Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2024; 30(1): 50-69
Published online Jan 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i1.50
Published online Jan 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i1.50
Figure 1 A practical approach to evaluating response to new therapy using a treat-to-target approach.
1Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease II endorsed treatment targets: Consider treatment modification if not met. PRO2: Patient reported outcome 2; CRP: C-reactive protein; FCP: Faecal calprotectin; IUS: Intestinal ultrasound.
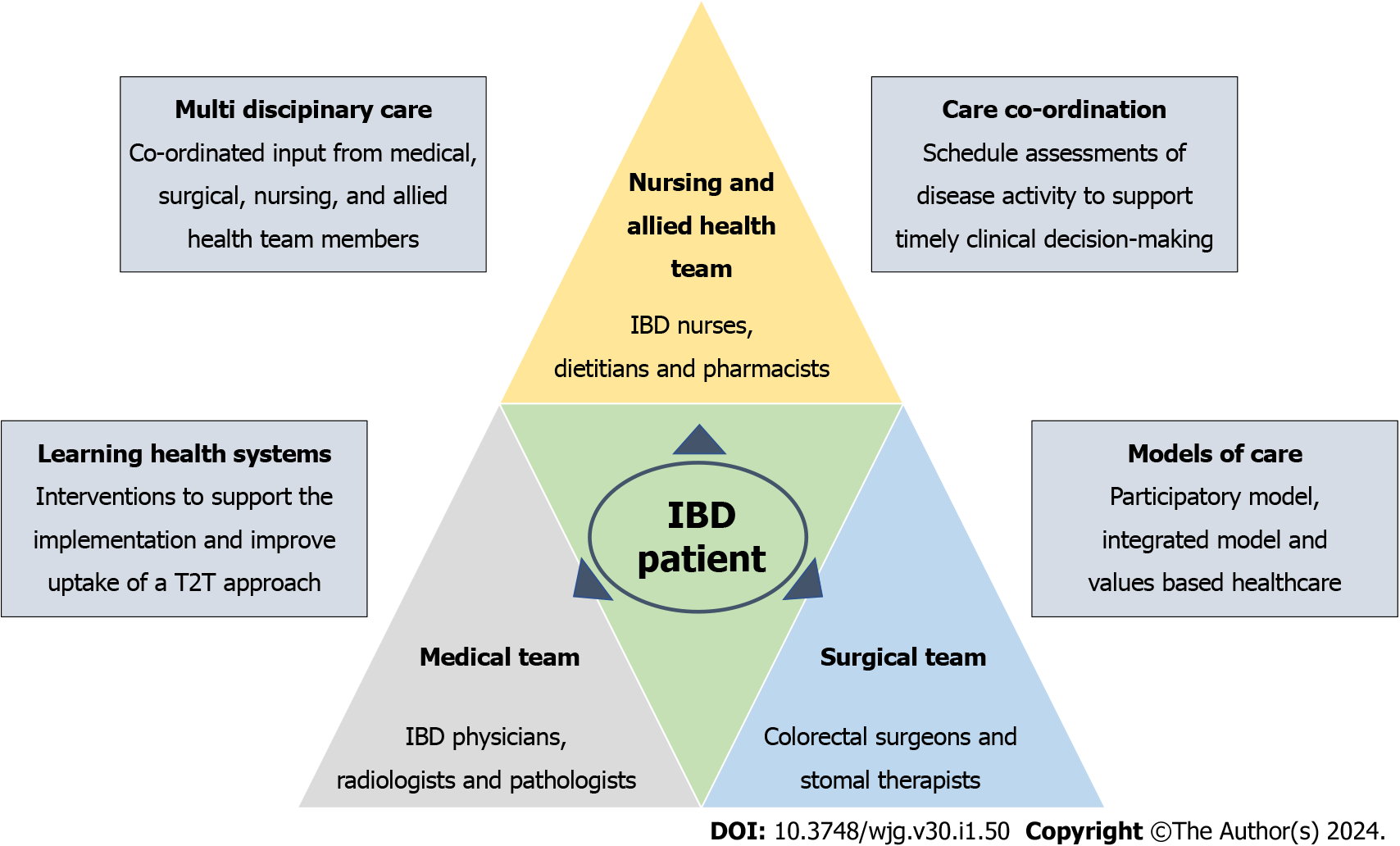
Figure 2 A treat-to-target approach requires multidisciplinary care.
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; T2T: Treat-to-target.
Figure 3 A practical approach to the clinical application of a treat-to-target strategy in clinical practice.
1Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease II endorsed treatment target: Consider changing therapy if not met. 2Transmural healing is an adjuvant to endoscopic remission. HBI: Harvey Bradshaw Index; PROM: Patient reported outcome measure; PRO2: Patient reported outcome 2; QoL: Quality of life; AP: Abdominal pain; SF: Stool frequency; CRP: C-reactive protein; ULN: Upper limit of normal; FCP: Faecal calprotectin; SES-CD: Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease; CDEIS: Crohn's Disease Endoscopic Index of Severity; IUS: Intestinal ultrasound; MRE: Magnetic resonance enterography.
- Citation: Srinivasan AR. Treat to target in Crohn’s disease: A practical guide for clinicians. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(1): 50-69
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i1/50.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i1.50