Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2023; 29(47): 6148-6160
Published online Dec 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i47.6148
Published online Dec 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i47.6148
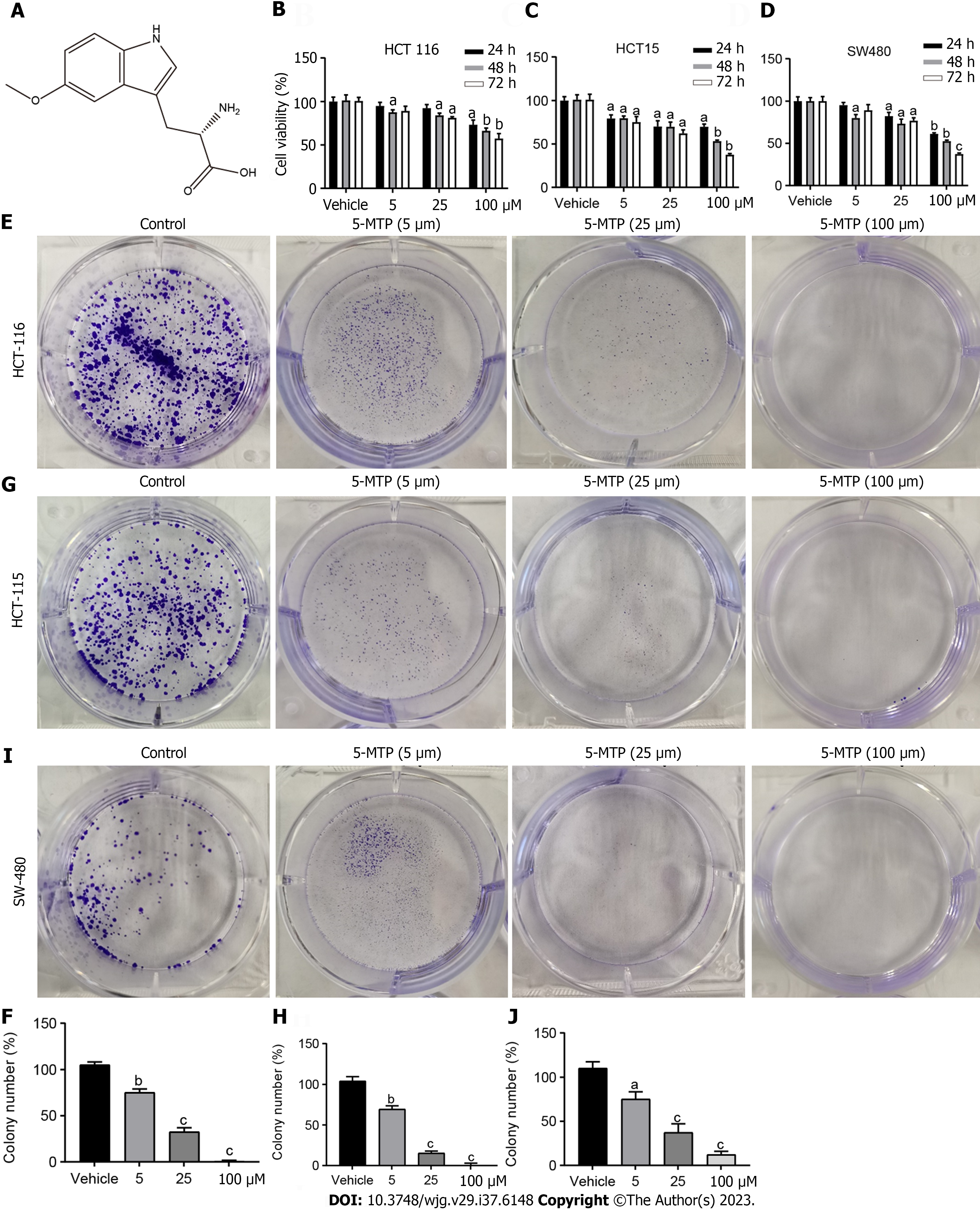
Figure 1 5-methoxytryptophan inhibited human colorectal cancer cell proliferation.
A: The structure of 5-methoxytryptophan (5-MTP) is shown; B-D: The Cell Counting Kit 8 assays were used to measure the viability of the colorectal cancer cells treated with 5-MTP at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM; E-J: Colony formation assay were used to measure the viability of the HCT-116 (E and F), HCT-15 (G and H), SW480 (I and J) cells treated with 5-MTP at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. 5-MTP: 5-Methoxytryptophan.
Figure 2 5-methoxytryptophan induced apoptosis and reactive oxygen species in HCT-116 cells.
A and B: The Hoechst staining was used to measure the viability of HCT-116 cells treated with 5-methoxytryptophan (5-MTP) at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM; C and D: Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry by double staining with PI and Annexin V of HCT-116 cells treated with 5-MTP at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM; E and F: Flow cytometry were used to analyses the JC-1 level of HCT-116 cells treated with 5-MTP at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM; G and H: 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate assays were used to test the reactive oxygen species production of HCT-116 cells treated with 5-MTP at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. 5-MTP: 5-Methoxytryptophan; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; PI: Propyl iodide.
Figure 3 5-methoxytryptophan induced cell cycle arrest in HCT-116 cells.
A and B: The HCT-116 cells were treated with 5-methoxytryptophan at the dose of 5, 25, and 100 μM. The cycle arrest was detected by flow cytometry.
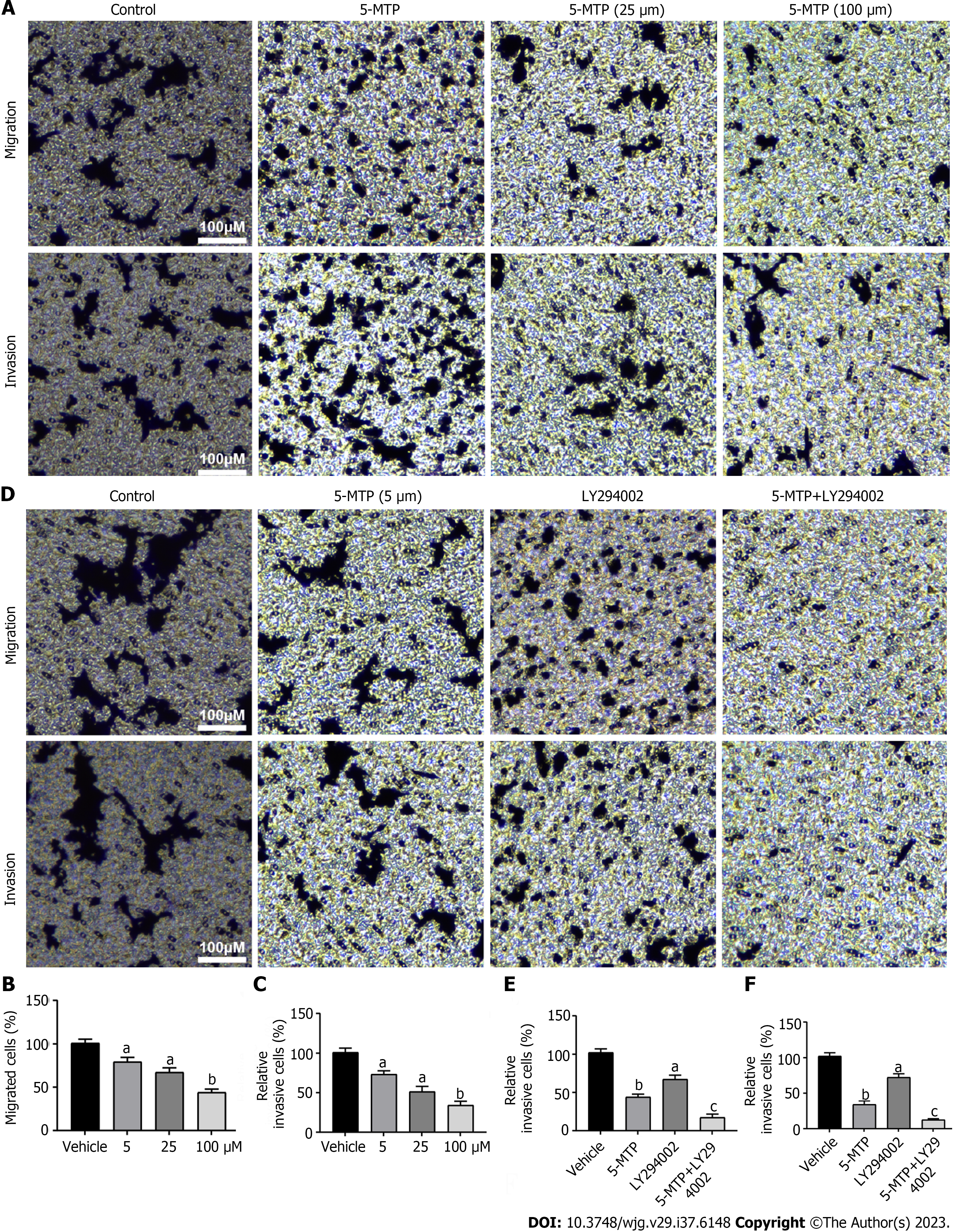
Figure 4 5-methoxytryptophan inhibited migration and invasion in HCT-116 cells.
A-C: Detection of migration and invasion in HCT-116 cells were treated with 5-methoxytryptophan (5-MTP) at the dose of 5, 25 and 100 μM by transwell test; D-F: The HCT-116 cells were treated with 5-MTP and/or LY294002. Detection of migration and invasion in HCT-116 cells by transwell test. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. 5-MTP: 5-Methoxytryptophan.
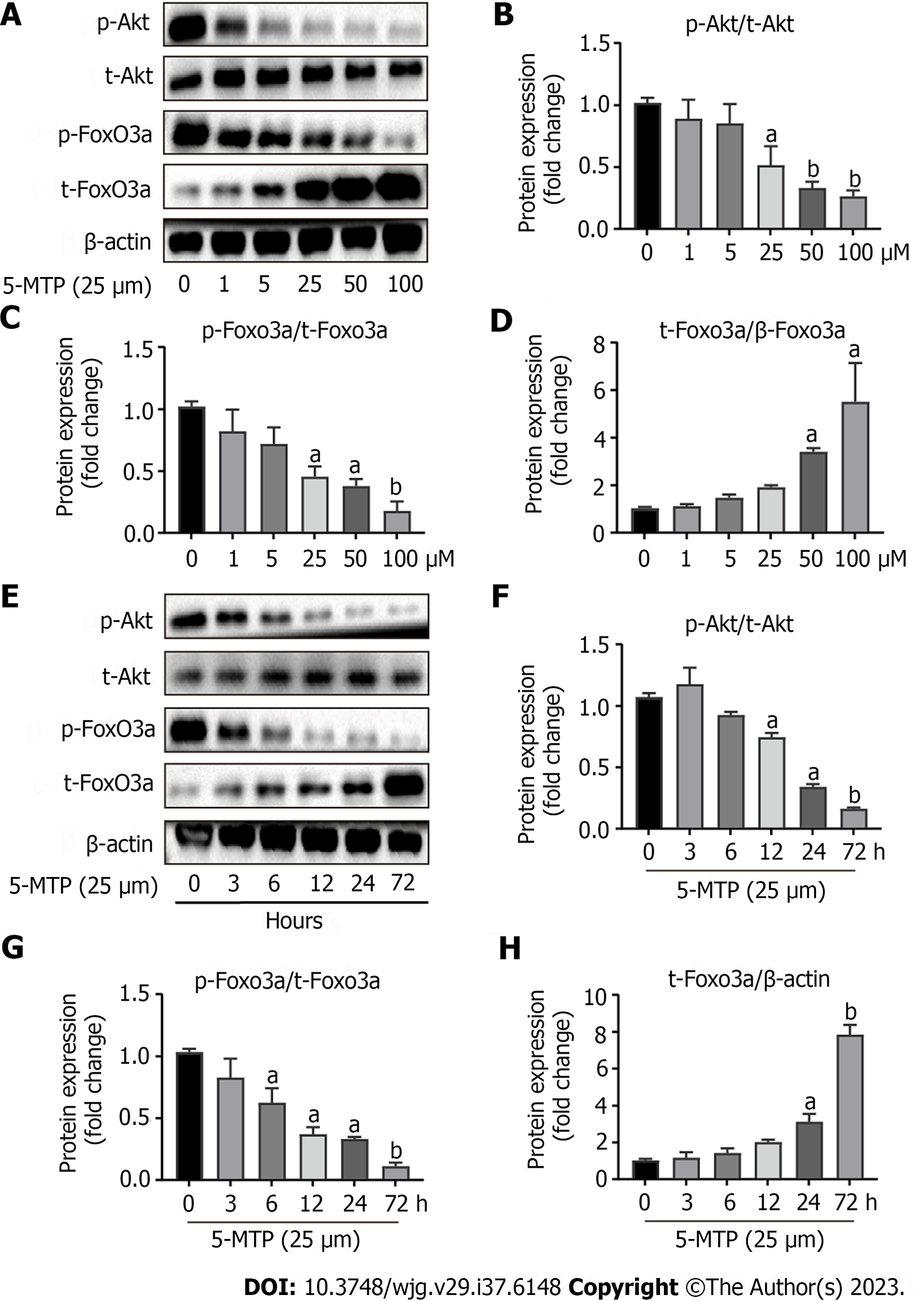
Figure 5 5-methoxytryptophan induced dose-response and time course inhibition of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway in HCT-116 cells.
A-D: The HCT-116 cells were treated with 5-methoxytryptophan (5-MTP) at the dose of 0, 1, 5, 25, 50 and 100 μM. The expression of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway protein was detected by western blotting; E-H: The HCT-116 cells were treated with the dose of 25 μM of 5-MTP at the time of 0, 3, 6, 12, 24 and 72 h. The expression of p-Akt, t-AKT, p-FoxO3a and t-FoxO3a was detected by western blotting. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. 5-MTP: 5-Methoxytryptophan.
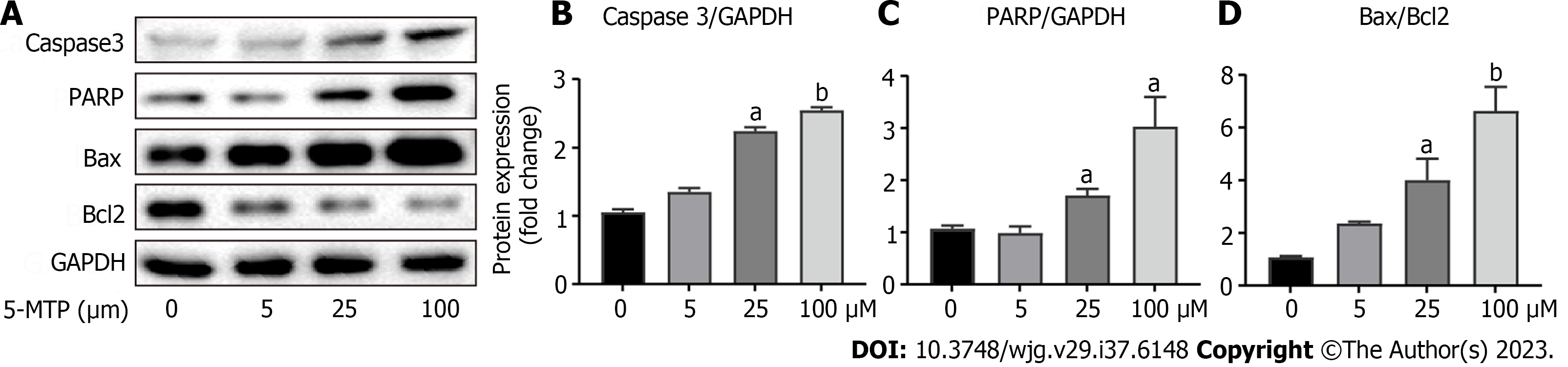
Figure 6 5-methoxytryptophan induced apoptosis in HCT-116 cells.
A-D: The expression of apoptosis-associated protein was detected by western blotting. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. 5-MTP: 5-Methoxytryptophan; Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma-2.
Figure 7 Apparent correlations between 5-methoxytryptophan-induced cell cycle and apoptosis-associated proteins or inhibition of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway in HCT-116 cells.
A-D: The HCT-116 cells were treated with 5-methoxytryptophan (5-MTP) and/or LY294002. The expression of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway and cycle arrest protein was detected by Western blotting; E-H: The HCT-116 cells were treated with the dose of 25 μM of 5-MTP and/or AKT siRNA. The expression of p-Akt, t-AKT, p-FoxO3a, t-FoxO3a, Bim, Cyclin D1 and P27 was detected by western blotting. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. 5-MTP: 5-Methoxytryptophan; NC: Normal control; siRNA: Small interfering RNA.
- Citation: Zhao TL, Qi Y, Wang YF, Wang Y, Liang H, Pu YB. 5-methoxytryptophan induced apoptosis and PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a phosphorylation in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(47): 6148-6160
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i47/6148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i47.6148