Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2023; 29(35): 5125-5137
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5125
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5125
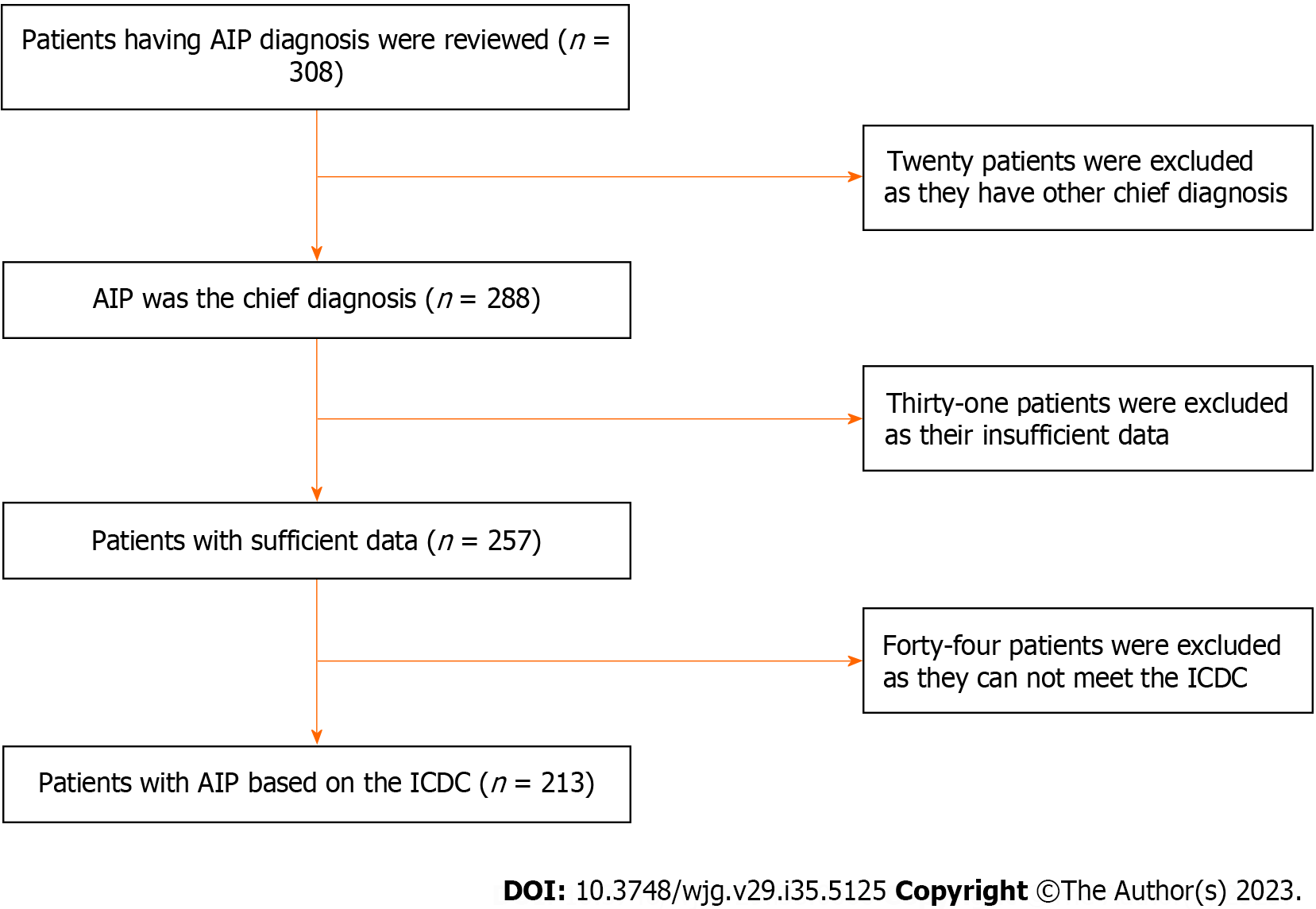
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the study design.
A total of 308 patients were reviewed. Ninety-five patients were excluded due to other chief diagnoses (n = 20), insufficient data (n = 31), and non-fulfillment of the international consensus diagnostic criteria (n = 44). AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; ICDC: International consensus diagnostic criteria.
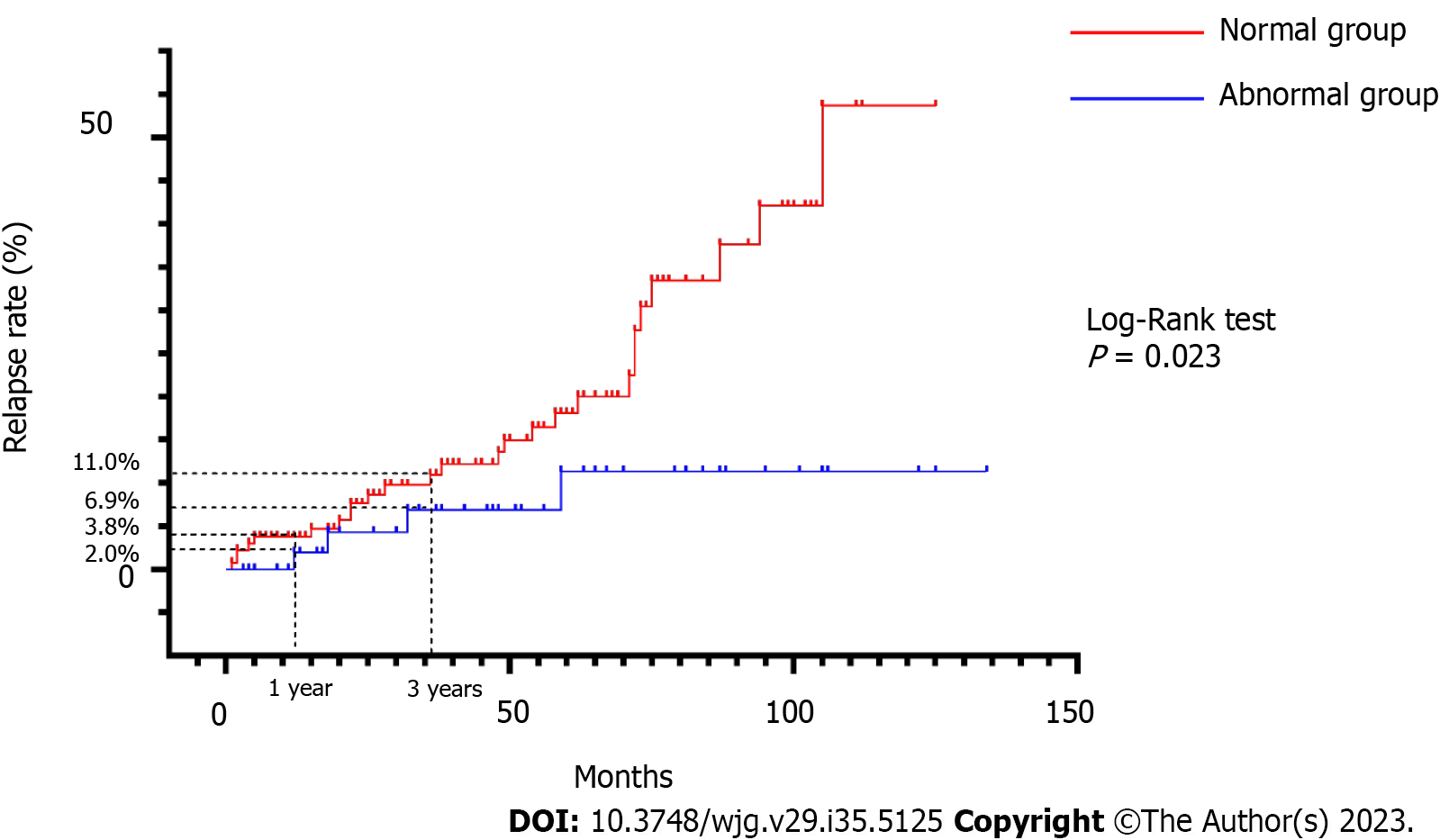
Figure 2 Cumulative relapse rates in the normal and abnormal groups.
The cumulative relapse rates at 1 and 3 years were 3.8% and 11.0%, respectively, for the abnormal group and 2.0% and 6.9%, respectively, for the normal group (Log-Rank test, P = 0.023).
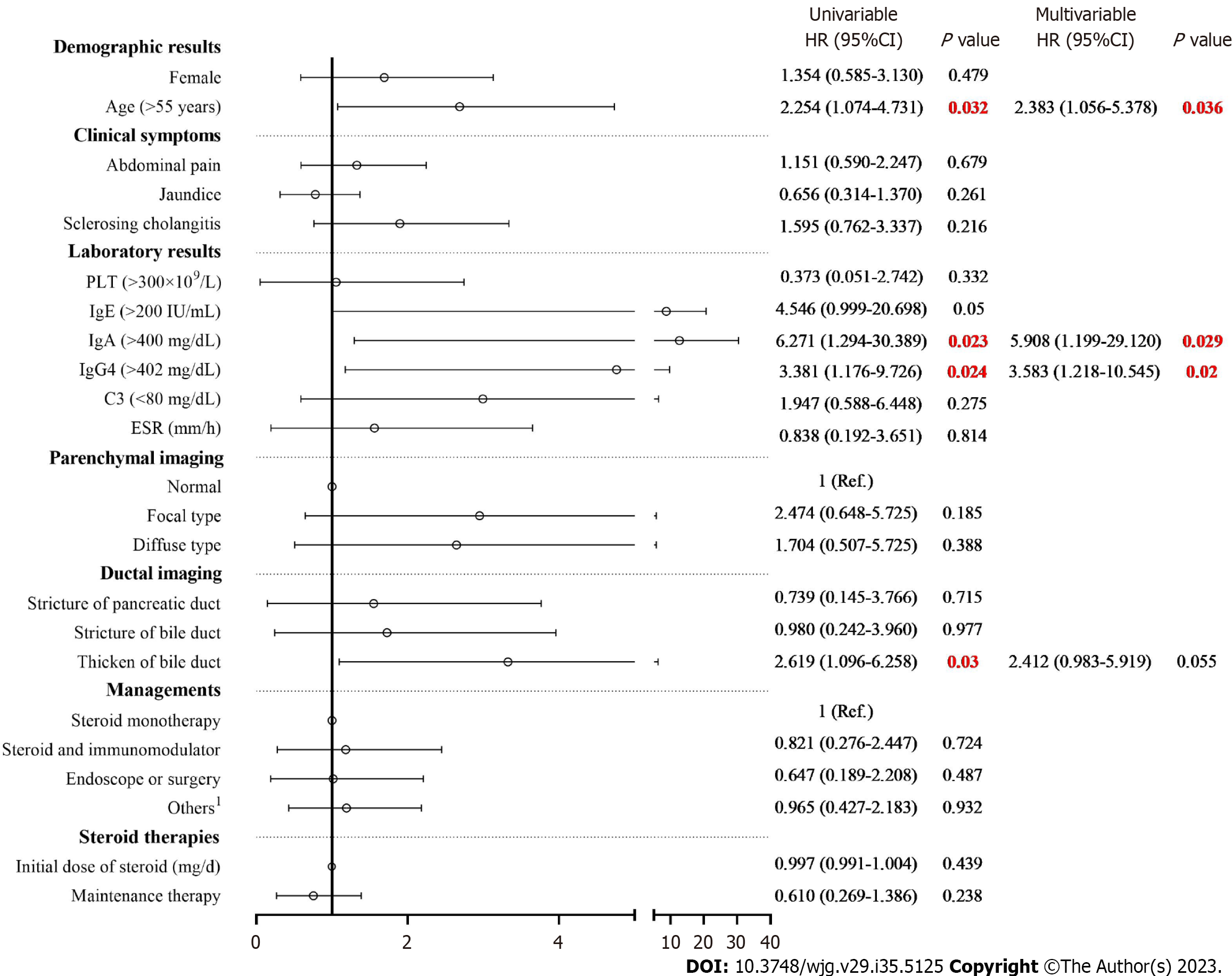
Figure 3 Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis for relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis.
Univariate Cox regression analysis indicated that age (> 55 years), immunoglobulin (Ig)A (> 400 mg/dL), IgG4 (> 402 mg/dL), presence of thickened bile duct were risk factors of relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified three risk factors of relapse, including age (> 55 years), IgA (> 400 mg/dL) and IgG4 (> 402 mg/dL). 1Others : Hepatic protectors, antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors. PLT: Hemoglobin; Ig: Immunoglobulin; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; C3: Complement C3.
- Citation: Zhou GZ, Zeng JQ, Wang L, Liu M, Meng K, Wang ZK, Zhang XL, Peng LH, Yan B, Pan F. Clinical characteristics and outcome of autoimmune pancreatitis based on serum immunoglobulin G4 level: A single-center, retrospective cohort study. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(35): 5125-5137
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i35/5125.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5125