Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2024; 30(14): 2006-2017
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2006
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2006
Figure 1 Comparison of the regeneration indices at 3, 6 and 12 months among the right hepatectomy and trisegmentectomy, left hepatectomy, segmentectomy, and subsegmentectomy and nonanatomical hepatectomy groups.
A: Chronological changes in the regeneration index (RI) at 3, 6 and 12 months posthepatectomy, classified by hepatectomy type; B: Comparison of the RIs between patients who underwent hepatectomy at 3 months and 12 months. RH/Tri: Right hepatectomy and trisegmentectomy; LH: Left hepatectomy; Seg: Segmentectomy; Sub/Non: Subsegmentectomy and nonanatomical hepatectomy.
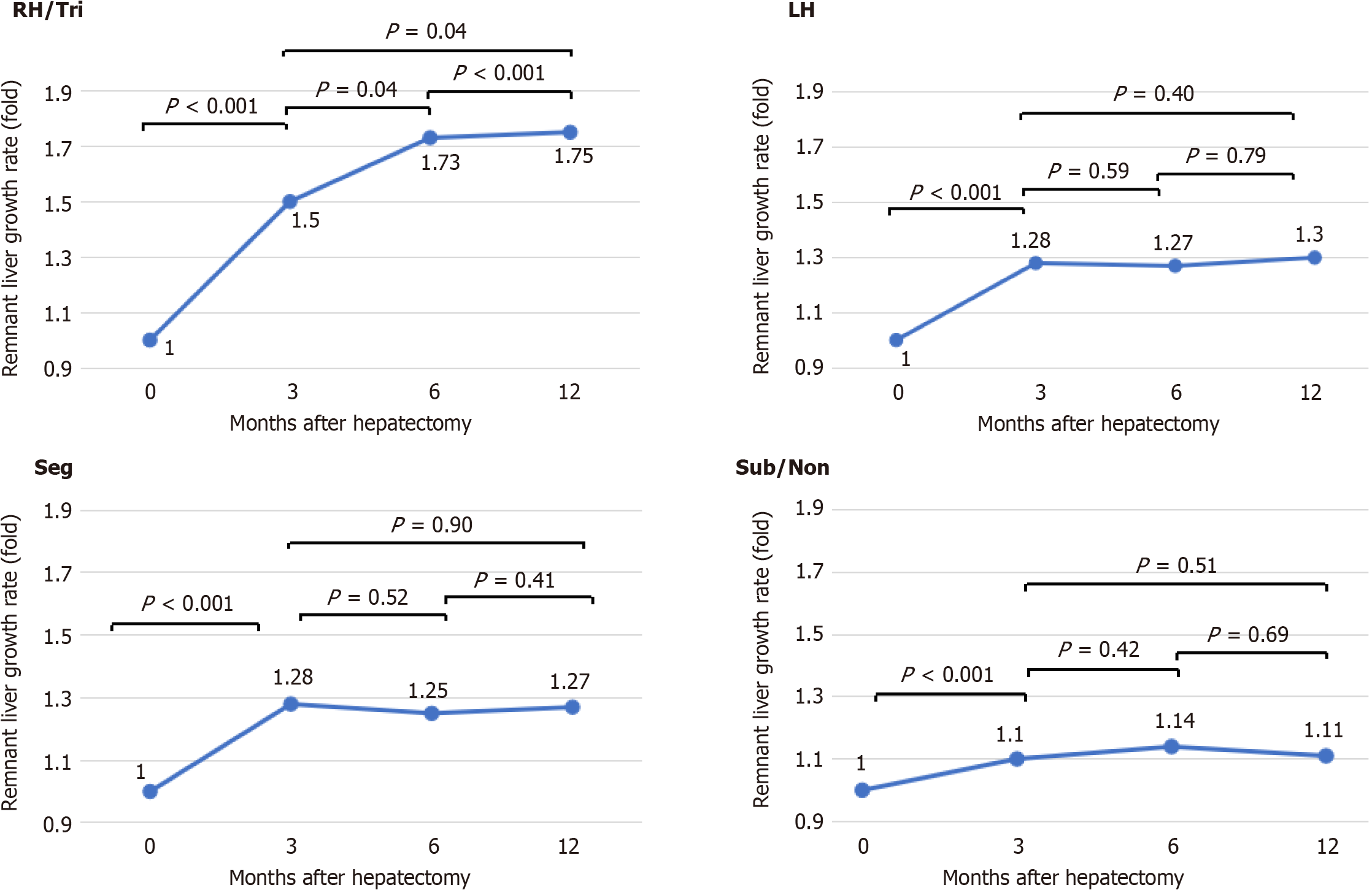
Figure 2 Comparison of the remnant liver growth rate at 3, 6 and 12 months among the right hepatectomy and trisegmentectomy, left hepatectomy, segmentectomy, and subsegmentectomy and nonanatomical hepatectomy groups.
The remnant liver growth rate plateaued at 3 months in the left hepatectomy, segmentectomy, and subsegmentectomy and nonanatomical hepatectomy groups, whereas it continued to increase until 12 months in the right hepatectomy and trisegmentectomy group. RH/Tri: Right hepatectomy and trisegmentectomy; LH: Left hepatectomy; Seg: Segmentectomy; Sub/Non: Subsegmentectomy and nonanatomical hepatectomy.
Figure 3 A heatmap for predicting the probability of volume restoration failure.
The gradient shows the risk level: Blue indicates a low risk of volume restoration failure (less than 10%), whereas red indicates a high risk of volume restoration failure (higher than 90%). ALBI: Albumin-bilirubin.
- Citation: Takahashi K, Gosho M, Miyazaki Y, Nakahashi H, Shimomura O, Furuya K, Doi M, Owada Y, Ogawa K, Ohara Y, Akashi Y, Enomoto T, Hashimoto S, Oda T. Preoperative albumin-bilirubin score and liver resection percentage determine postoperative liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(14): 2006-2017
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i14/2006.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2006