Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2023; 29(3): 487-502
Published online Jan 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i3.487
Published online Jan 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i3.487
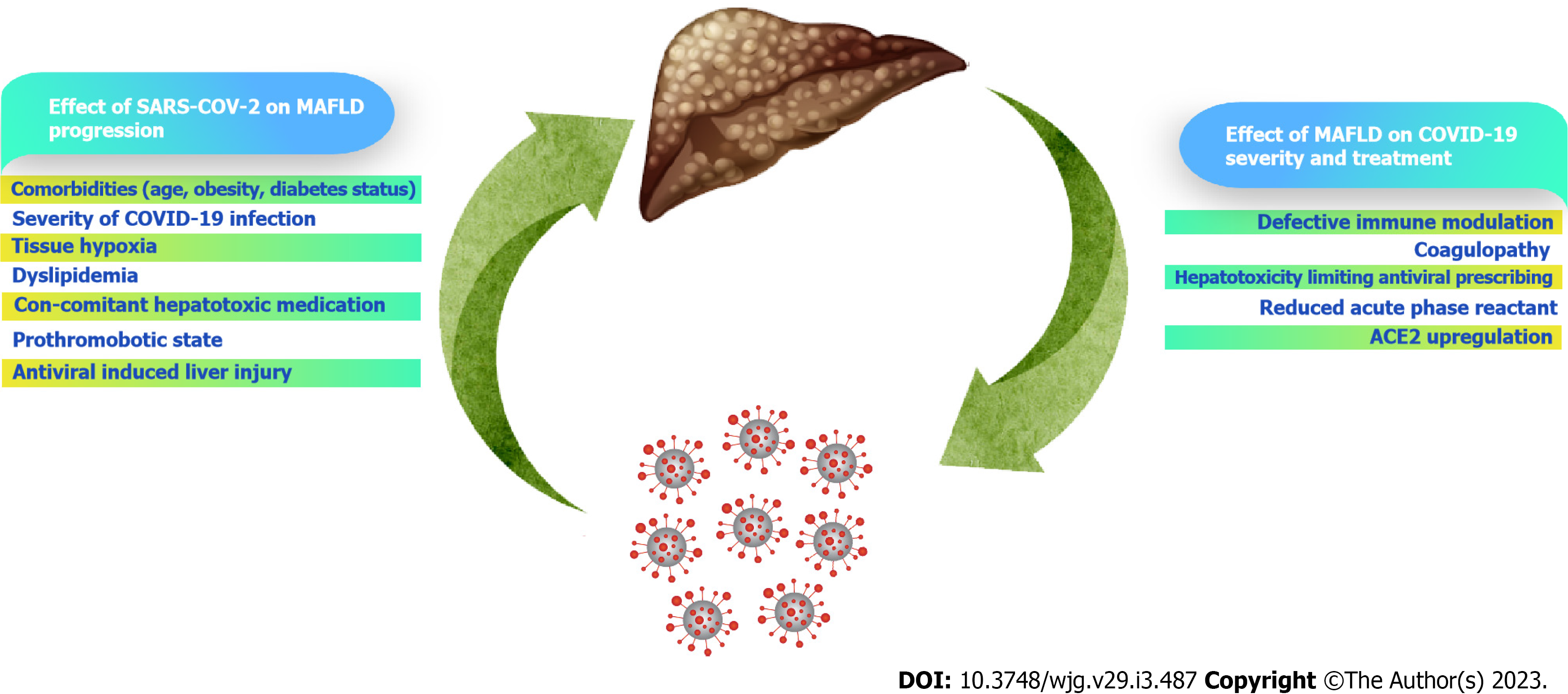
Figure 1 Interplay between coronavirus disease 2019 and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
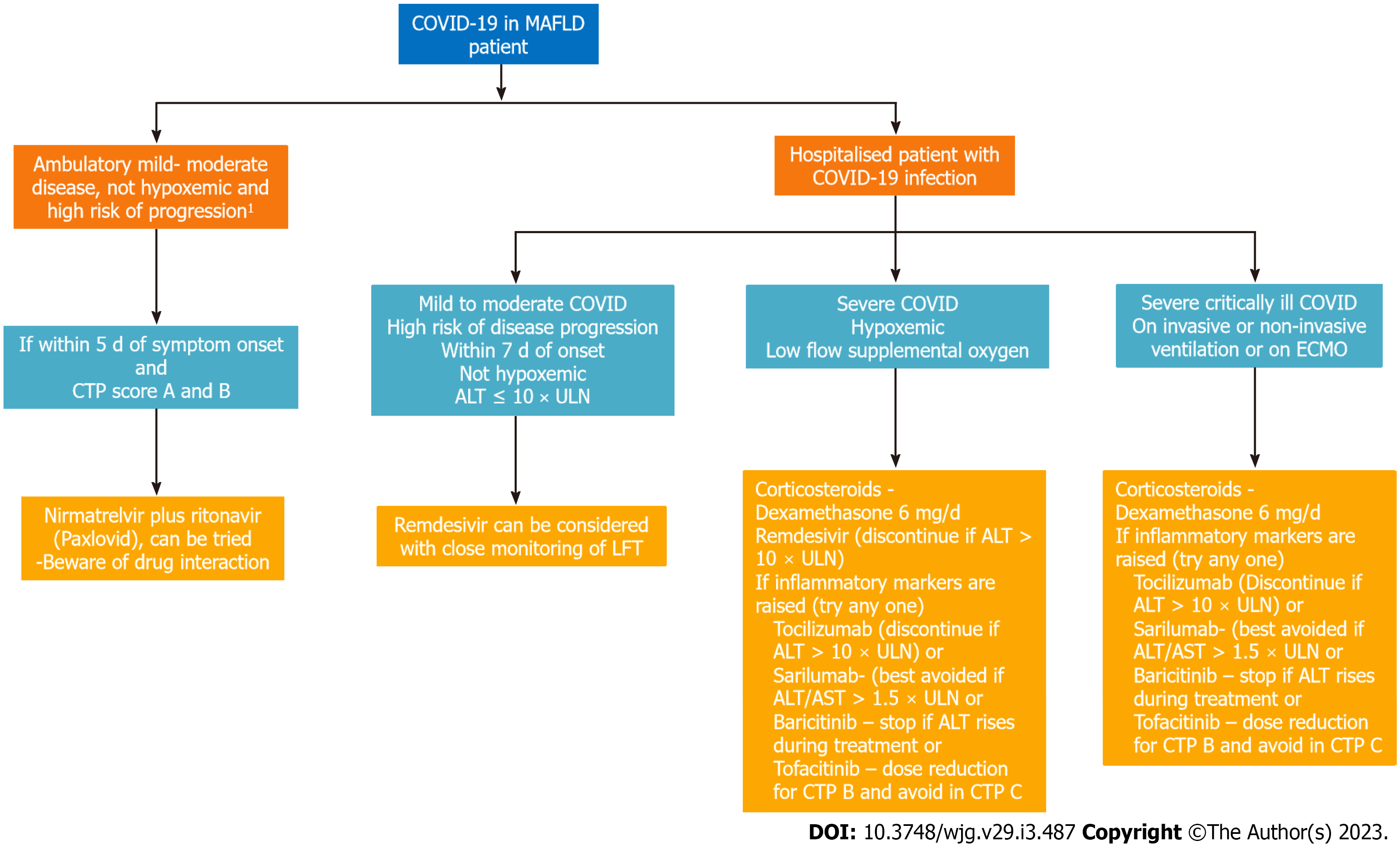
Figure 2 Selection of coronavirus disease 2019 therapy in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease patient.
1High risk of progression - advanced age ≥ 65-yr-old, immunocompromised state or multiple medical co-morbidities. Hypoxemia: SpO2 ≤ 94% on room air; ECMO: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; Mild disease: Cough, upper respiratory tract symptom and absence of dyspnea; Severe: Hypoxemia or need for supplemental oxygen; Moderate: Dyspneic patient and absence of severe disease features. ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; COVID: Coronavirus disease; CTP: Child Pugh score; LFT: Liver function test; ULN: Upper limit of normal.
- Citation: Jeeyavudeen MS, Chaudhari R, Pappachan JM, Fouda S. Clinical implications of COVID-19 in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(3): 487-502
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i3/487.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i3.487