Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2024; 30(24): 3076-3085
Published online Jun 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3076
Published online Jun 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3076
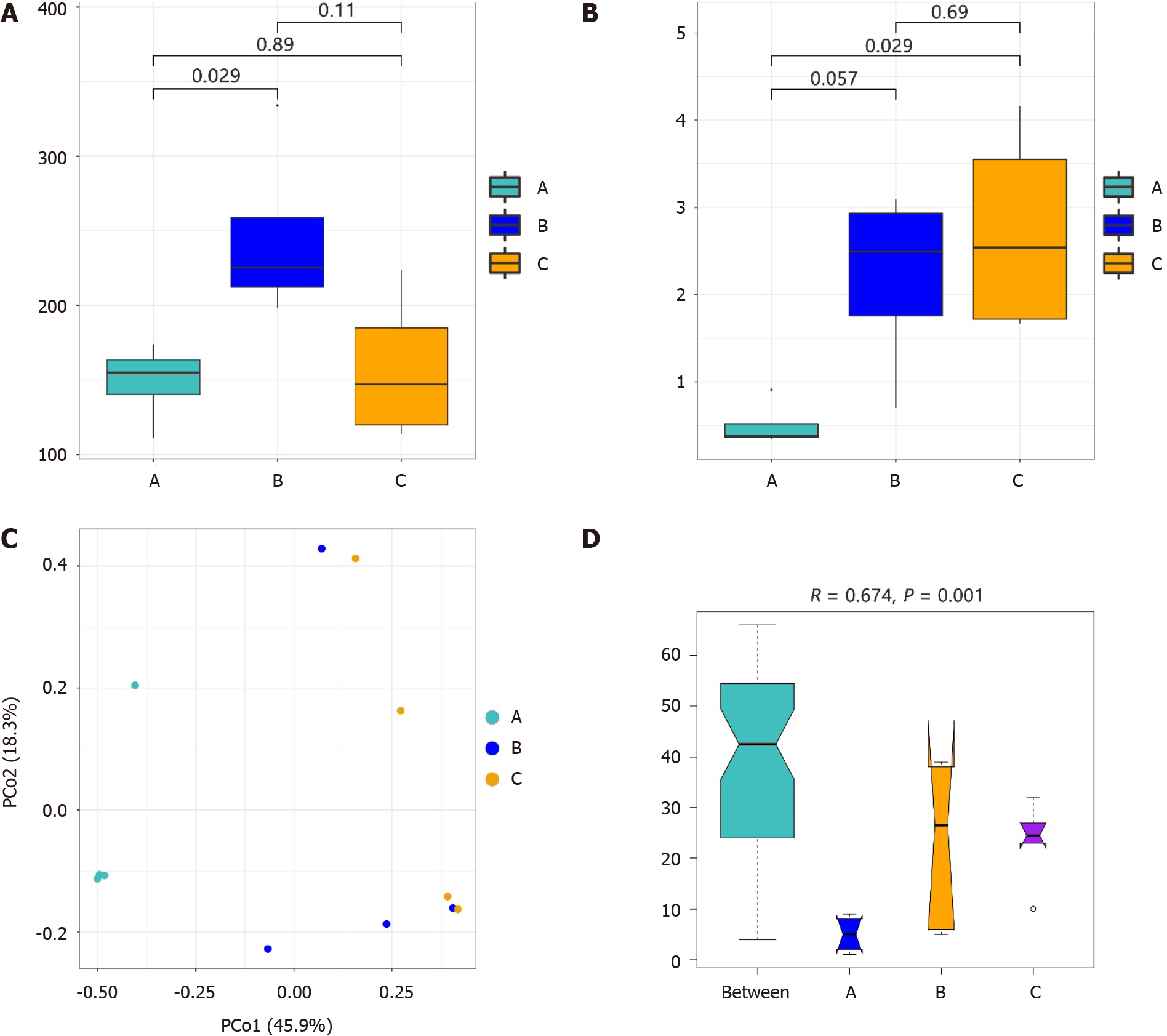
Figure 1 Alpha diversity and beta diversity of patients with Helicobacter pylori-positive gastric ulcer or Helicobacter pylori-positive duodenal ulcer and healthy individuals.
A: Chao1 index; B: Shannon index; C: Principal co-ordinates analysis; D: Analysis of similarities by Bray-Curtis distances among three groups. Group A: Patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-positive gastric ulcer; group B: Patients with H. pylori-positive duodenal ulcer; group C: H. pylori-negative healthy individuals.
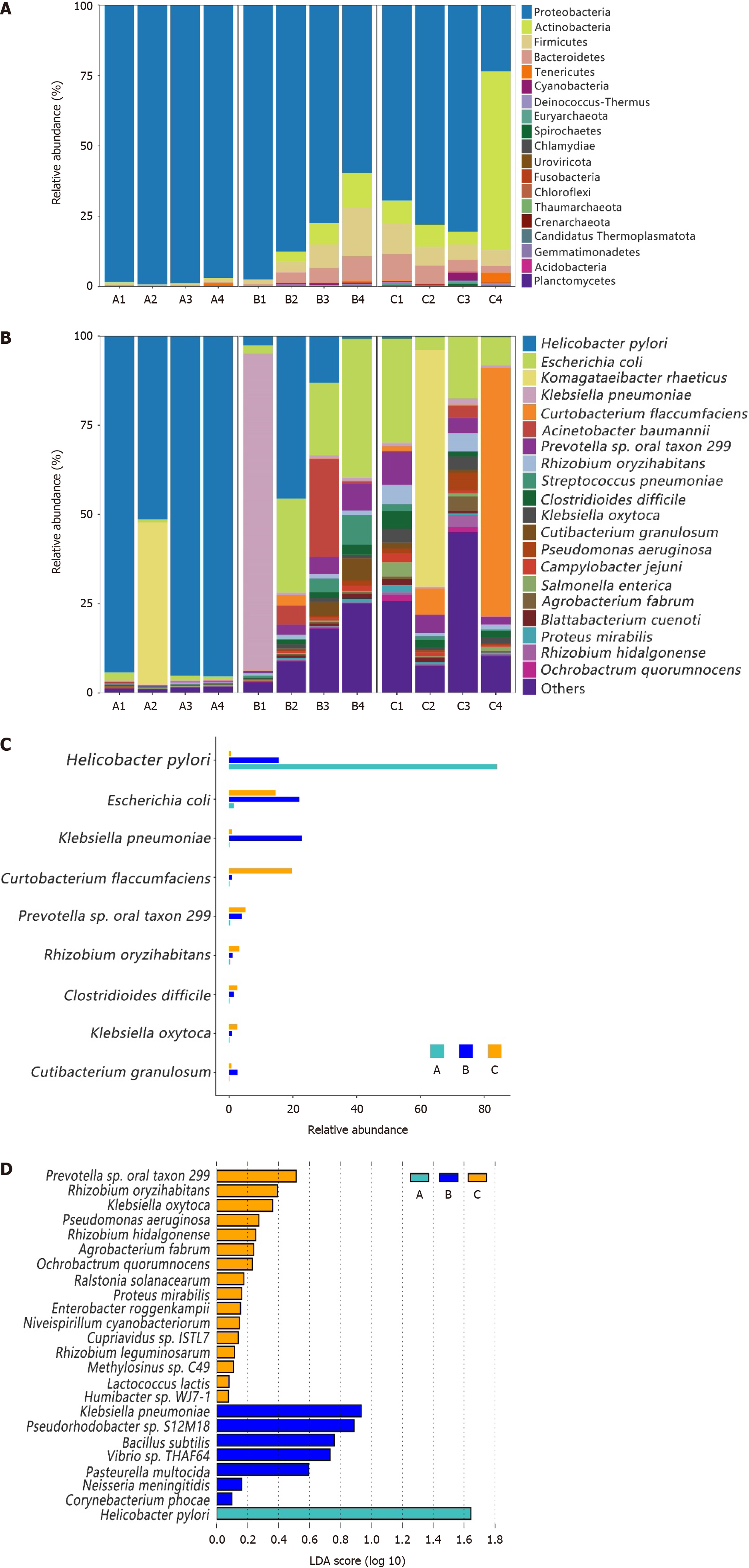
Figure 2 Microbial composition in patients with Helicobacter pylori-positive gastric ulcer or Helicobacter pylori-positive duodenal ulcer and healthy individuals.
A: Relative abundance of top 20 phyla; B: Relative abundance of top 20 species relative; C: Relative abundance of differential bacteria among groups; D: Specific taxa that most likely contributed to the differences among groups. Group A: Patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-positive gastric ulcer; group B: Patients with H. pylori-positive duodenal ulcer; group C: H. pylori-negative healthy individuals. LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
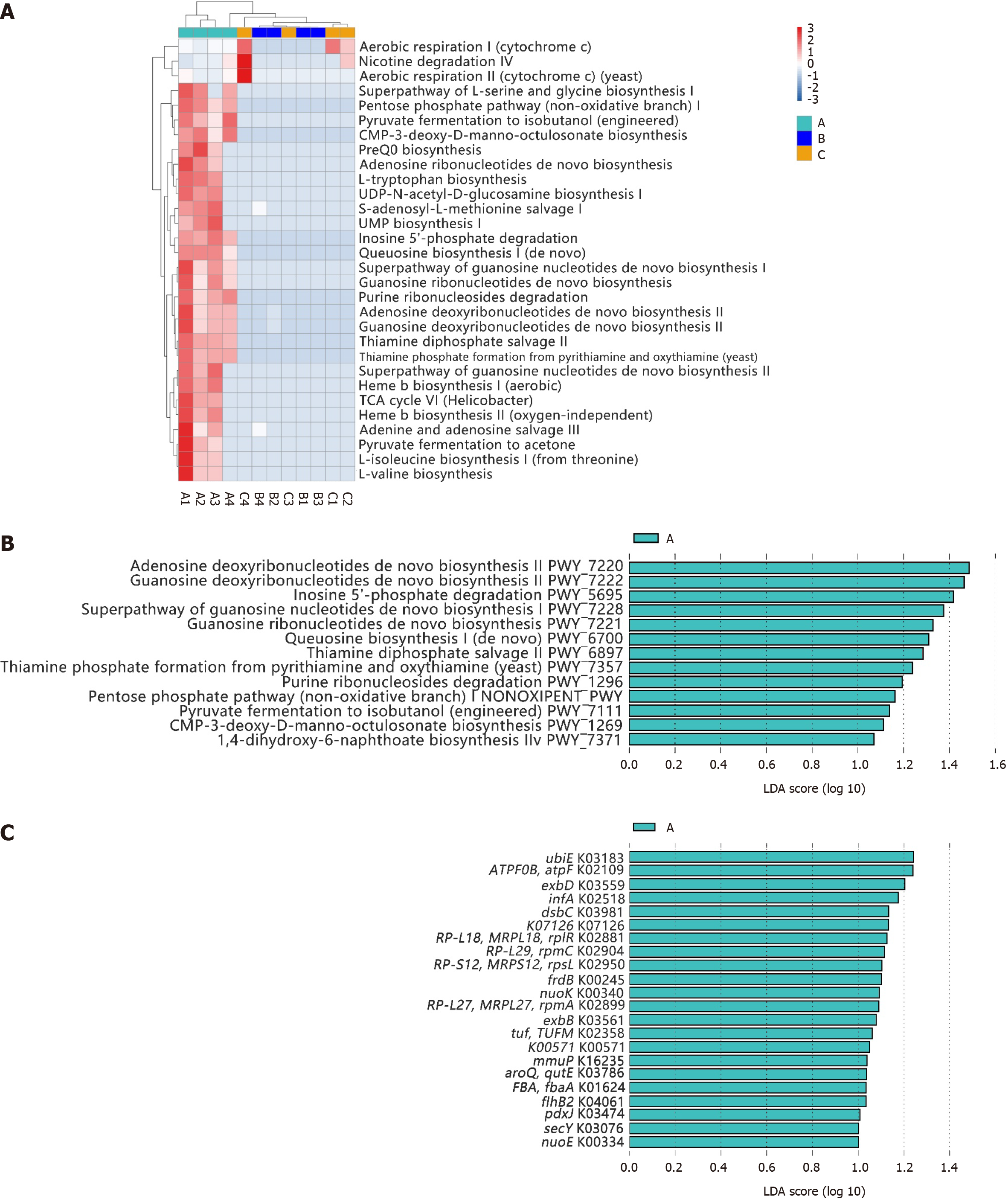
Figure 3 Mucosal function of patients with Helicobacter pylori-positive gastric ulcer or Helicobacter pylori-positive duodenal ulcer and healthy individuals.
A: Clustering heat map of functions of three groups; B: Differential functions of patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-positive gastric ulcer (group A) by linear discriminant analysis effective size algorithm; C: Different functional genes of patients with H. pylori-positive gastric ulcer (group A) by linear discriminant analysis effective size algorithm. LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
- Citation: Jin LX, Fang YP, Xia CM, Cai TW, Li QQ, Wang YY, Yan HF, Chen X. Helicobacter pylori infection alters gastric microbiota structure and biological functions in patients with gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(24): 3076-3085
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i24/3076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3076