Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
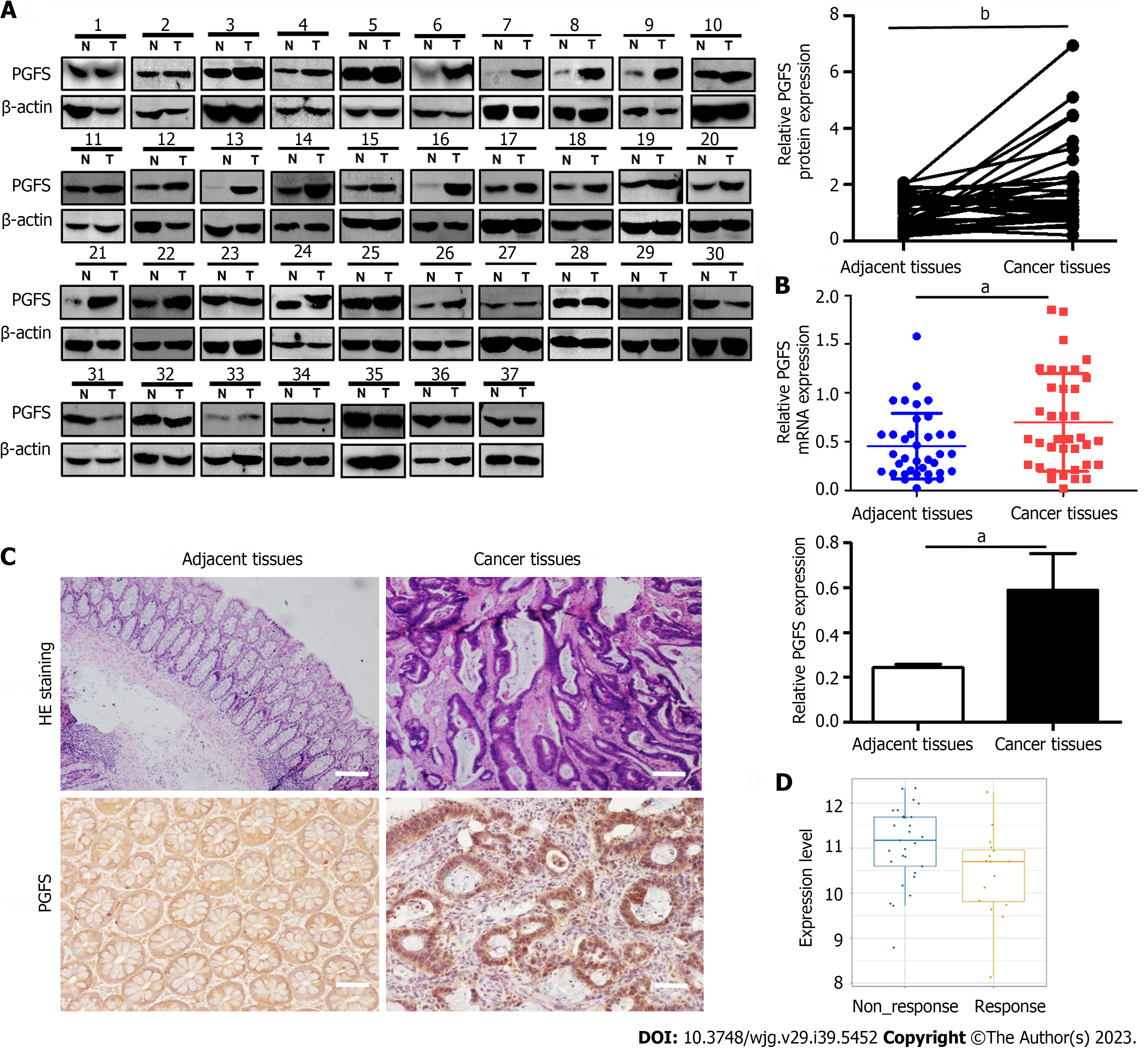
Figure 1 Prostaglandin F2α synthase is upregulation in patients with colorectal cancer.
A: Prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGFS) protein expression was verified using western blot in 37 pairs of colorectal cancer (CRC) and adjacent normal tissues; B: Real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of PGFS mRNA expression in 37 pairs of CRC and adjacent normal tissues; C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry for PGFS expression (scale bar, 50 μm); D: PGFS expression in non-response and response patients analyzed by the Cancer Treatment Response gene signature DataBase (http://ctrdb.ncpsb.org.cn/). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. T: Tumor; N: Adjacent normal tissues; PGFS: Prostaglandin F2α synthase; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin.
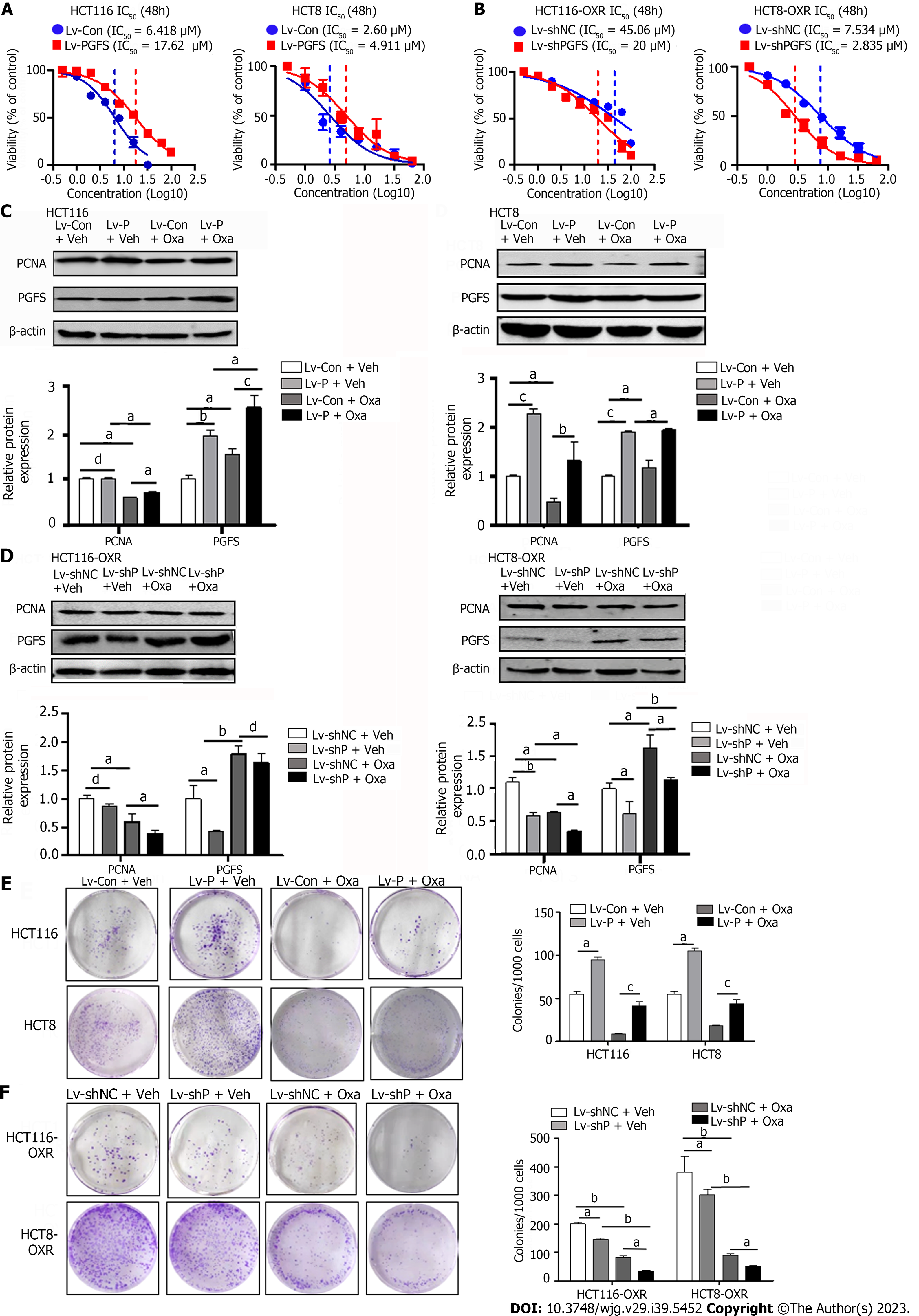
Figure 2 Prostaglandin F2α synthase resists the inhibitory effect of oxaliplatin on colorectal cancer cell proliferation.
A: The effects of prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGFS) overexpression on cell viability in HCT116 and HCT8 cells; B: The effects of PGFS knockdown on cell viability in HCT116-OxR and HCT8-OxR cells; C and D: Western blot analysis showed proliferating cell nuclear antigen levels in parental and oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) colorectal cancer (CRC) cells; E and F: Plate colony formation assay in parental and OR CRC cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dNo significance. PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PGFS: Prostaglandin F2α synthase; Oxa: Oxaliplatin; IC50: Half-inhibitory concentration.
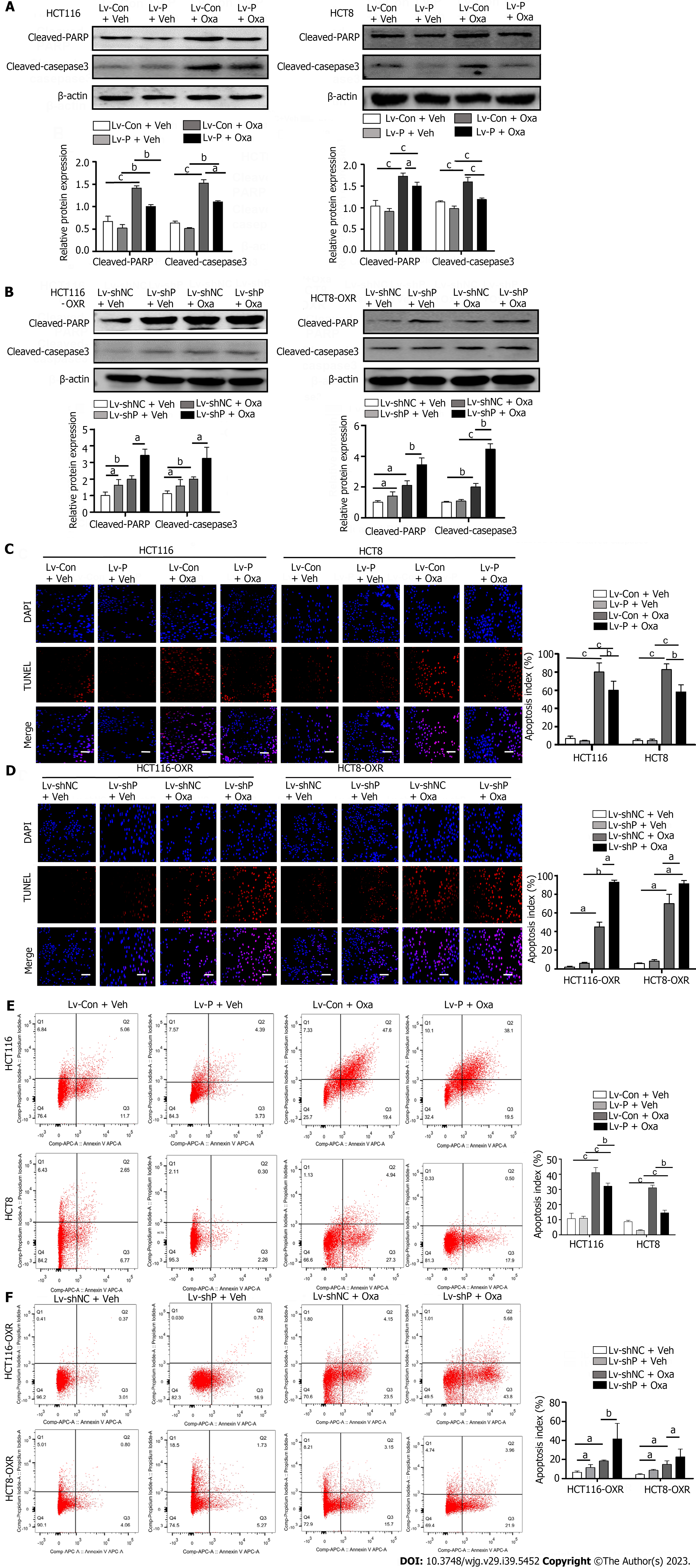
Figure 3 Prostaglandin F2α synthase suppresses apoptosis induced by oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cell lines.
A and B: Western blot analysis showed cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase and cleaved caspase-3 were assessed in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells or in oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) CRC cells; C and D: Apoptosis of parental and OR CRC cells evaluation by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assay, scale bar 100 μm; E and F: Apoptosis was measured by the Annexin V-PI staining in parental and OR CRC cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Oxa: Oxaliplatin; PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase.
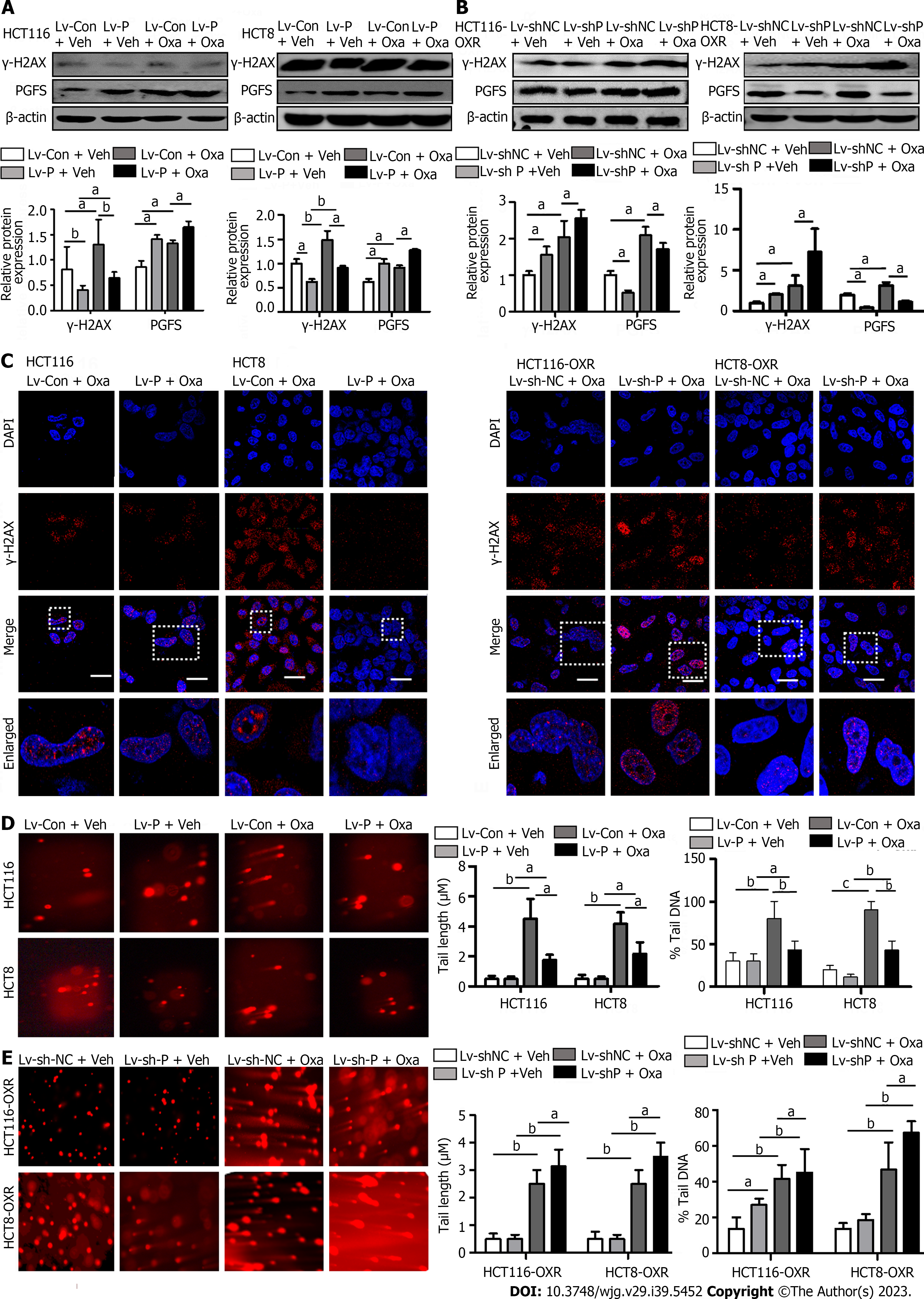
Figure 4 The protective effect of prostaglandin F2α synthase on DNA damage induced by oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells.
A and B: DNA damage marker protein γ-H2A histone family member X (γ-H2AX) was determined using western blot in HCT116 and HCT8 cells and HCT116-OxR and HCT8-OxR cells; C: γ-H2AX fluorescent spots were detected using immunofluorescence staining; D and E: Detection of DNA damage using single-cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay) in parent and drug-resistant cells (scale bar, 50 μm). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. PGFS: Prostaglandin F2α synthase; Oxa: Oxaliplatin; γ-H2AX: γ-H2A histone family member X.
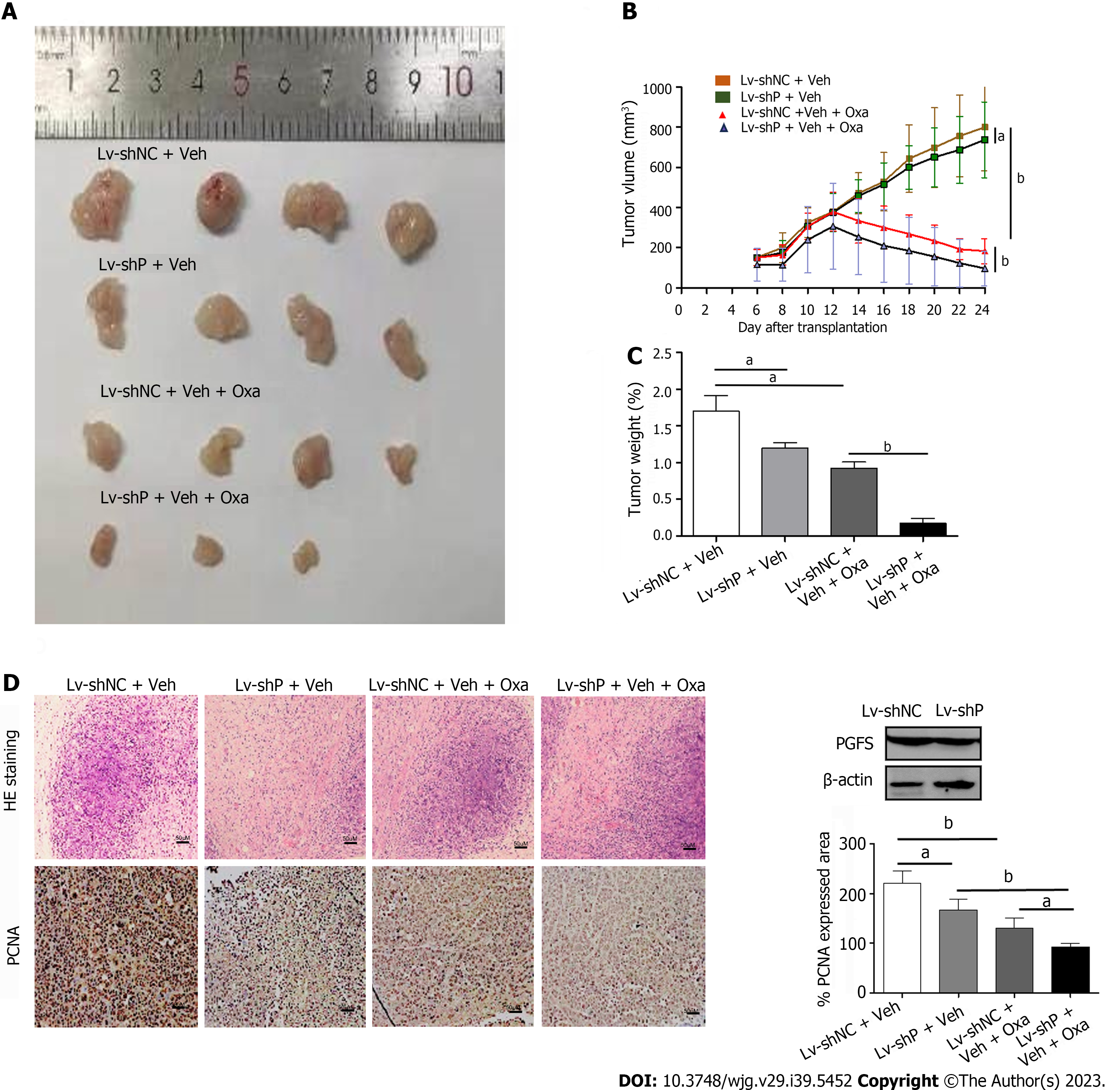
Figure 5 Prostaglandin F2α synthase knockdown improves oxaliplatin efficiency in vivo.
A: Morphologies of collected tumors in subcutaneous HCT8-OxR xenografts in nude mice; B: Curves of tumor growth in each group; C: Tumor weights were measured after collection; D: Hematoxylin-eosin (upper panel; magnification, × 200) and immunohistochemical staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen (bottom panel; magnification, × 200) using xenograft tumor samples from each group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PGFS: Prostaglandin F2α synthase; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; Oxa: Oxaliplatin.
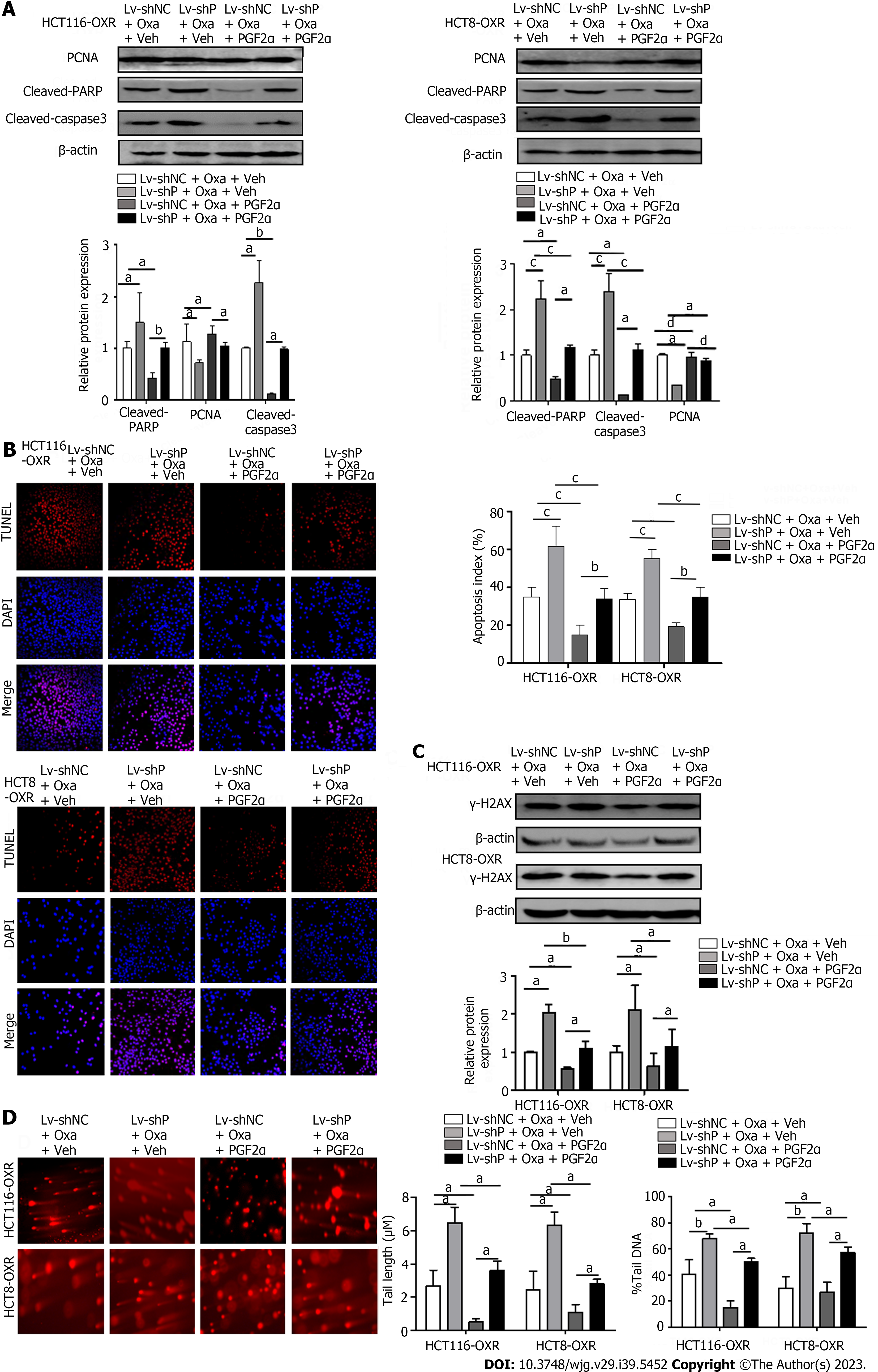
Figure 6 The inhibitory effect of prostaglandin F2α on oxaliplatin-induced cytotoxicity.
A: Western blots showed the effect of prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGF2α) (PGFS) on the expressions of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, cleaved-poly ADP-ribose polymerase, and γ-H2A histone family member X (γ-H2AX) in PGFS knockdown, oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) cells; B: The effect of PGF2α on apoptosis in PGFS knockdown, OR cells evaluated by immunofluorescence. scale bar 100 uM; C: The effect of PGF2α on the cleavage of γ-H2AX protein expressions in PGFS knockdown, OR cells; D: The effect of PGF2α on DNA damage in PGFs knockdown, OR cells evaluated by single-cell gel electrophoresis. scale bar 50 μm). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dNo significance. PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase; γ-H2AX: γ-H2A histone family member X; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.
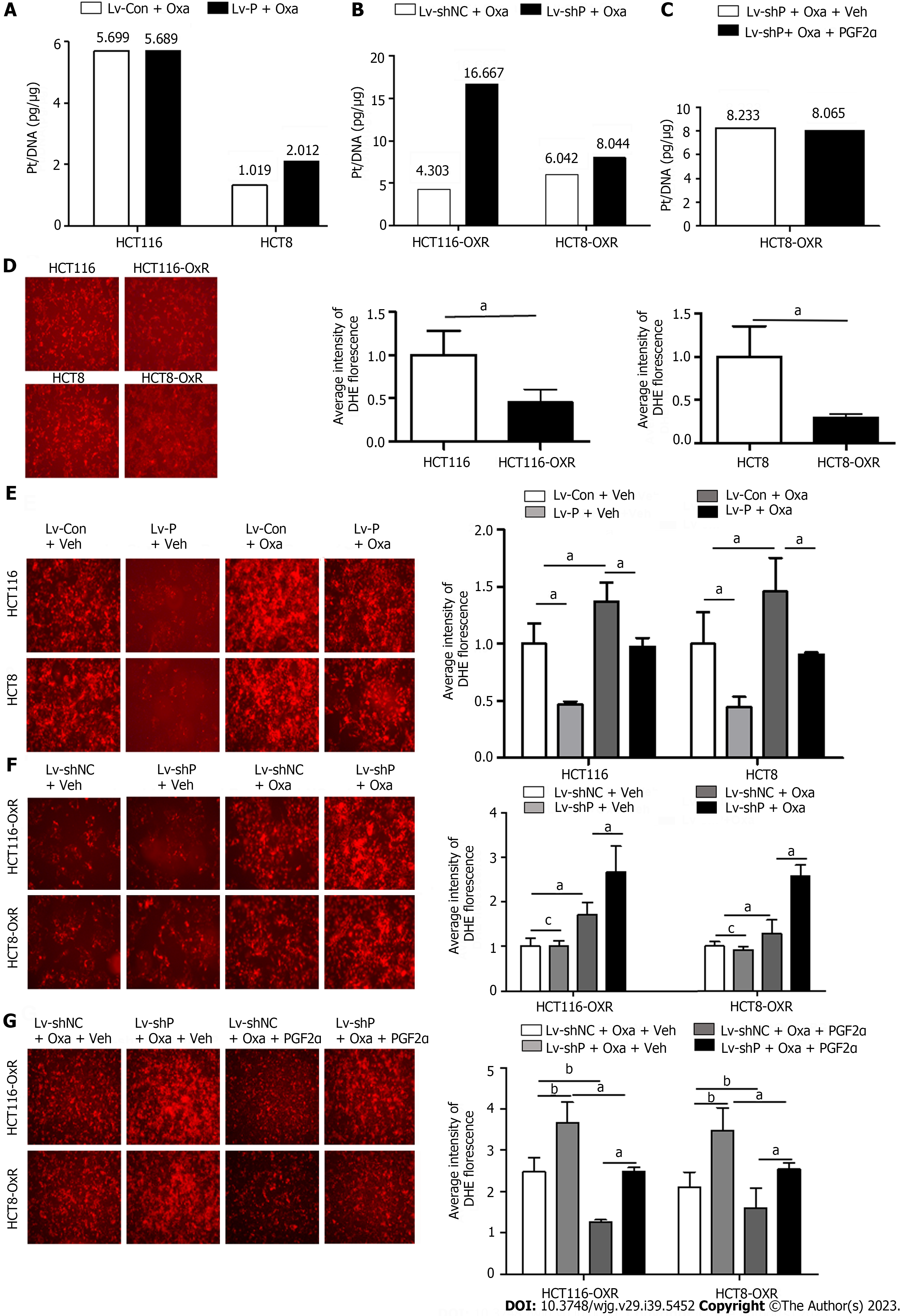
Figure 7 Prostaglandin F2α synthase may suppresses the formation of platinum-DNA adducts.
A: The effect of Prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGF2α) (PGFS) overexpression on the formation of platinum-DNA adducts was determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells; B: The effect of PGFS knockdown on the formation of platinum-DNA adducts in oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) CRC cells; C: The effect of PGF2α on the formation of platinum-DNA adducts in OR CRC cells; D: The reactive oxygen species (ROS) content were significantly decreased in OR CRC cells; E: PGFS overexpression significantly decreased ROS content in CRC cells; F: PGFS knockdown significantly decreased ROS content in OR CRC cells; G: PGFS knockdown significantly decreased ROS content in OR CRC cells (scale bar, 50 μm). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01; cNo significance. PGF2α: Prostaglandin F2α; Oxa: Oxaliplatin.
- Citation: Wang YJ, Xie XL, Liu HQ, Tian H, Jiang XY, Zhang JN, Chen SX, Liu T, Wang SL, Zhou X, Jin XX, Liu SM, Jiang HQ. Prostaglandin F2α synthase promotes oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through prostaglandin F2α-dependent and F2α-independent mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i39/5452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452