Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2024; 30(14): 1982-1989
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1982
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1982
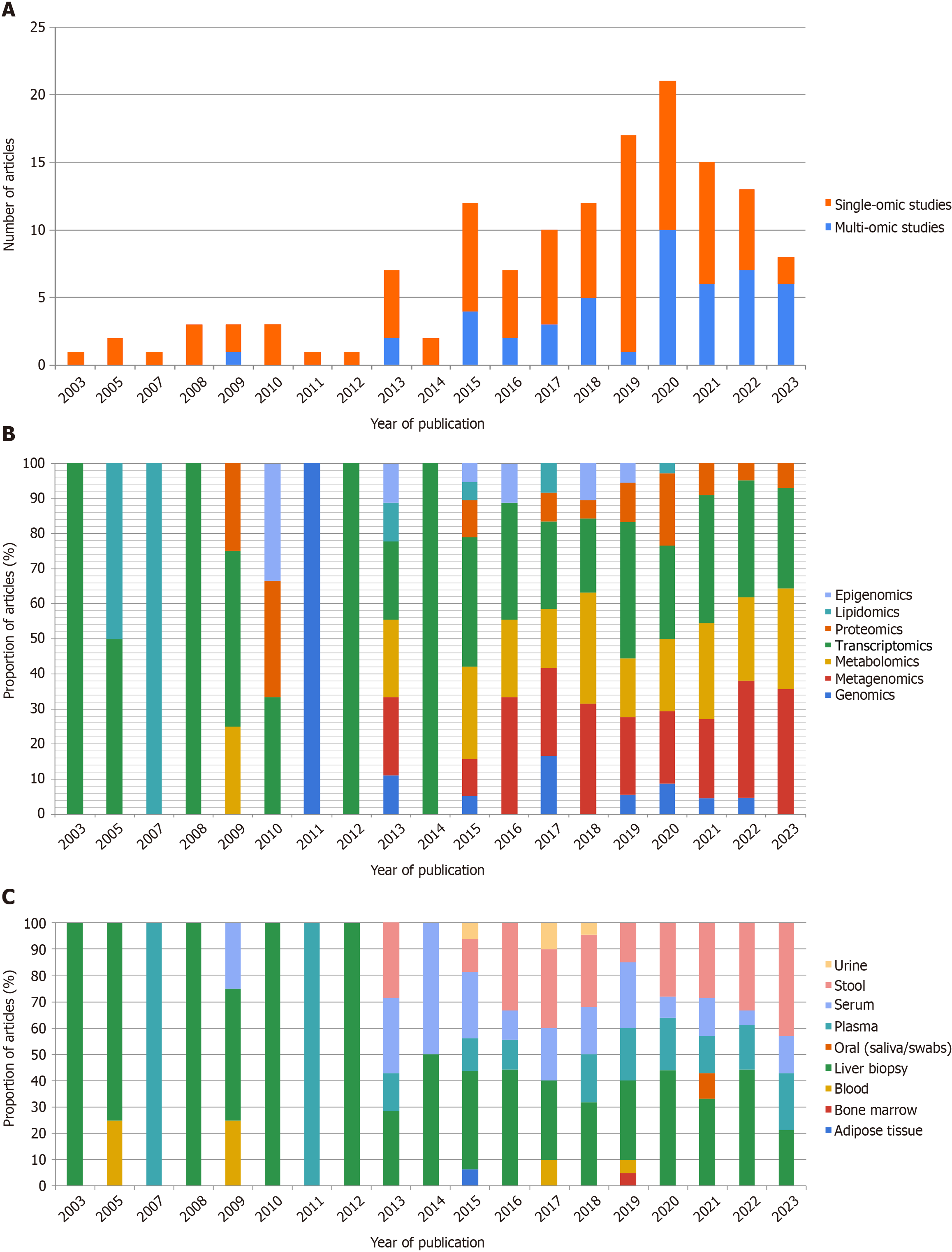
Figure 1 Characterization of omics literature based on a systematic screen of PubMed indexed research articles on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease biomarker (up to December 2023).
A: Plot representing the rapidly increasing number of omics articles indexed in PubMed indicating the use of single-omic (red) or multi-omic technologies (blue); the dip in 2023 can be attributed to indexing delay which was not accounted for in the current plot; B: Proportion of omics and combinations of omics (grouped by the characterized entities) commonly used in the analyzed articles; C: Distribution of sample types used in the analyzed articles. The details of articles included in the analysis are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Figure 2 A roadmap for the improvement of biomarker research in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Discovery of a biologically, and perhaps clinically, interesting omics-based biomarker; analytical, biological/clinical validation of the discovered biomarker; and finally, the evaluation for its clinical utility and use, and the evaluation for its economic benefits (cost-effectiveness or cost-utility studies).
A summary of the criteria for the development path of omics-based predictors proposed by the United States National Cancer Institute are also included in the roadmap. Modified from freepik.com.
- Citation: Trinks J, Mascardi MF, Gadano A, Marciano S. Omics-based biomarkers as useful tools in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease clinical practice: How far are we? World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(14): 1982-1989
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i14/1982.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1982