Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2024; 30(45): 4781-4790
Published online Dec 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4781
Published online Dec 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4781
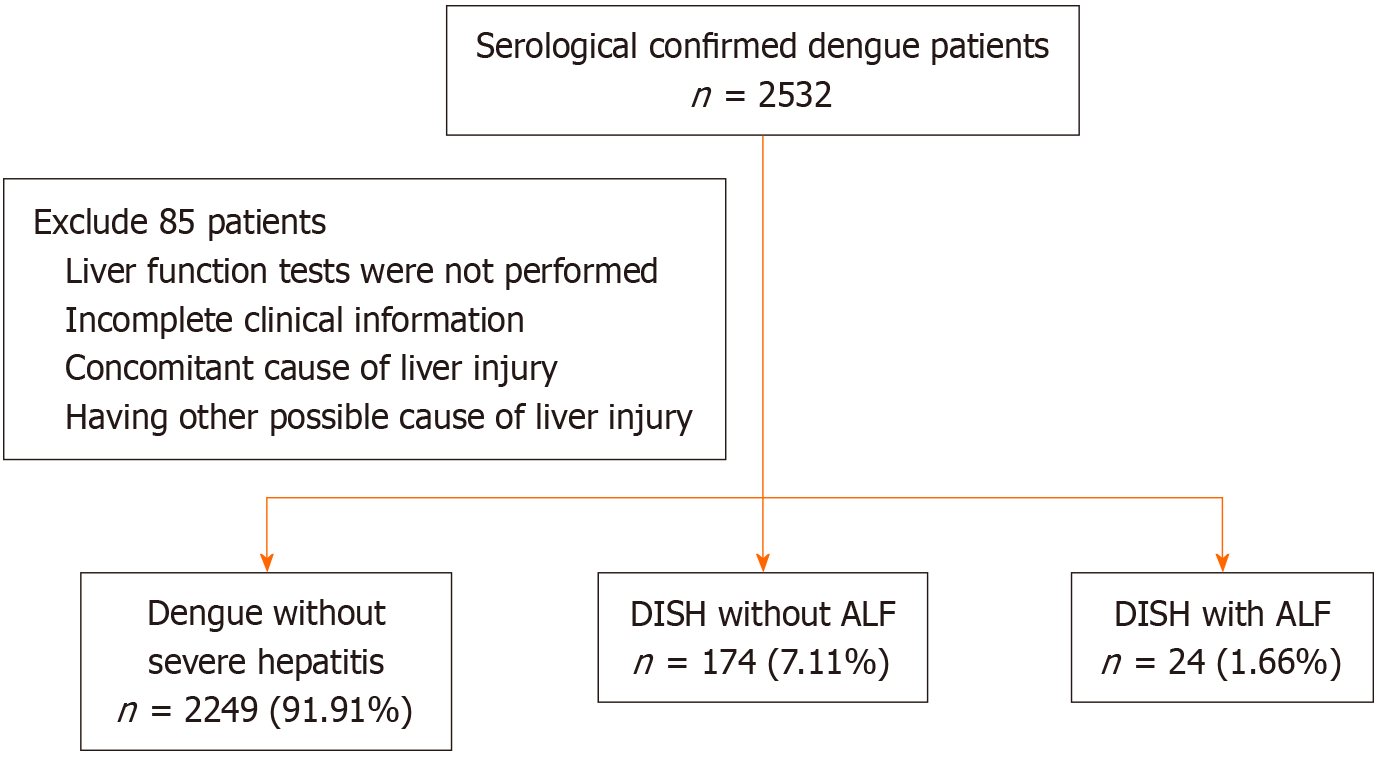
Figure 1 Study algorithm.
DISH: Dengue-induced severe hepatitis; ALF: Acute liver failure.
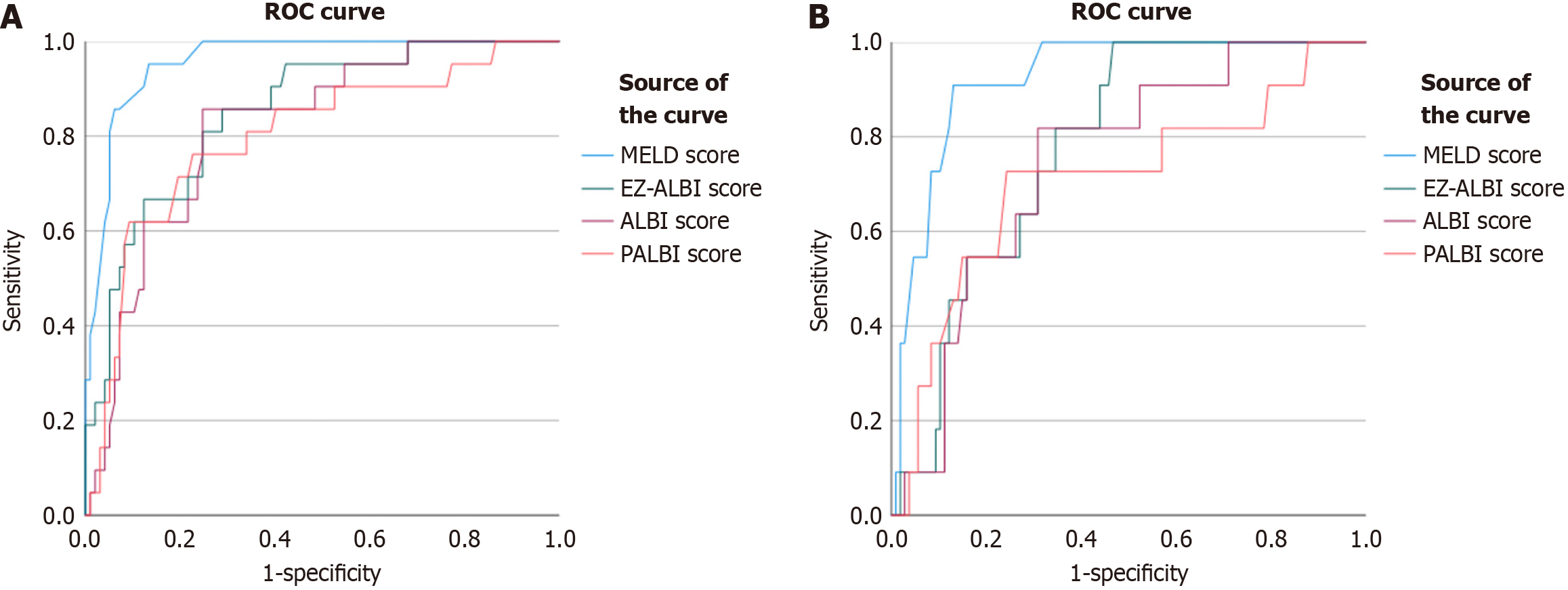
Figure 2 Area under receiver operating characteristic curve values of prognostic scores.
A: Predicting acute liver failure (ALF) from dengue-induced severe hepatitis (DISH). Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) scores had the best performance in predicting ALF [area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) 0.929], followed by easy albumin-bilirubin (ALBI), ALBI, and platelet-ALBI (PALBI) scores (AUROC 0.865, 0.832, and 0.797, respectively); B: Predicting death from DISH. MELD score had the best performance in predicting death (AUROC 0.822), followed by easy ALBI, ALBI, and PALBI scores (AUROC 0.807, 0.774, and 0.708, respectively). ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; MELD: Model for end-stage liver disease; EZ-ALBI: Easy albumin-bilirubin; ALBI: Albumin-bilirubin; PALBI: Platelet-albumin-bilirubin.
- Citation: Teerasarntipan T, Thanapirom K, Chaiteerakij R, Komolmit P, Treeprasertsuk S. Validation of prognostic scores for predicting acute liver failure and in-hospital death in patients with dengue-induced severe hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(45): 4781-4790
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i45/4781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4781