Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2024; 30(5): 429-439
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.429
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.429
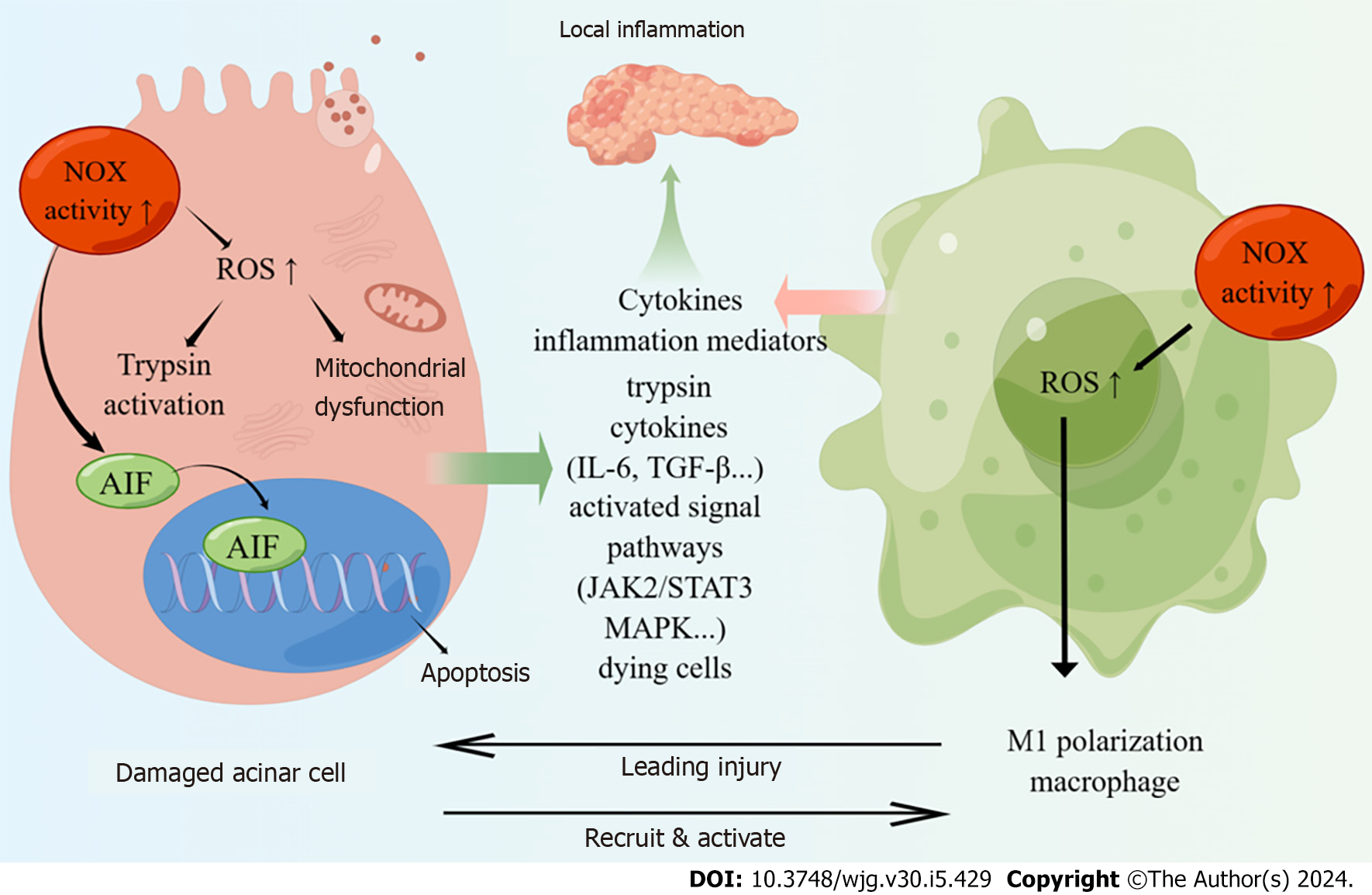
Figure 1 The scheme of the potential roles of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen oxides in pancreatic acinar cells and macrophages, which leading the development of acute pancreatitis.
NOX: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen oxides; AIF: Apoptosis inducing factor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; PSC: Pancreatic stellate cell; DPI: Diphenylene iodium.
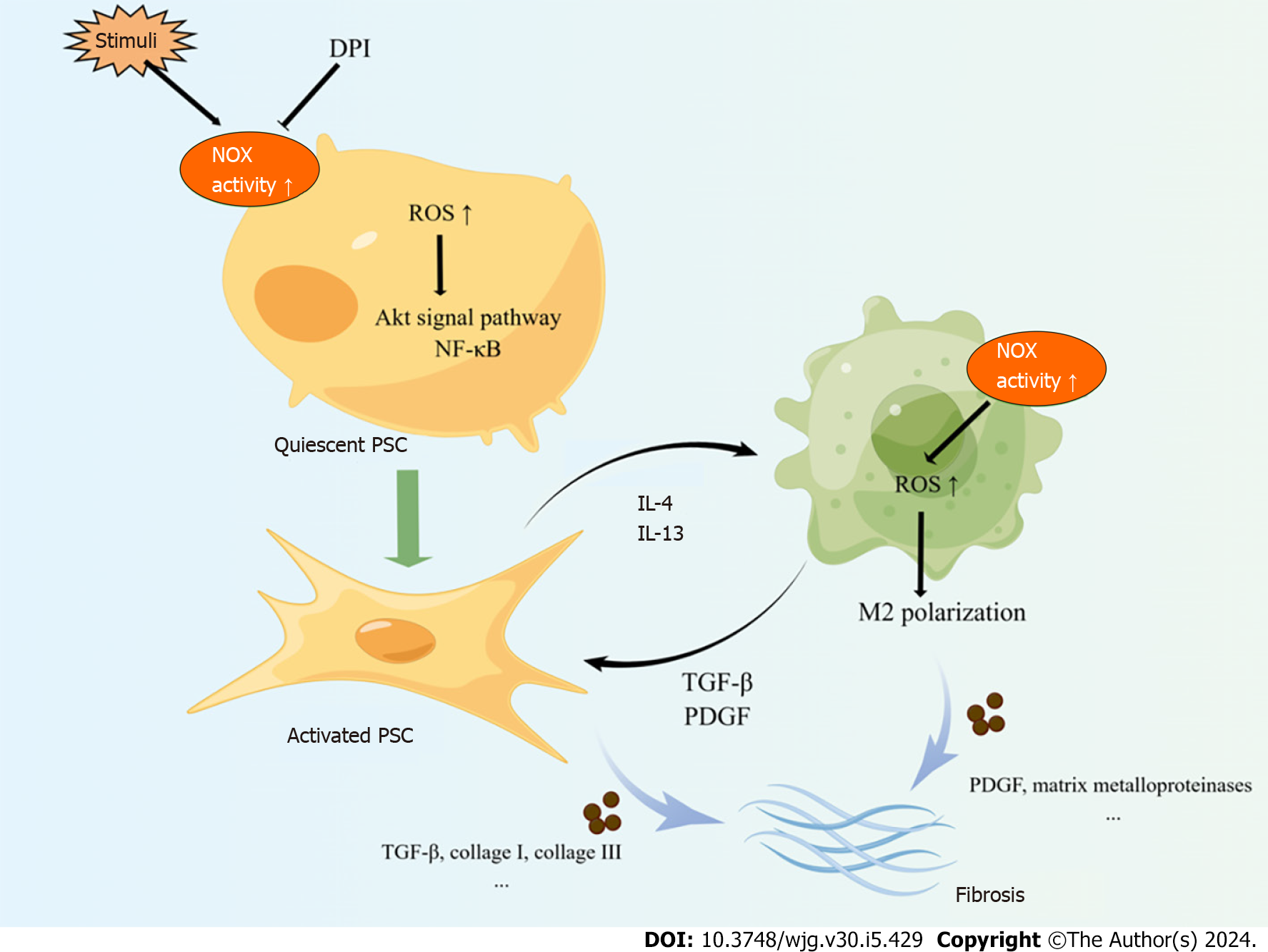
Figure 2 The scheme of the potential roles of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen oxides in pancreatic stellate cells and macrophages, which facilitating pancreatic fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis.
NOX: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen oxides; AIF: Apoptosis inducing factor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF: Transforming growth; IL: Interleukin; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
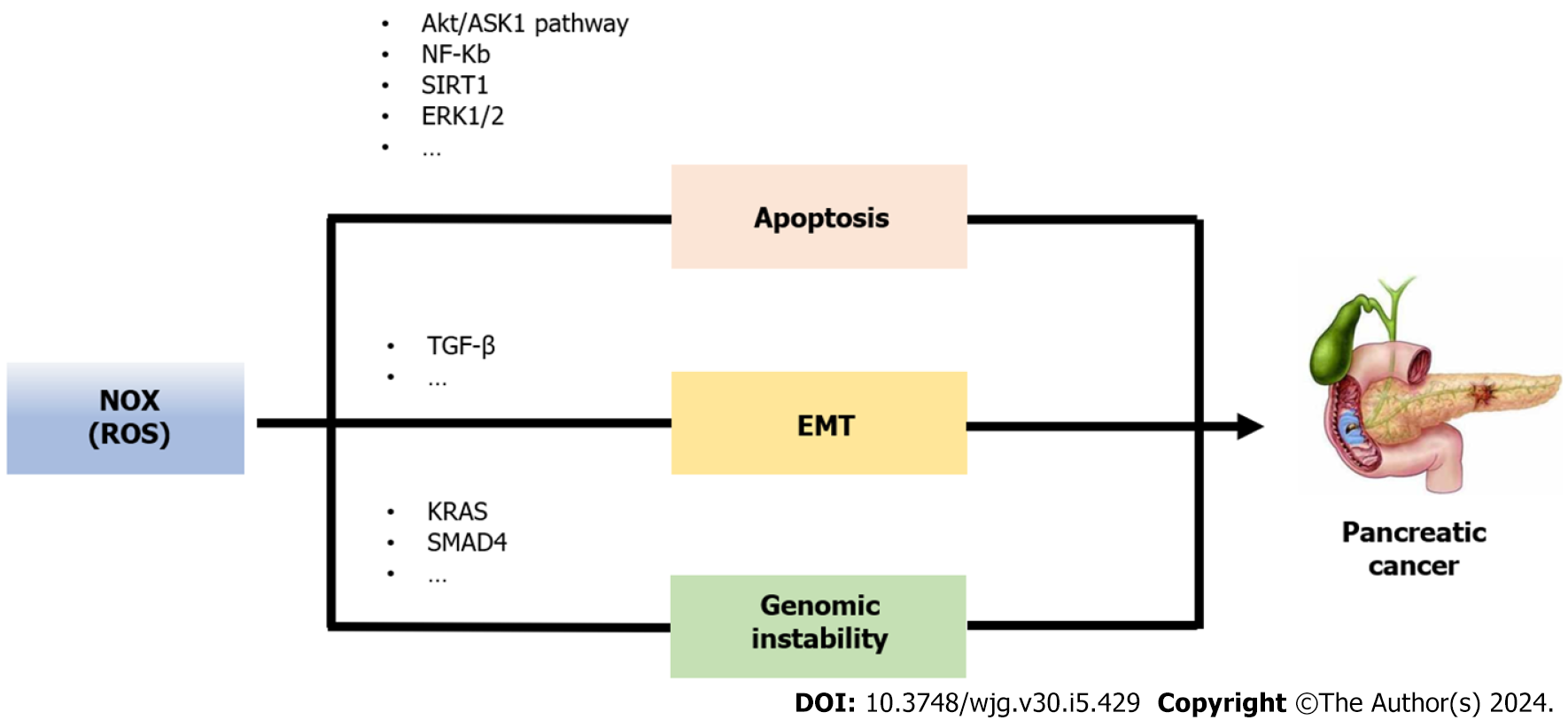
Figure 3 The scheme of the potential roles of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen oxides in pancreatic cancer.
ASK: Apoptosis signal regulating kinase; TGF: Transforming growth; SIRT: Silent information regulator; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinases; SMAD: Drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic protein; NOX: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen oxides; AIF: Apoptosis inducing factor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; EMT: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
- Citation: Bi YW, Li LS, Ru N, Zhang B, Lei X. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in pancreatic diseases: Mechanisms and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(5): 429-439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i5/429.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.429