Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2024; 30(17): 2354-2368
Published online May 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i17.2354
Published online May 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i17.2354
Figure 1 Scheme of the minocyclines’ mechanism of action.
Amino acids and tRNAs are linked together by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to produce specific Aminoacyl-tRNAs. ribosomes on the ribosomal complex then read the code along the 5’-3’ direction of the mRNAs while linking various aminoacyl-tRNA-transported amino acids according to the instructions of the mRNA coding sequences for the process of protein synthesis. When minocycline enters into bacteria, it specifically binds to the A site of bacterial ribosomal 30S subunit aminoacyl group, thus blocking the aminoacyl-tRNA binding at this site, preventing peptide chain elongation and bacterial protein synthesis, and exerting bactericidal effects. AA: Amino acids.
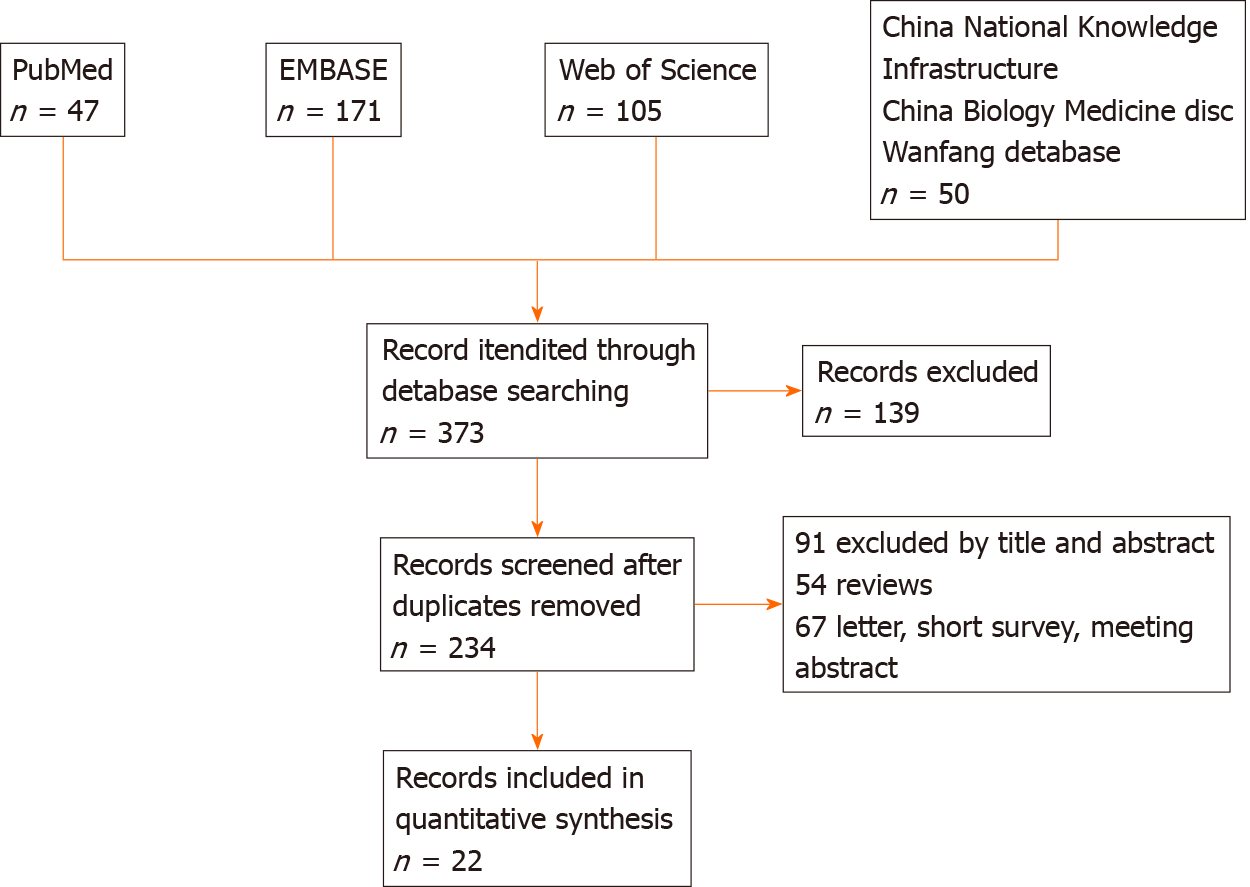
Figure 2 Literature identification process.
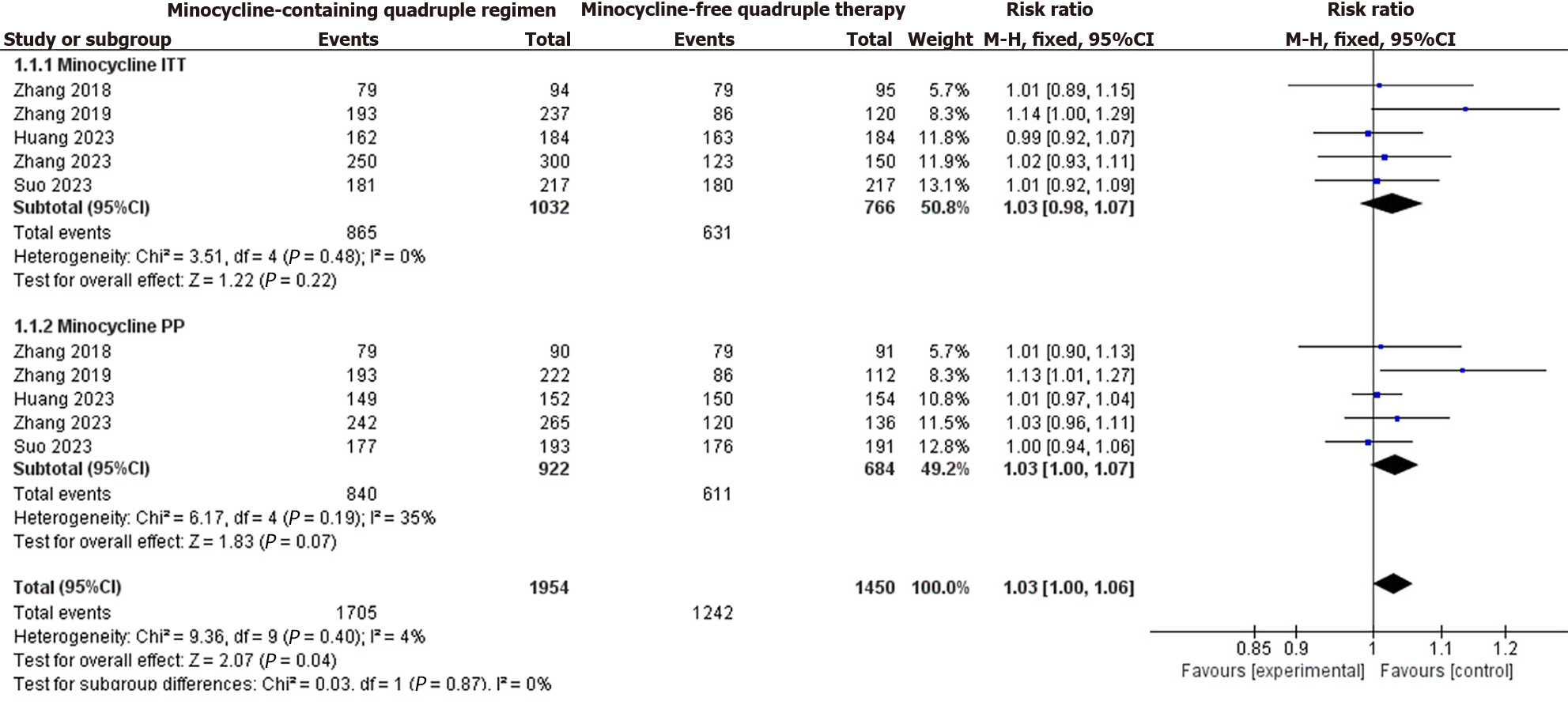
Figure 3 Forest plots comparing eradication rates for intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses of quadruple regimens with and without minocycline.
CI: Confidence interval.
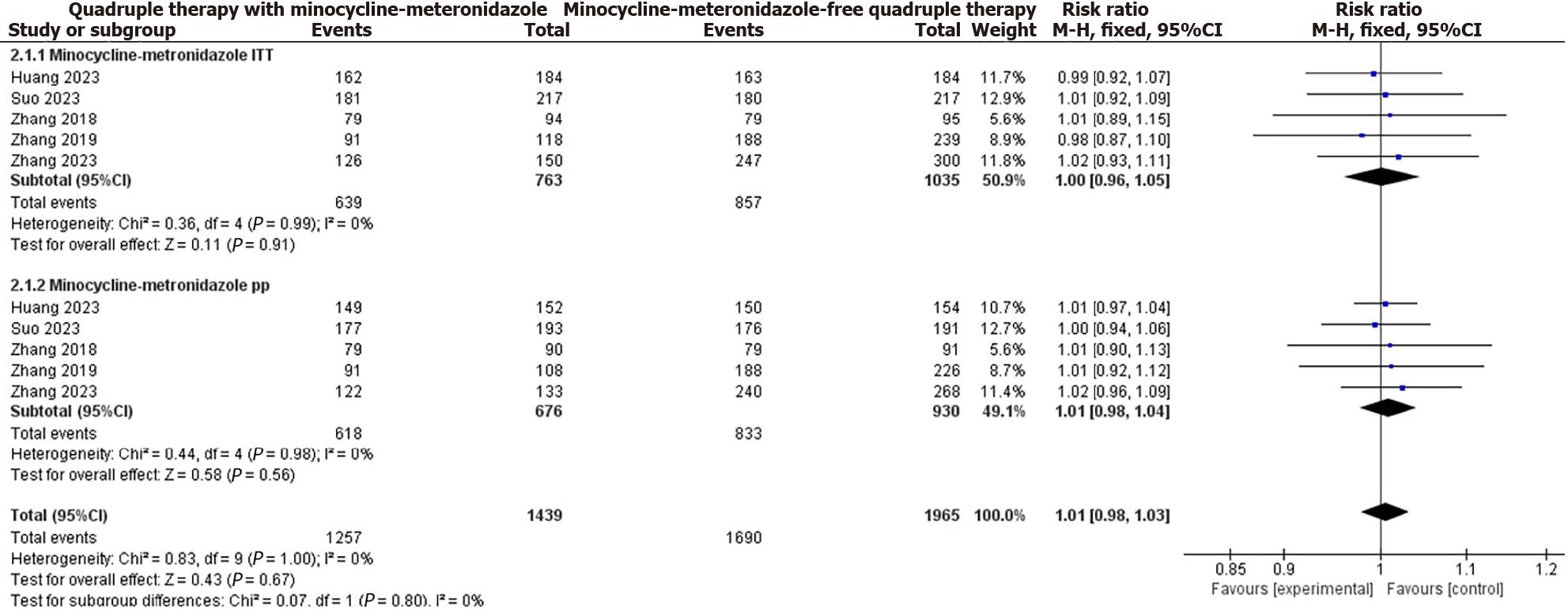
Figure 4 Forest plots comparing eradication rates for intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses of quadruple regimens with and without minocycline-metronidazole.
CI: Confidence interval.
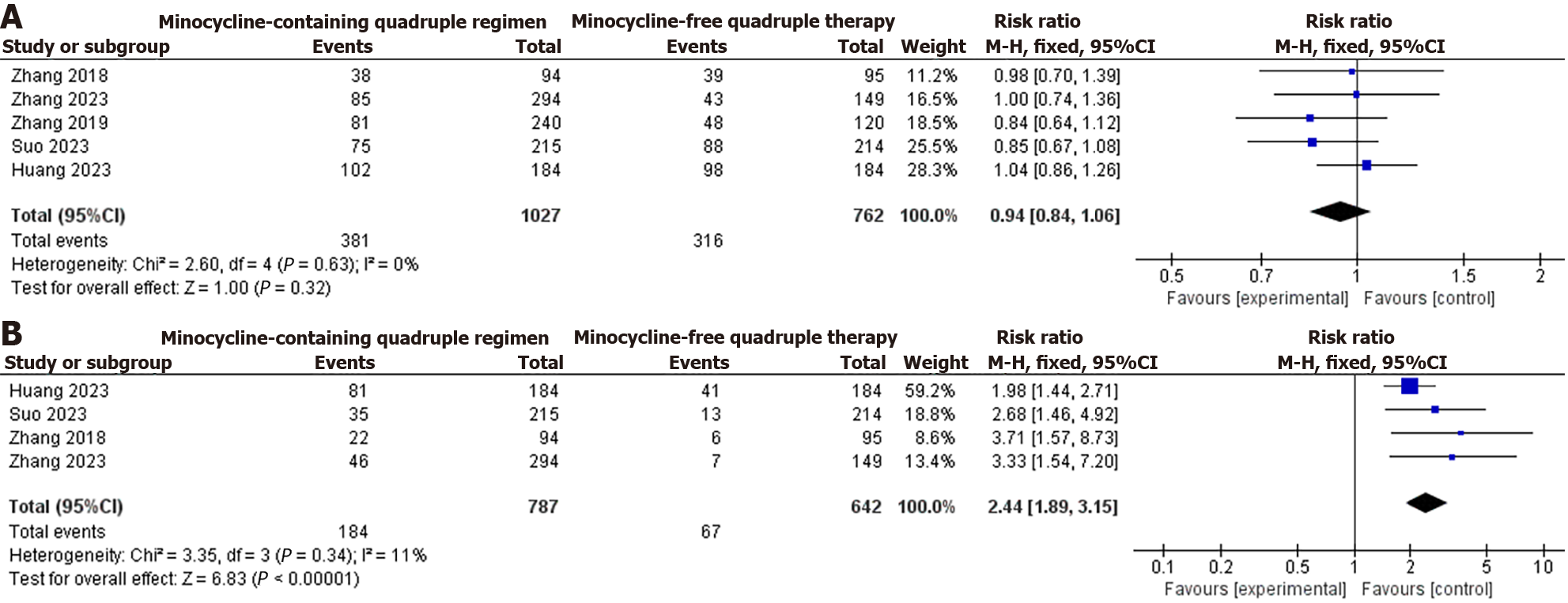
Figure 5 Comparison of the incidence of adverse reactions of quadruple therapy and dizziness in quadruple therapy with and without minocycline.
A: Comparison of the incidence of adverse reactions of quadruple therapy with and without minocycline; B: Comparison of the incidence of dizziness in quadruple therapy with and without minocycline. CI: Confidence interval.
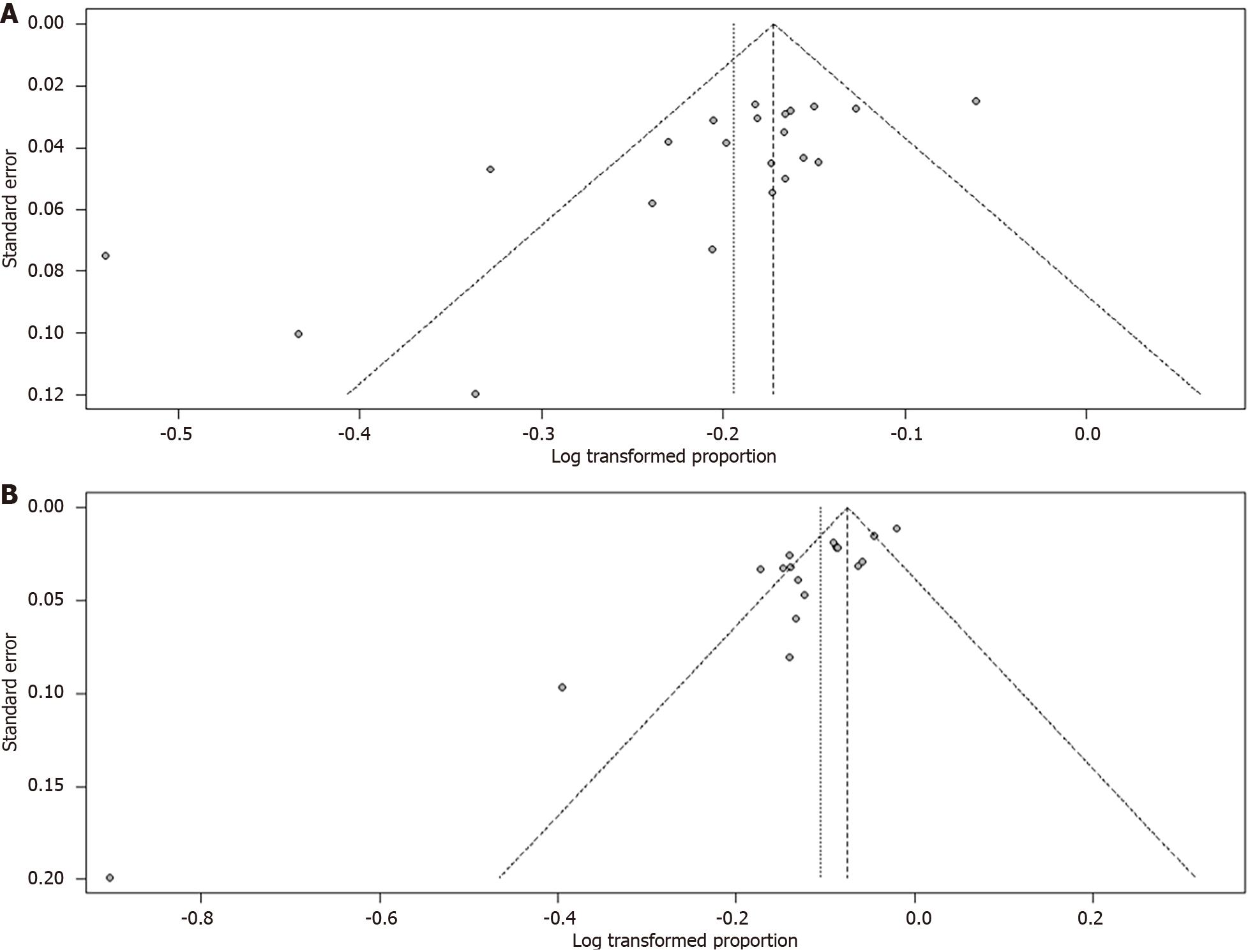
Figure 6 Funnel plots of all included studies through intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses.
A: Intention-to-treat analyses; B: Per-protocol analyses.
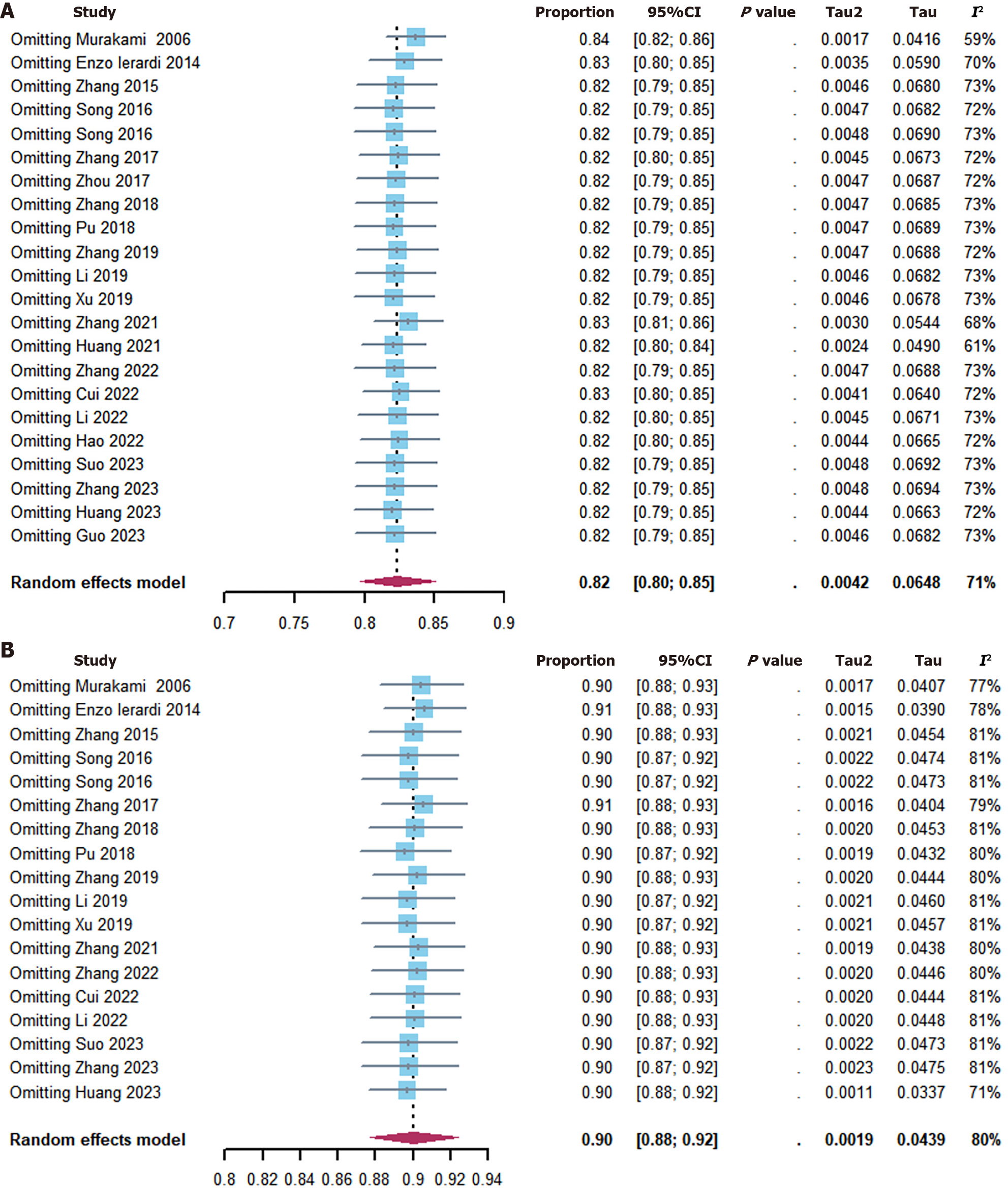
Figure 7 Sensitivity analysis of all included studies by sequentially removing each study with intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses.
A: Intention-to-treat analyses; B: Per-protocol analyses. CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Zhou K, Li CL, Zhang H, Suo BJ, Zhang YX, Ren XL, Wang YX, Mi CM, Ma LL, Zhou LY, Tian XL, Song ZQ. Minocycline in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(17): 2354-2368
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i17/2354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i17.2354