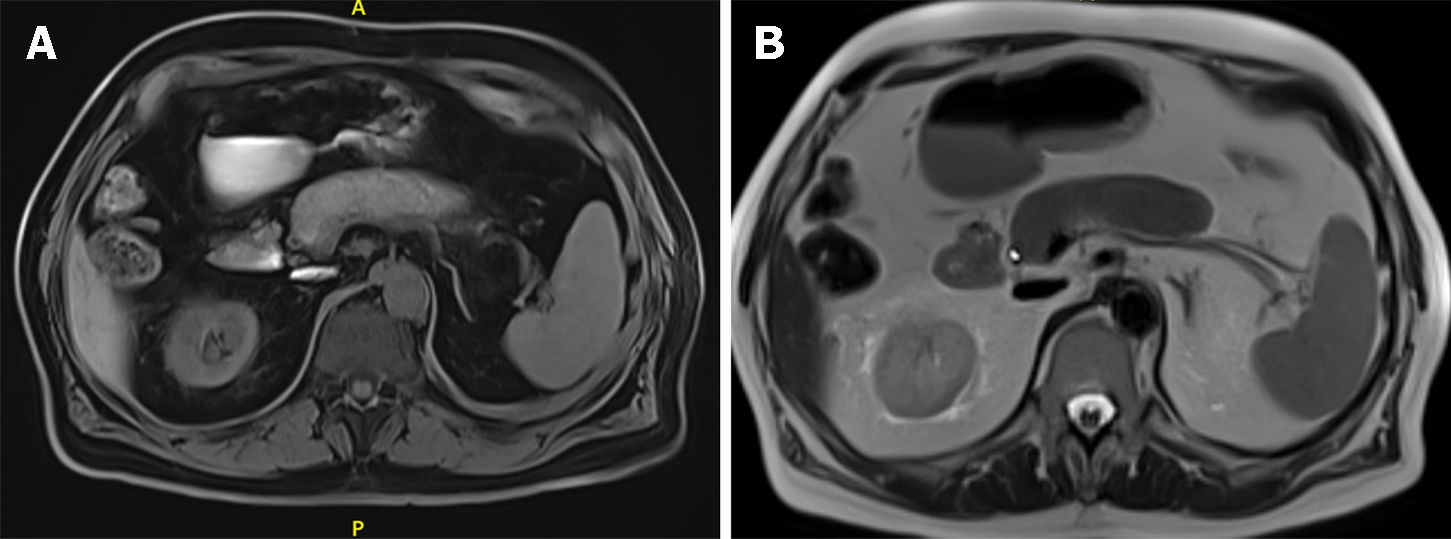
Figure 3 Radiological appearance of autoimmune pancreatitis-part 2.
A: Unenhanced T1 weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP): Diffuse hypointense pancreas, with an even more hypointense fibrotic capsule-rim; B: Unenhanced T2 weighted MRI images of diffuse AIP: The affected parenchyma shows a moderately higher intensity signal, with a persistently low-intensity fibrotic rim.
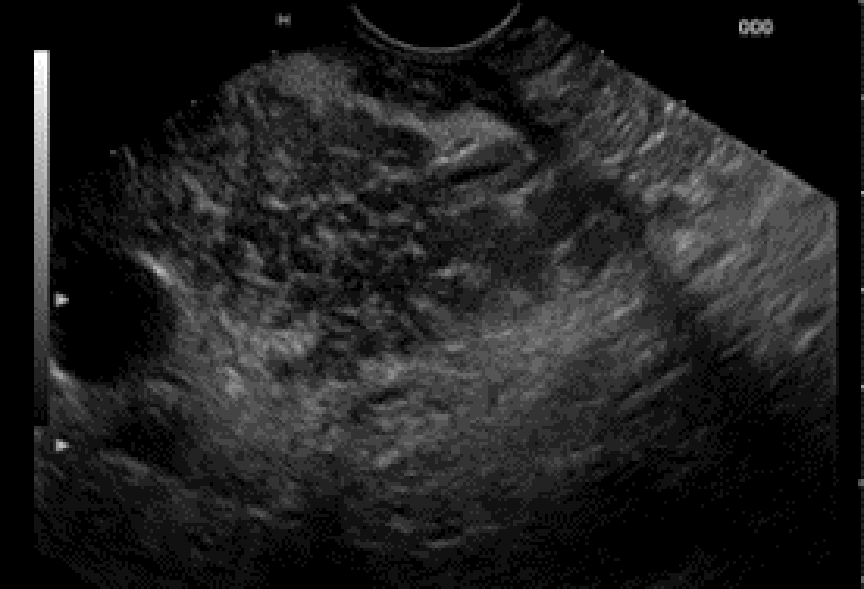
Figure 4 Endoscopic ultrasound appearance of autoimmune pancreatitis.
Endoscopic ultrasound aspect of a mass-forming autoimmune pancreatitis: Solitary, irregular hypoechoic mass, located in the head of the pancreas, without upstream dilatation of the main pancreatic duct.
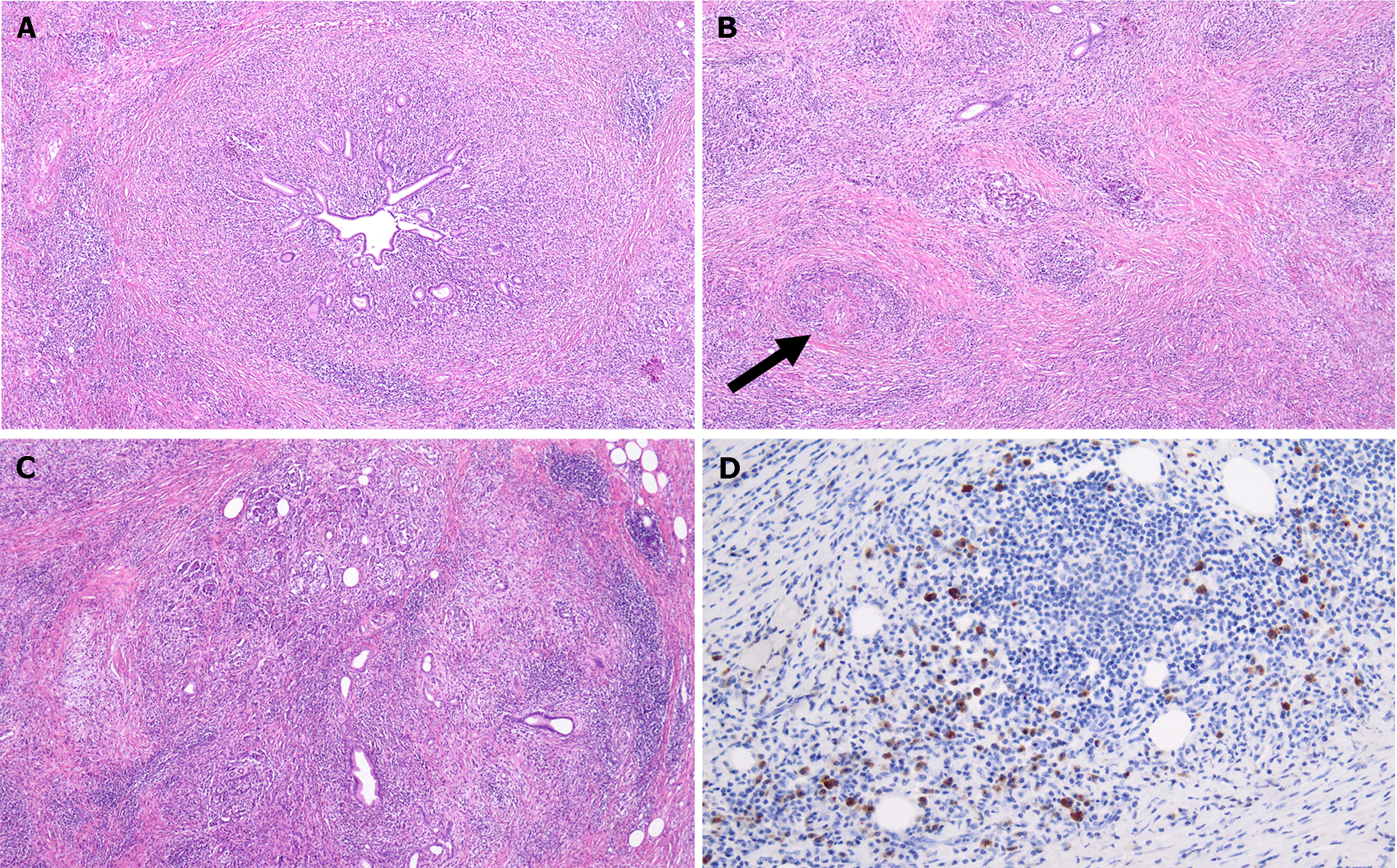
Figure 5 Histology of autoimmune pancreatitis.
A: Histological samples of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. Hematoxylin eosin (HE) 4, Duct centric lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate; B: HE 10, storiform fibrosis with intense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and obliterative phlebitis (arrow); C: HE 4, lobule complete effacement by inflammatory cells and fibrosis; D: Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) IIC 20, moderate increase of IgG4+ plasma cells.
- Citation: Gallo C, Dispinzieri G, Zucchini N, Invernizzi P, Massironi S. Autoimmune pancreatitis: Cornerstones and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(8): 817-832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i8/817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.817