Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2024; 30(16): 2195-2208
Published online Apr 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2195
Published online Apr 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2195
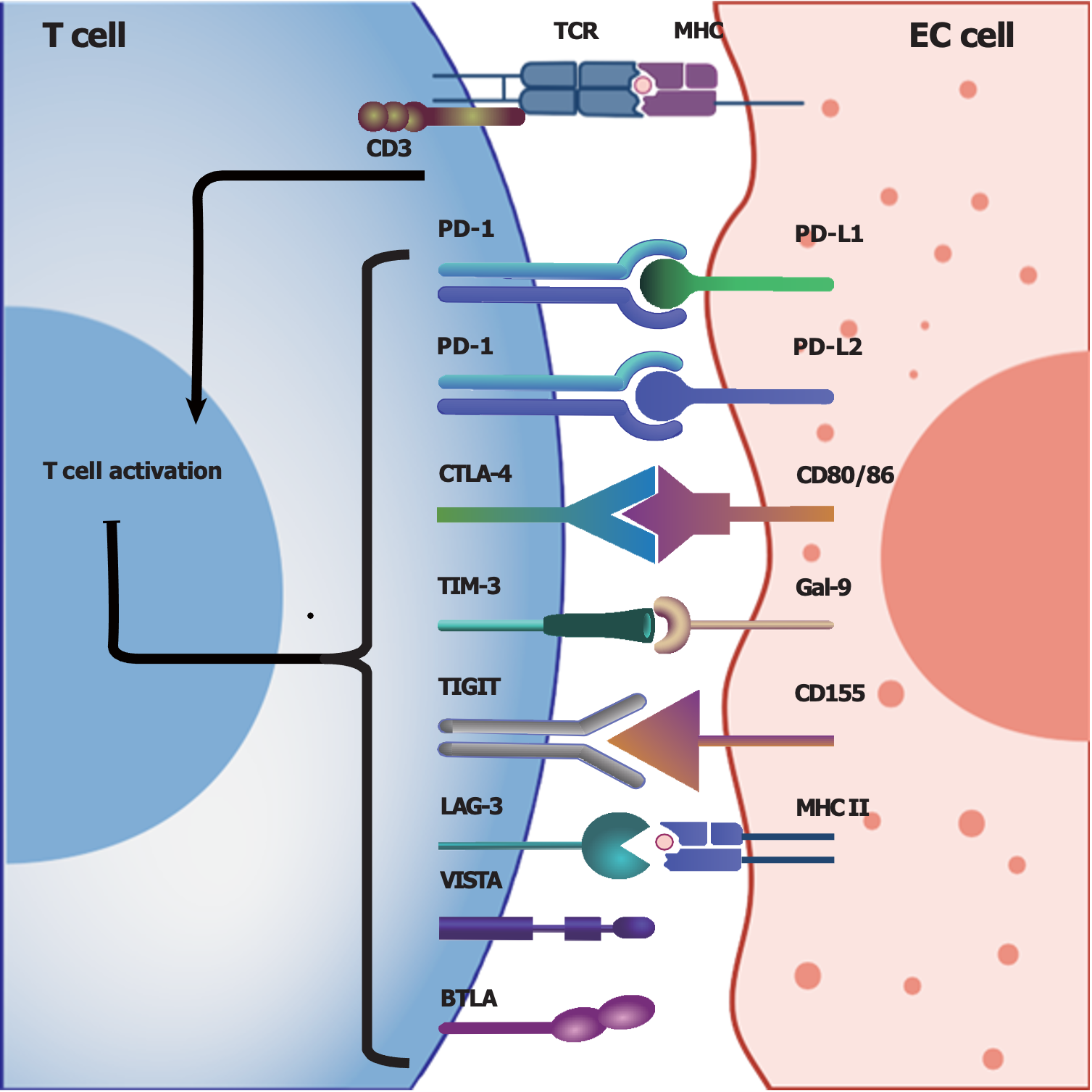
Figure 1 Summary of potentially involved immune checkpoints in esophageal cancer.
T cells can be activated by interacting with major histocompatibility complexes expressed on esophageal cancer (EC) cells, and the presence and interaction of immune checkpoints with their ligands can suppress T-cell activation and function to achieve immunosuppression. Herein, we summarize the immune checkpoints and their ligands that are potentially involved in the tumor microenvironment of EC. Programmed cell death protein 1, cytolytic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (TIM-3), T-cell immunoglobulin and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif domain (TIGIT), lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3), V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation and B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator are expressed on T cells, while TIM-3, TIGIT and LAG-3 are also expressed on natural killer cells. EC: Esophageal cancer; TCR: T cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; CD: Cluster of differentiation; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; PD-L2: Programmed cell death ligand 2; CTLA-4: Cytolytic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; Gal-9: Galectin-9; TIGIT: T-cell immunoglobulin and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif domain; LAG-3: Lymphocyte activation gene 3; VISTA: V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation; BTLA: B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator.
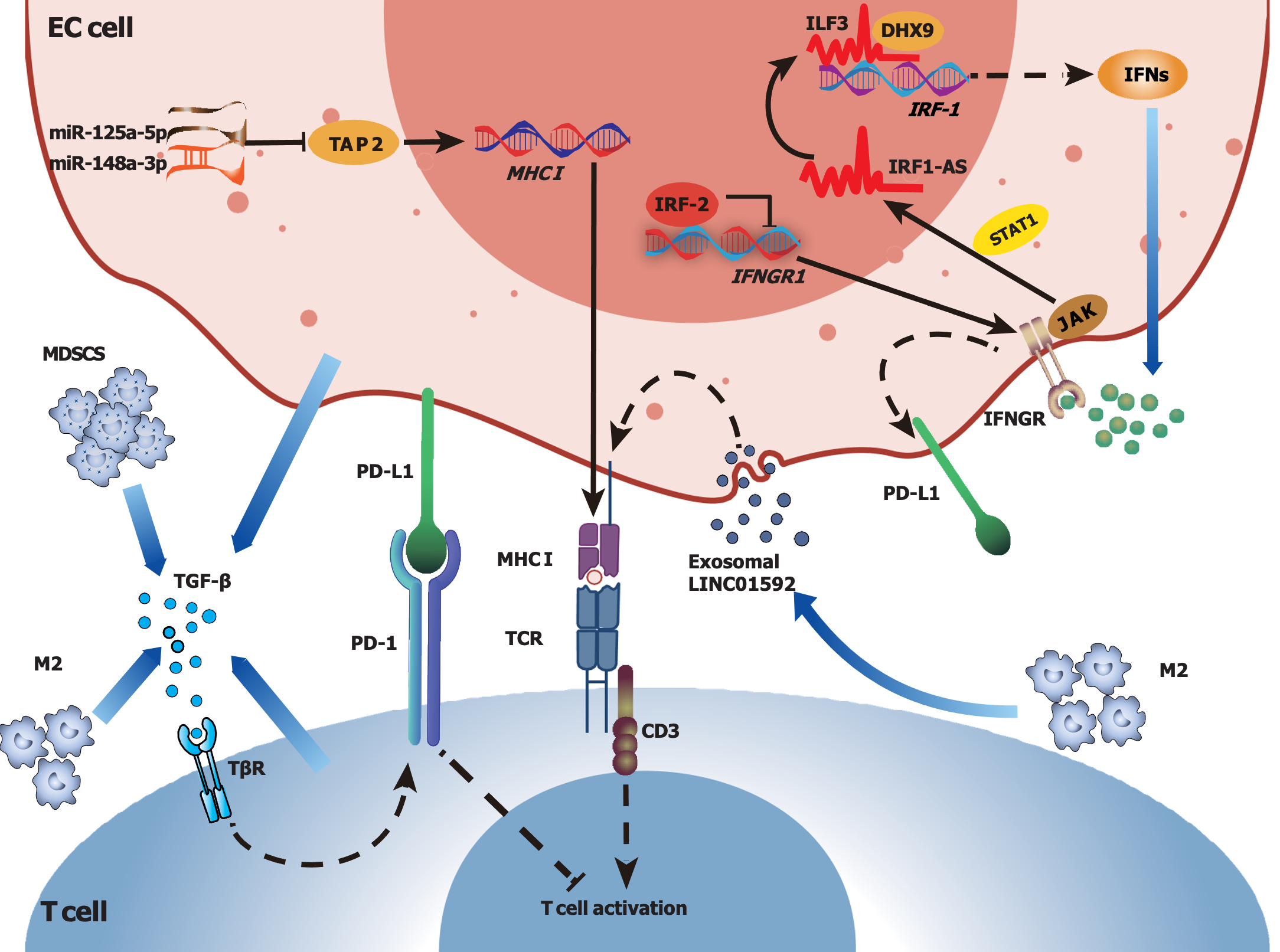
Figure 2 Potential mechanisms of tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment formation in esophageal cancer: Major histo-compatibility complex downregulation and immunosuppressive factors.
In esophageal cancer (EC) cells, miR-125a-5p and miR-148a-3p may downregulate ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 2 translation and major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-I expression, and exosomal LINC01592 released by M2 macrophages may also downregulate MHC-I expression. Transforming growth factor beta secreted by various cells can enhance programmed cell death protein 1 expression on T cells, and interferon (IFN)-γ can upregulate programmed cell death ligand 1 expression on EC cells, subsequently contributing to immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, EC cells may acquire immune resistance by downregulating the expression of IFN-γ receptors and suppressing the activation of Janus-activated kinase signaling. EC: Esophageal cancer; TCR: T-cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; M2: Type 2 macrophage/suppressive macrophage; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; TβR: Transforming growth factor beta receptor; IFN: Interferon; IFNGR: Interferon gamma receptor; IRF-1: Interferon regulatory factor 1; IRF-2: Interferon regulatory factor 2; IRF1-AS: Interferon regulatory factor 1 antisense RNA; ILF3: Interleukin enhancer binding factor 3; DHX9: DExH-box helicase 9; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; JAK: Janus-activated kinase; TAP2: ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 2.
- Citation: Zhang XJ, Yu Y, Zhao HP, Guo L, Dai K, Lv J. Mechanisms of tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment formation in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(16): 2195-2208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i16/2195.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2195