Copyright
©The Author(s) 1997.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 1997; 3(2): 72-74
Published online Jun 15, 1997. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v3.i2.72
Published online Jun 15, 1997. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v3.i2.72
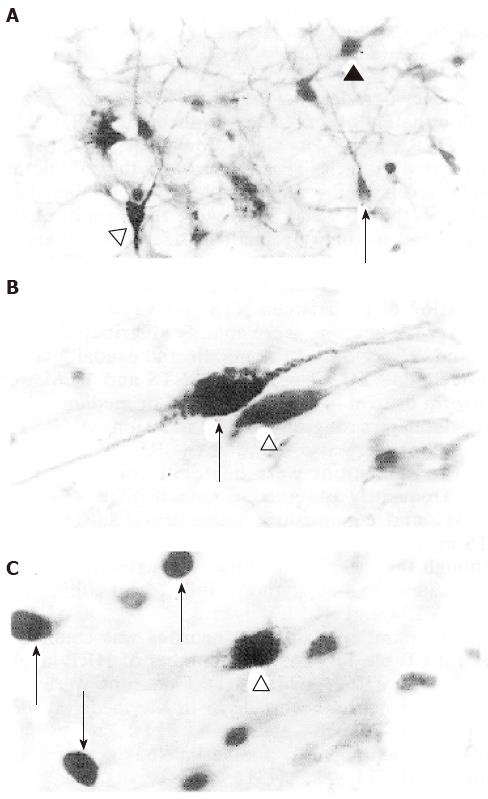
Figure 1 A: Horseradish peroxidase labeled neuron (open triangle), Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive neuron (arrow) and Fos-like immunoreactive/Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive double-labeled neuron (black triangle) in the ventrolateral medulla and reticular formation of medulla, × 200; B: Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive neuron (open triangle) and Horseradish peroxidase/Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive double-labeled neuron (arrow in the nucleus tractus solitarii of medulla, × 400; C: Fos-like immunoreactive neuron (arrows) and Fos-like immunoreactive/Horseradish peroxidase double-labeled neuron (open triangle) in the nucleus tractus solitarii of medulla, × 400.
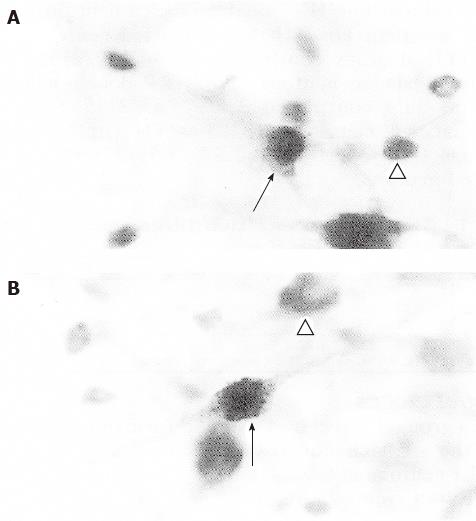
Figure 2 A: Fos-like immunoreactive neurons (open triangle) and Fos-like immunoreactive/Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive double-labeled neuron (arrow) in the nucleus tractus solitarii of medulla; B: Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive (open triangle) and Fos-like immunoreactive/Horseradish peroxidase/Tyrosin hydroxylase-like immunoreactive triple-labeled neuron (arrow) in the nucleus tractus solitarii of medulla, × 400.
- Citation: Dong YX, Xiong KH, Rao ZR, Shi JW. Fos expression in catecholaminergic medullary neurons induced by chemical stimulation of stomach projecting to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in rats. World J Gastroenterol 1997; 3(2): 72-74
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v3/i2/72.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v3.i2.72