Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2023; 29(37): 5292-5304
Published online Oct 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5292
Published online Oct 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5292
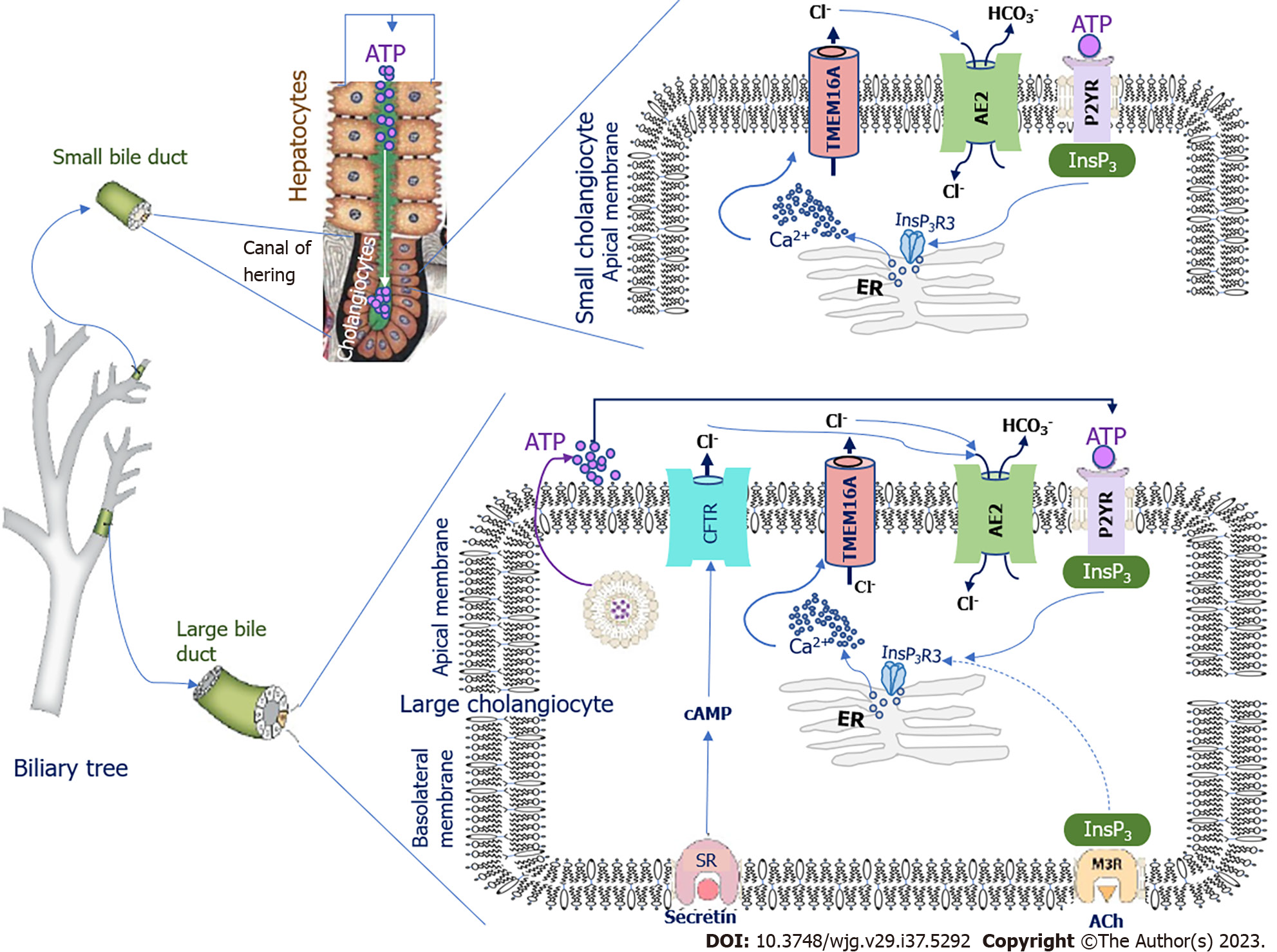
Figure 1 Schematic of bicarbonate secretion by small and large cholangiocytes.
AE2: Chloride/bicarbonate anion exchanger 2; TMEM16A: Transmembrane 16A chloride channels; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; P2YR: Purinergic receptor family; InsP3: Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; InsP3R3: Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; SR: Secretin receptor; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Ach: Acetylcholine; CFTR: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; M3R: Muscarinic acetylcholine M3 receptor; HCO3-: Bicarbonate; Cl-: Chloride; Ca2+: Calcium.
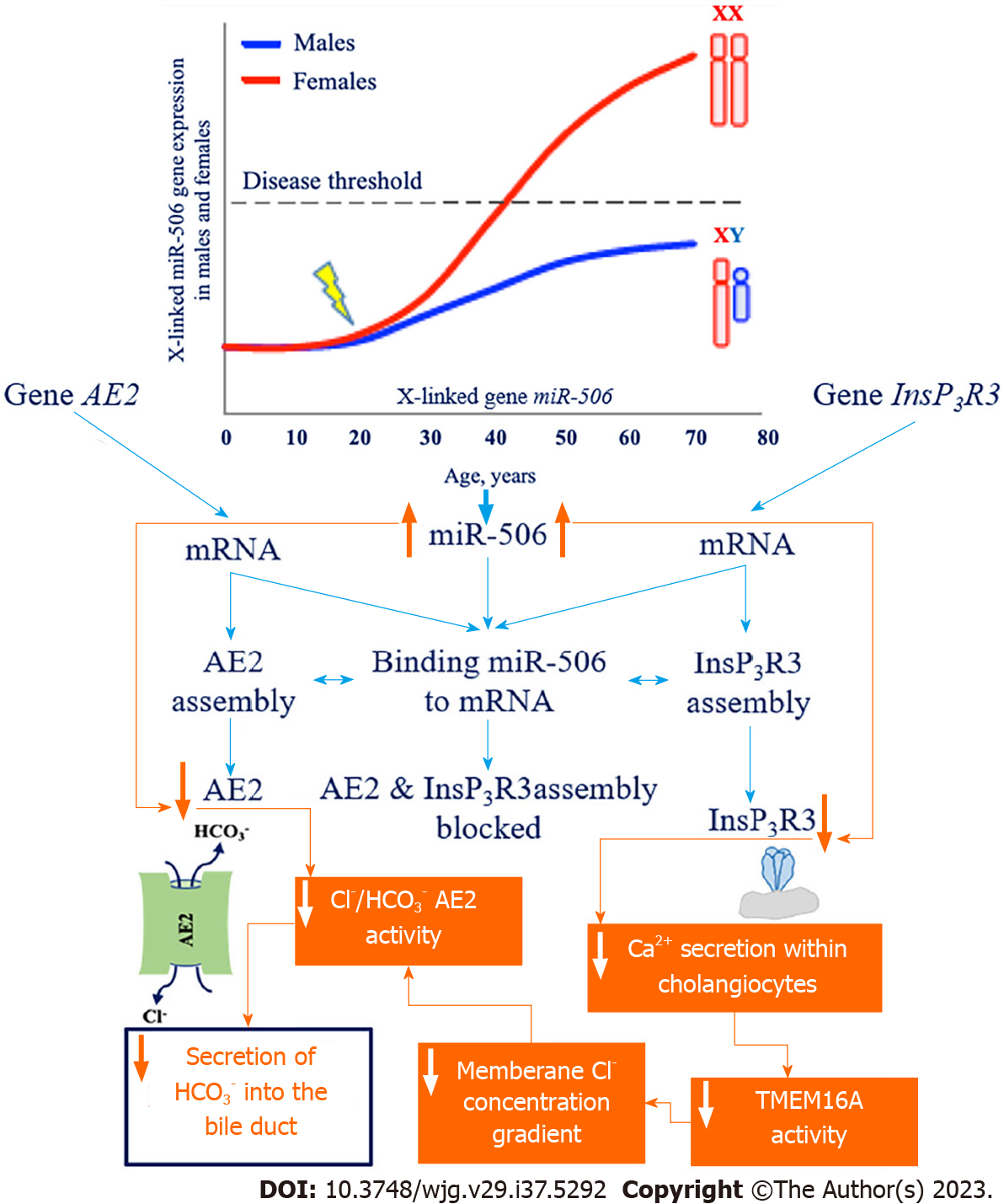
Figure 2 Mechanism of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 and chloride/carbonate (chloride/bicarbonate) anion exchanger 2 gene expression reduction due to the increase in the amount of micro-RNA 506 and its activity.
InsP3R3: Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3; AE2: Chloride/bicarbonate anion exchanger 2; miR-506: Micro-RNA 506; TMEM16A: Transmembrane 16A chloride channels; HCO3-: Bicarbonate; Cl-: Chloride.
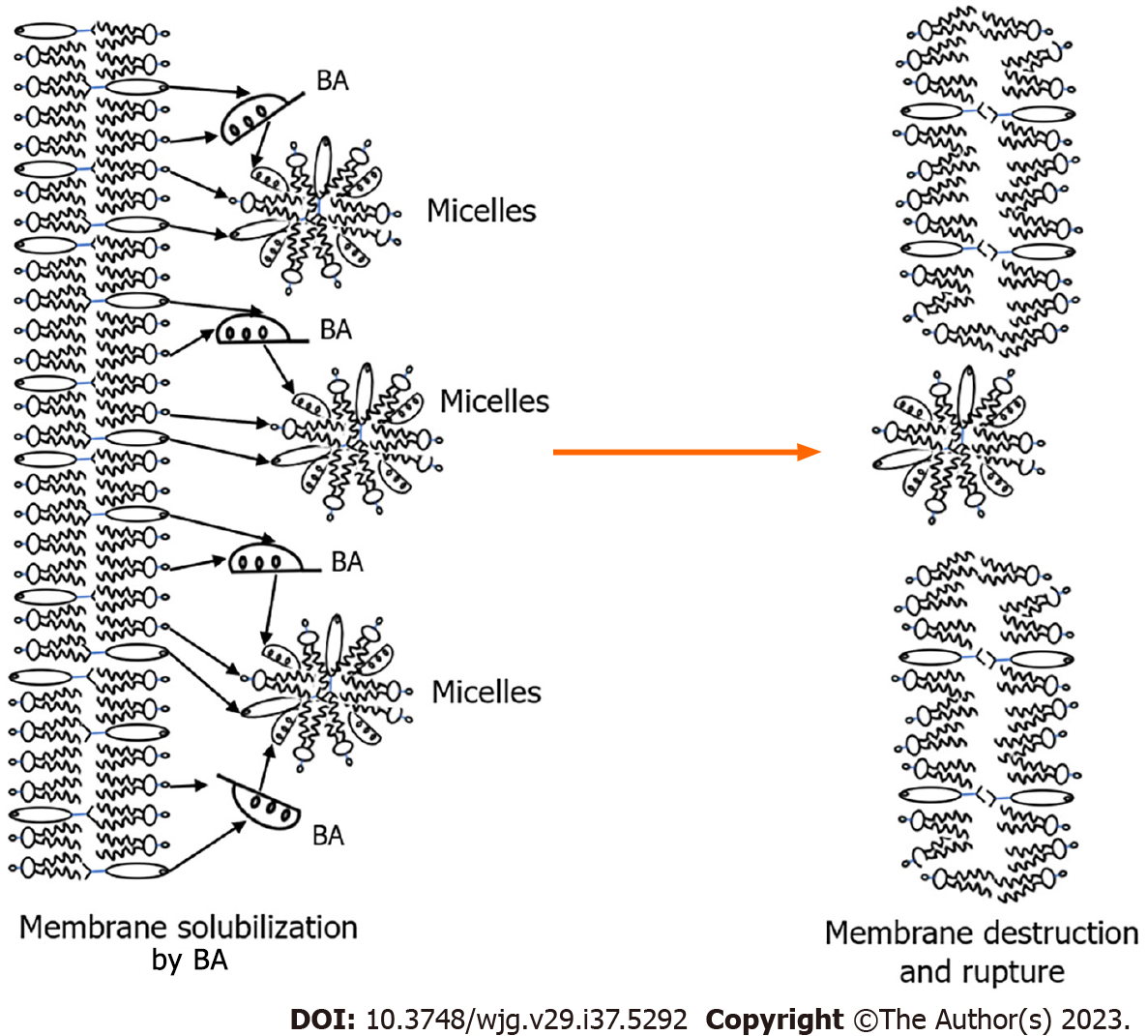
Figure 3 Solubilization of phospholipids and cholesterol from membrane structures by bile acids.
BA: Bile acids.
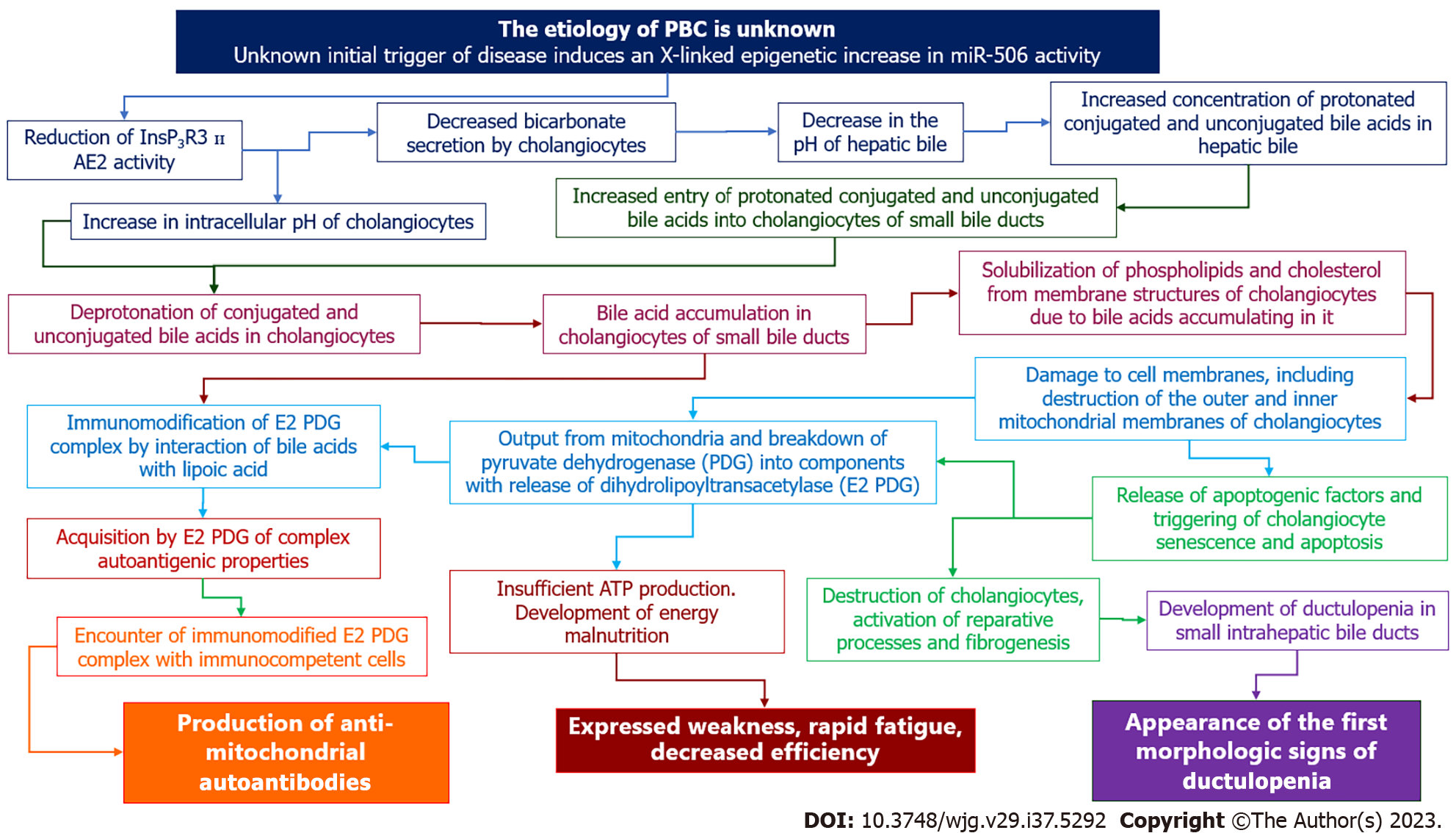
Figure 4 Mechanism of anti-mitochondrial antibody formation, development of ductulopenia, weakness, fatigue and malaise in the asymptomatic stage of primary biliary cholangitis: hypothesis.
InsP3R3: Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3; AE2: Chloride/bicarbonate anion exchanger 2; PDG: Pyruvate dehydrogenase; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate.
- Citation: Reshetnyak VI, Maev IV. New insights into the pathogenesis of primary biliary cholangitis asymptomatic stage. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(37): 5292-5304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i37/5292.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5292