Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2023; 29(6): 1054-1075
Published online Feb 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1054
Published online Feb 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1054
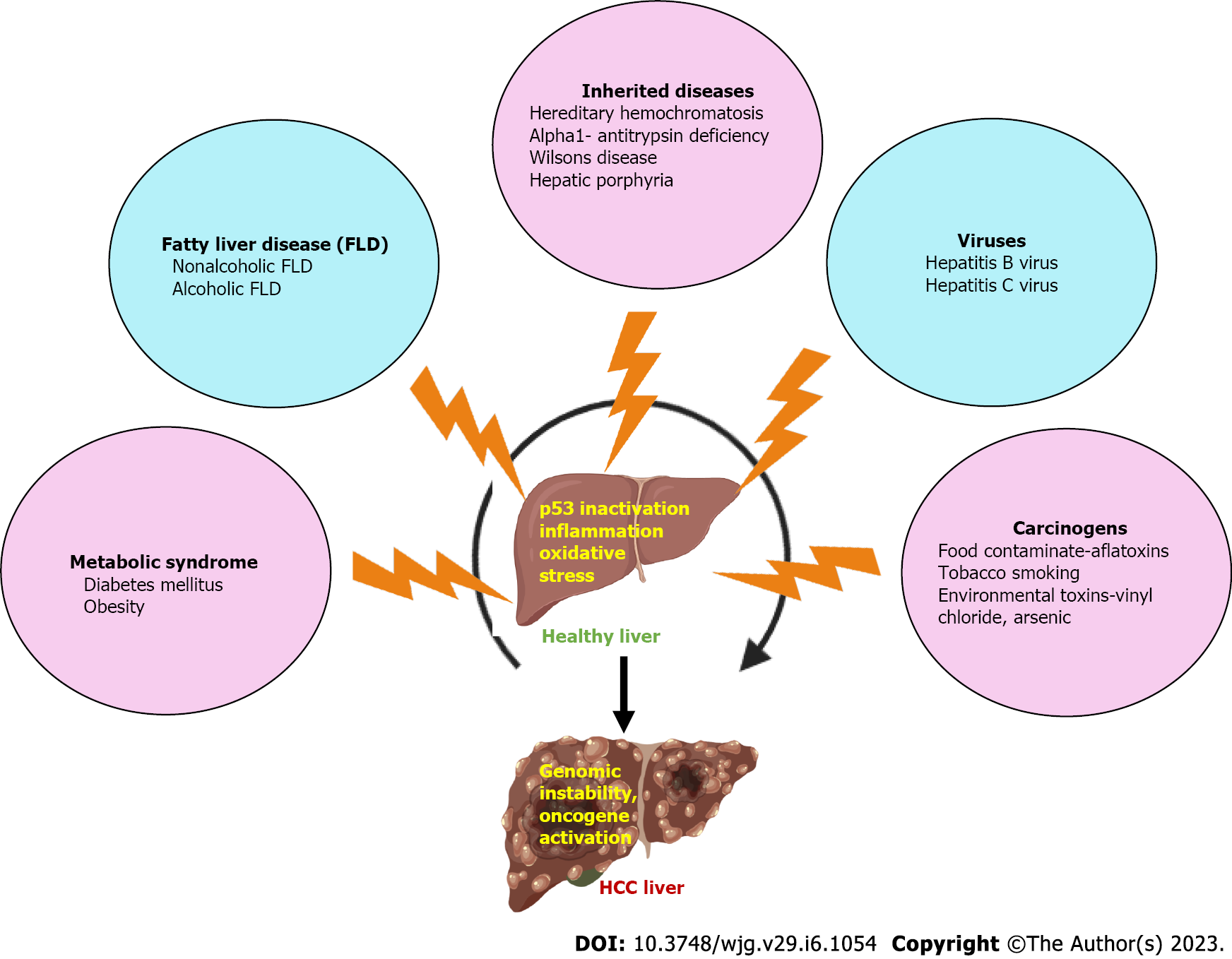
Figure 1 Etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma.
FLD: Fatty liver disease; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
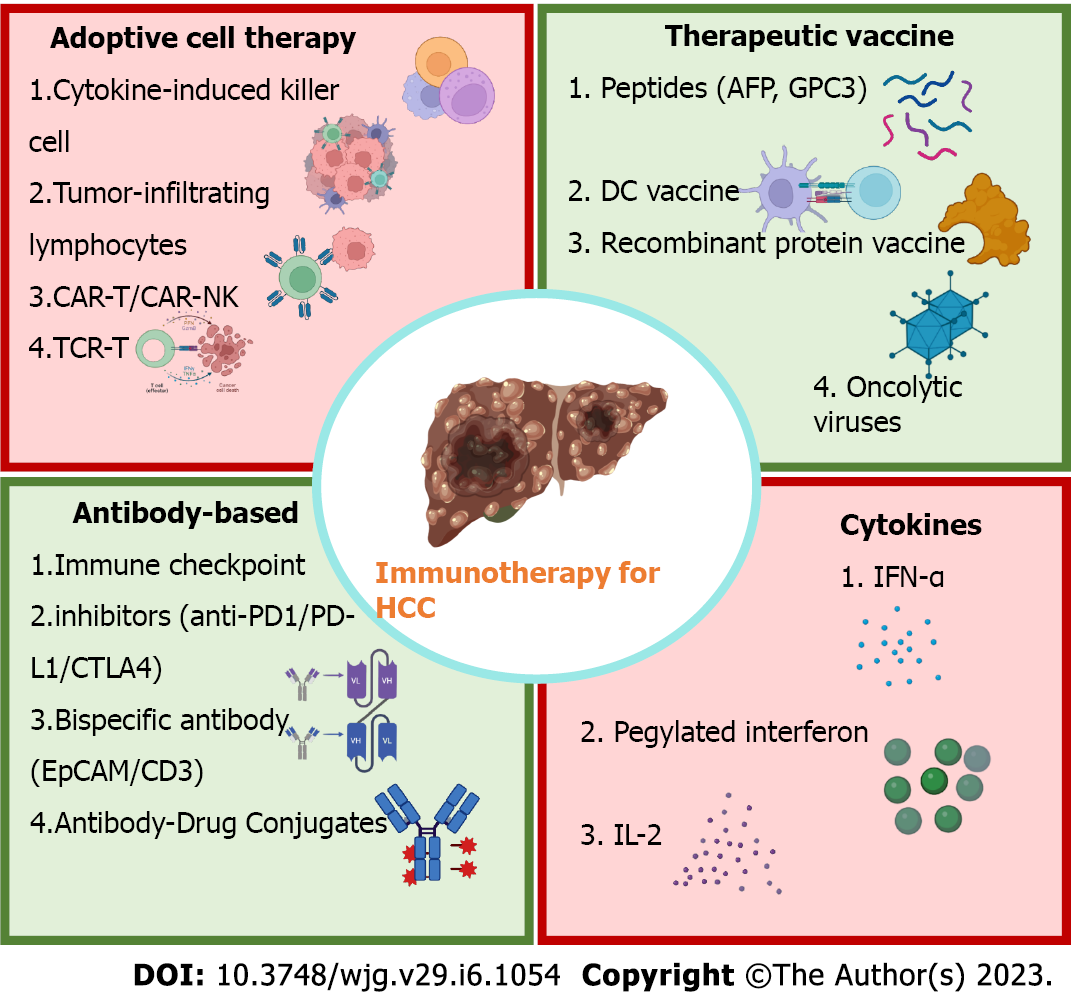
Figure 2 Current immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma.
AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptors engineered T cell; CTLA4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; IFN: Interferon-alpha; IL-2: Interleukin-2; NK: Natural killer; PD-1: Programmed cell death-1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death-ligand 1.
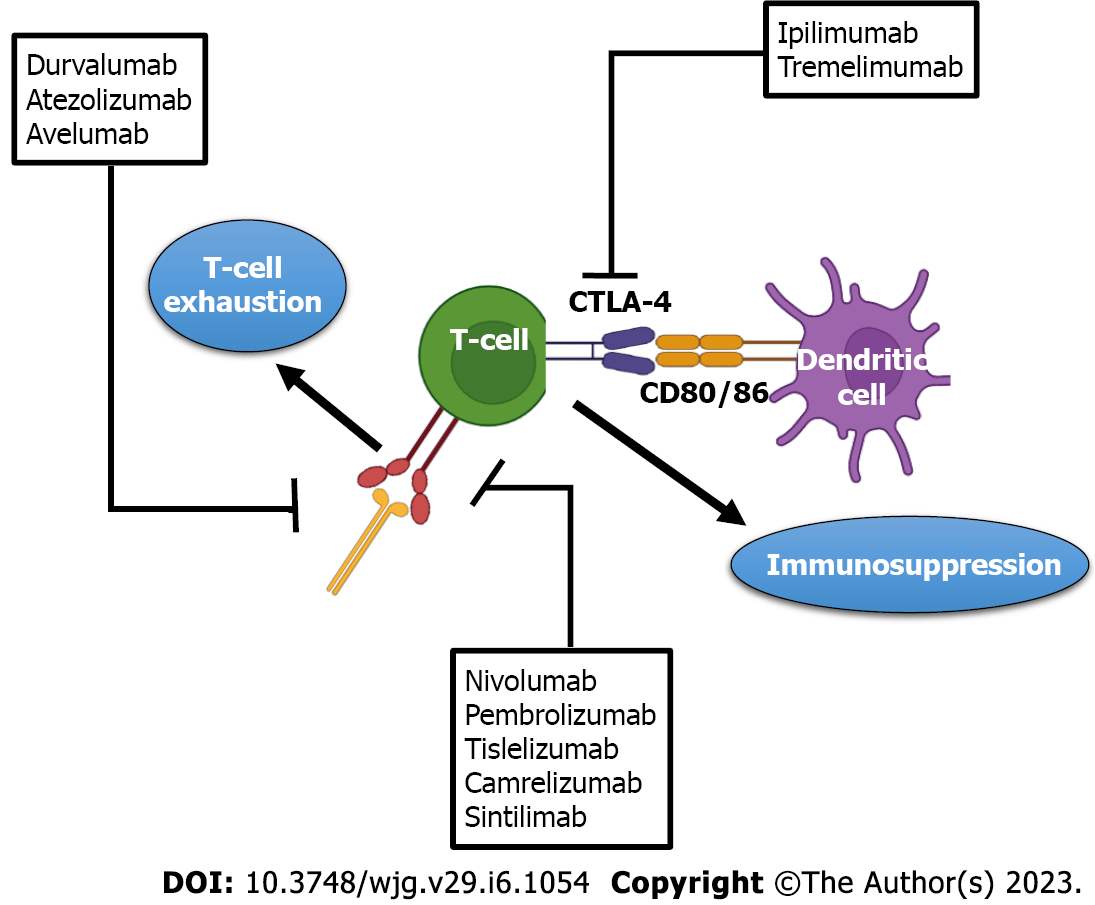
Figure 3 Immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma.
CTLA4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; PD-1: Programmed cell death-1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death-ligand 1.
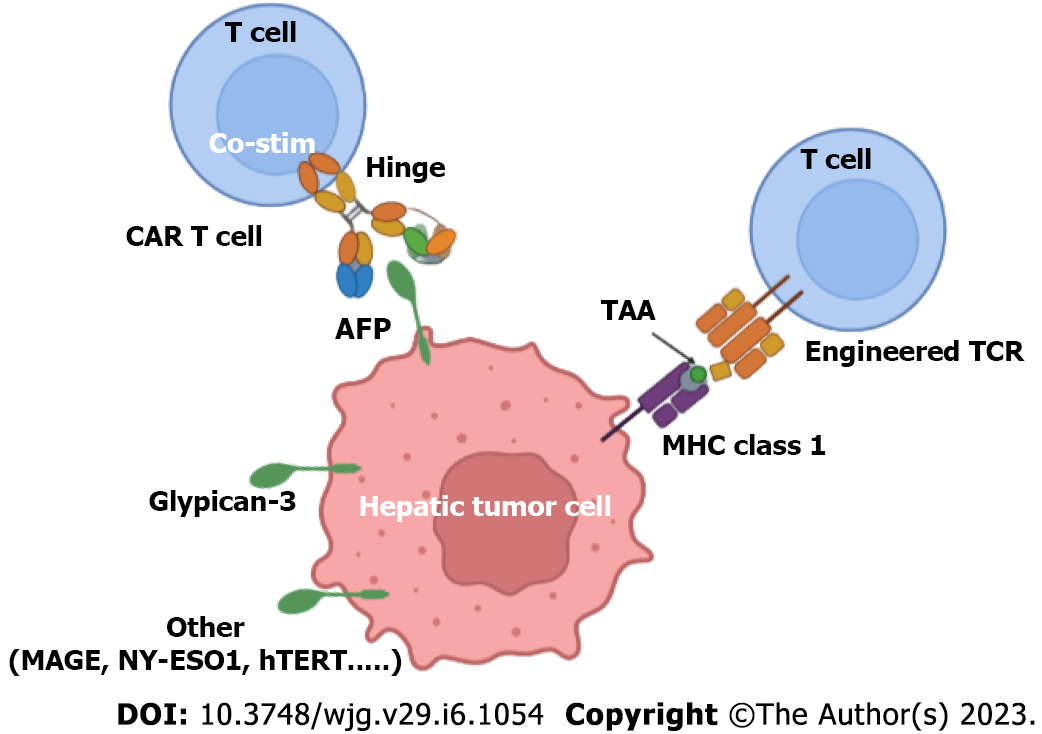
Figure 4 Schematic representation of T cell receptor engineered T cells and chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) engineered T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptors engineered T cell; MAGE: Melanoma-associated antigen; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; TAA: Tumor-associated antigens; TCR: T cell receptor.
- Citation: Mandlik DS, Mandlik SK, Choudhary HB. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(6): 1054-1075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i6/1054.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1054