Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2023; 29(8): 1359-1373
Published online Feb 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i8.1359
Published online Feb 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i8.1359
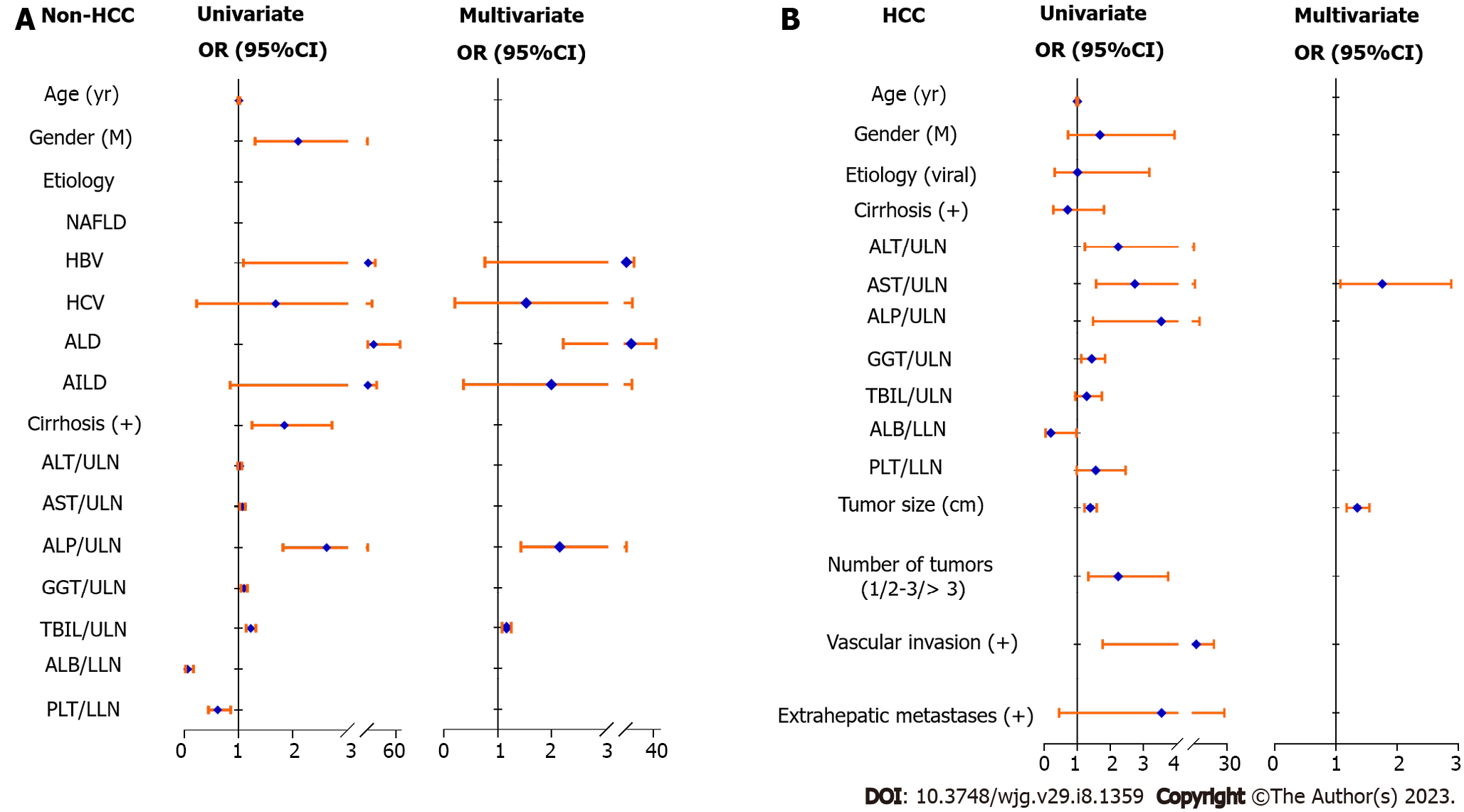
Figure 1 Forest plots of factors associated with abnormally elevated protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II by univariate and multivariate logistic analysis in patients with non-hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: In non- hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients; B: In HCC patients. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; ALD: Alcohol-related liver disease; AILD: Autoimmune liver disease; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ULN: Upper limit of normal; TBIL: Total bilirubin; PLT: Platelet; LLN: Lower limit of normal; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio.
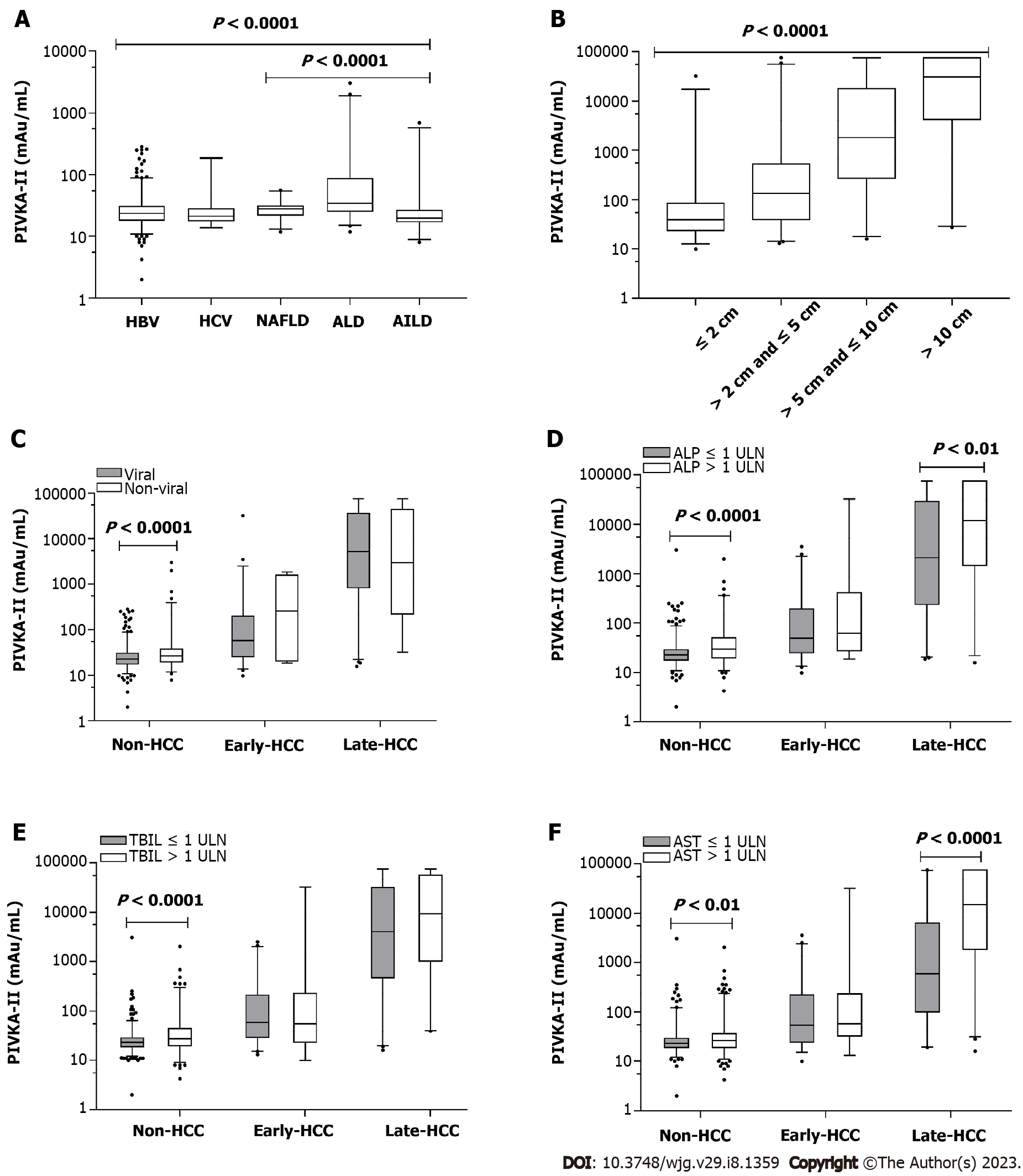
Figure 2 Distributions and comparisons of serum protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II in different subgroups.
A: Different etiologies of hepatitis B virus (HBV), HCV, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), autoimmune liver disease; B: Different tumor sizes of ≤ 2 cm (n = 60), > 2 cm and ≤ 5 cm (n = 88), > 5 cm and ≤ 10 cm (n = 65), > 10 cm (n = 54); C: Subgroups between viral and nonviral liver diseases; D: Subgroups between alkaline phosphatase (ALP) ≤ 1 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and ALP > 1 × ULN; E: Subgroups between total bilirubin (TBIL) ≤ 1 × ULN and TBIL > 1 × ULN; F: Subgroups between aspartate aminotransferase (AST) ≤ 1 × ULN and AST > 1 × ULN. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; ALD: Alcohol-related liver disease; AILD: Autoimmune liver disease; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ULN: Upper limit of normal; TBIL: Total bilirubin.
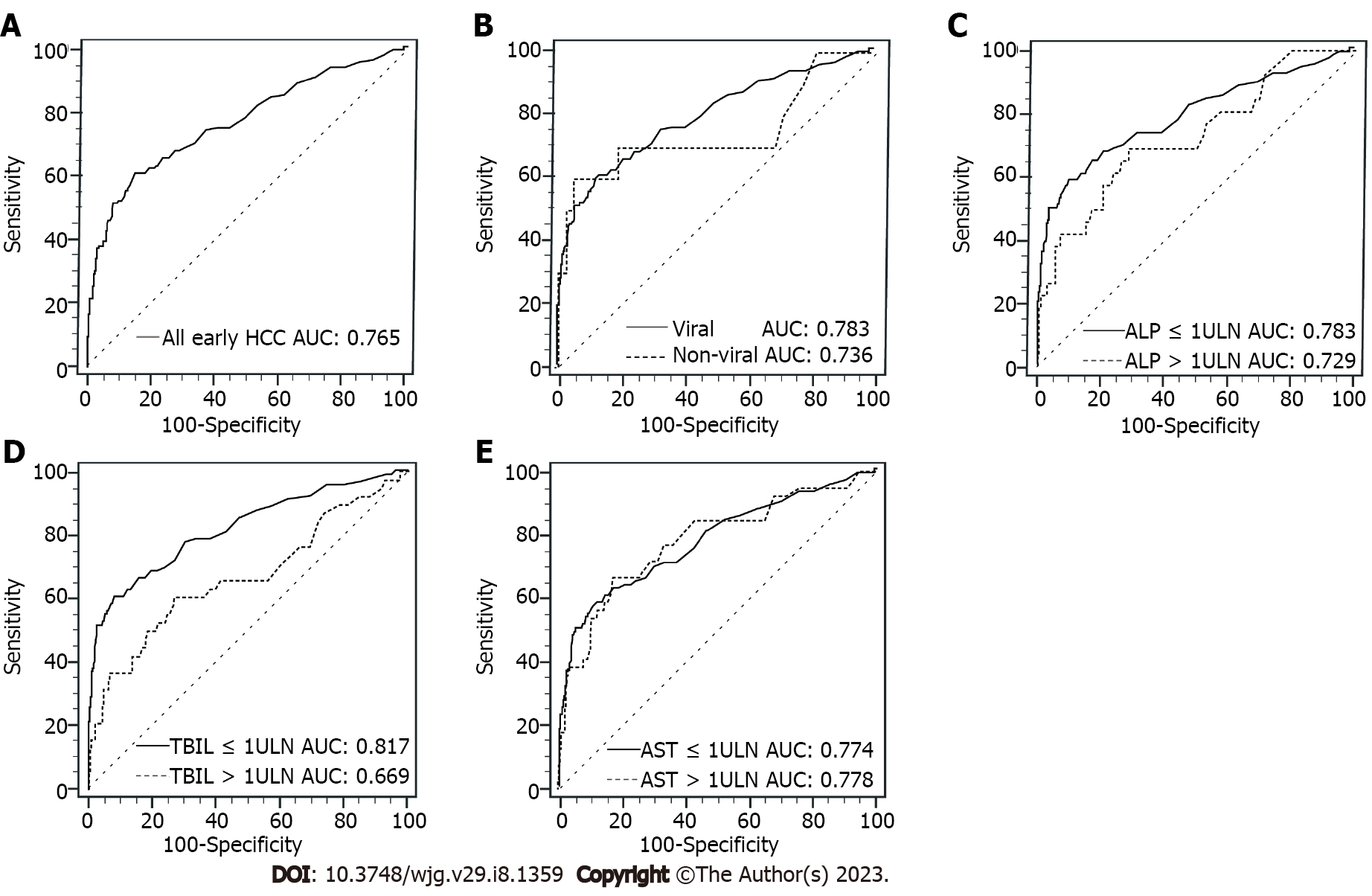
Figure 3 Comparisons of receiver operating characteristic curves of serum protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II for diagnosing early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in different subgroups.
A: For all early-stage patients; B: Between viral and nonviral subgroups; C: Between alkaline phosphatase ≤ 1 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and alkaline phosphatase > 1 × ULN subgroups; D: Between total bilirubin (TBIL) ≤ 1 × ULN and TBIL > 1 × ULN subgroups; E: Between aspartate aminotransferase (AST) ≤ 1 × ULN and AST > 1 × ULN subgroups. ULN: Upper limit of normal; TBIL: Total bilirubin; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase.
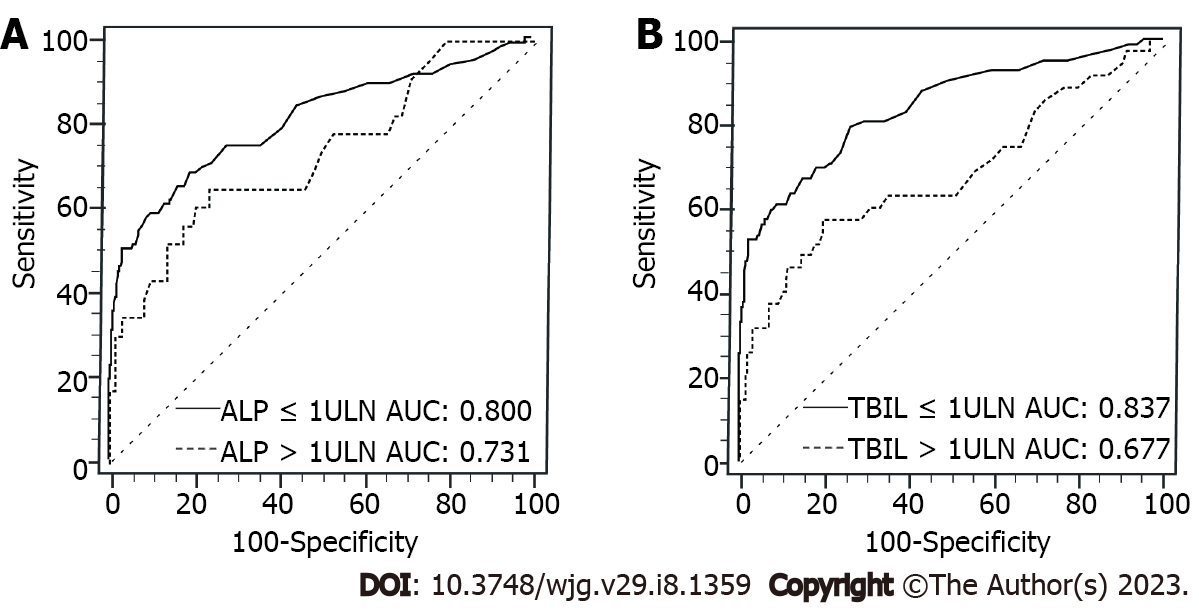
Figure 4 Comparisons of receiver operating characteristic curves of serum protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II for diagnosing early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in subgroups of alkaline phosphatase and total bilirubin for patients with viral etiology.
A: Between alkaline phosphatase (ALP) ≤ 1 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and ALP > 1 × ULN subgroups; B: Between total bilirubin (TBIL) ≤ 1 × ULN and TBIL > 1 × ULN subgroups. ULN: Upper limit of normal; TBIL: Total bilirubin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
- Citation: Qian XJ, Wen ZM, Huang XM, Feng HJ, Lin SS, Liu YN, Li SC, Zhang Y, Peng WG, Yang JR, Zheng ZY, Zhang L, Zhang DW, Lu FM, Liu LJ, Pan WD. Better performance of PIVKA-II for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease with normal total bilirubin. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(8): 1359-1373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i8/1359.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i8.1359