Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2024; 30(14): 1990-2005
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1990
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1990
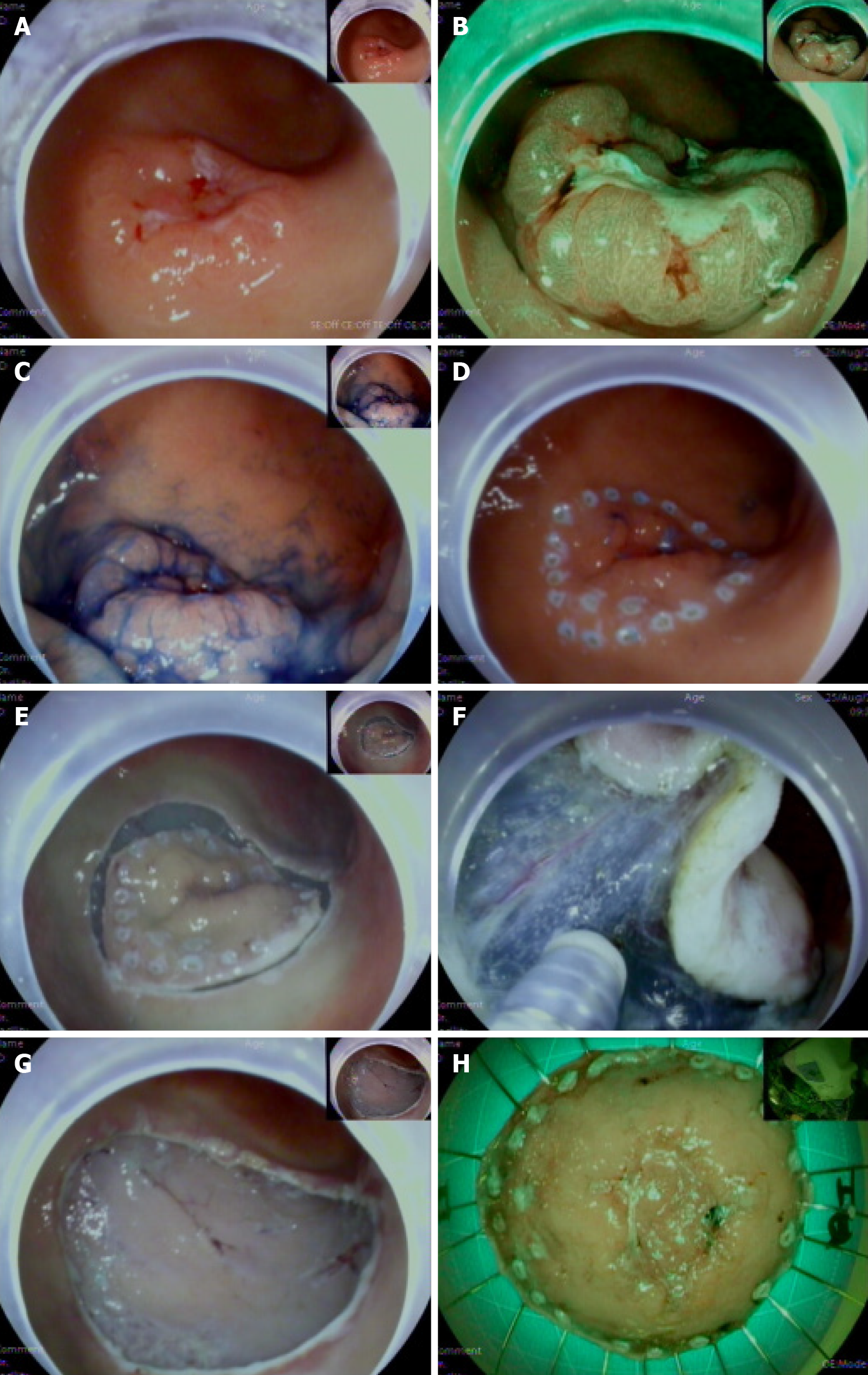
Figure 1 Endoscopic submucosal dissection process.
A: 0-IIa + 0-IIc lesion in the greater curvature of the antrum (white light), the lesion flattened after inflation; B: NBI + ME: DL (+), the lesion elevation was evident after inspiration; C: Indigo carmine staining; D: Peripherally marked lesion; E: The surrounding mucosa was incised; F: Submucosal dissection; G: The resected wound; H: Fixed specimen.
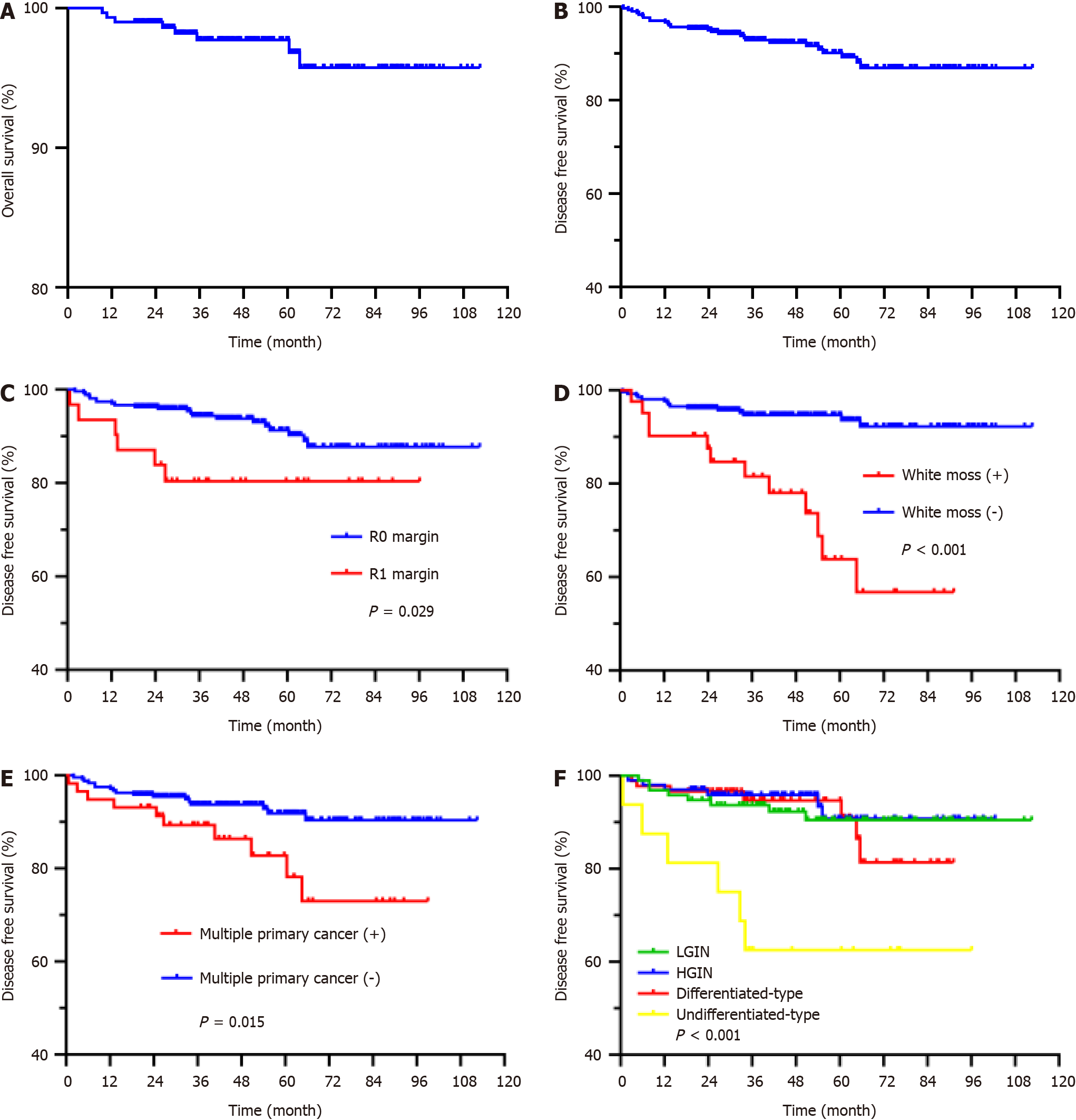
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier curves showed overall survival and disease-free survival during the follow-up period.
A: Overall survival; B: Disease-free survival (DFS); C: DFS based on complete resection; D: DFS based on white moss; E: DFS based on multiple primary cancer; F: DFS based on lesion differentiation. LGIN: Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia.
- Citation: Zhu HY, Wu J, Zhang YM, Li FL, Yang J, Qin B, Jiang J, Zhu N, Chen MY, Zou BC. Characteristics of early gastric tumors with different differentiation and predictors of long-term outcomes after endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(14): 1990-2005
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i14/1990.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1990