Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2023; 29(27): 4271-4288
Published online Jul 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4271
Published online Jul 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4271
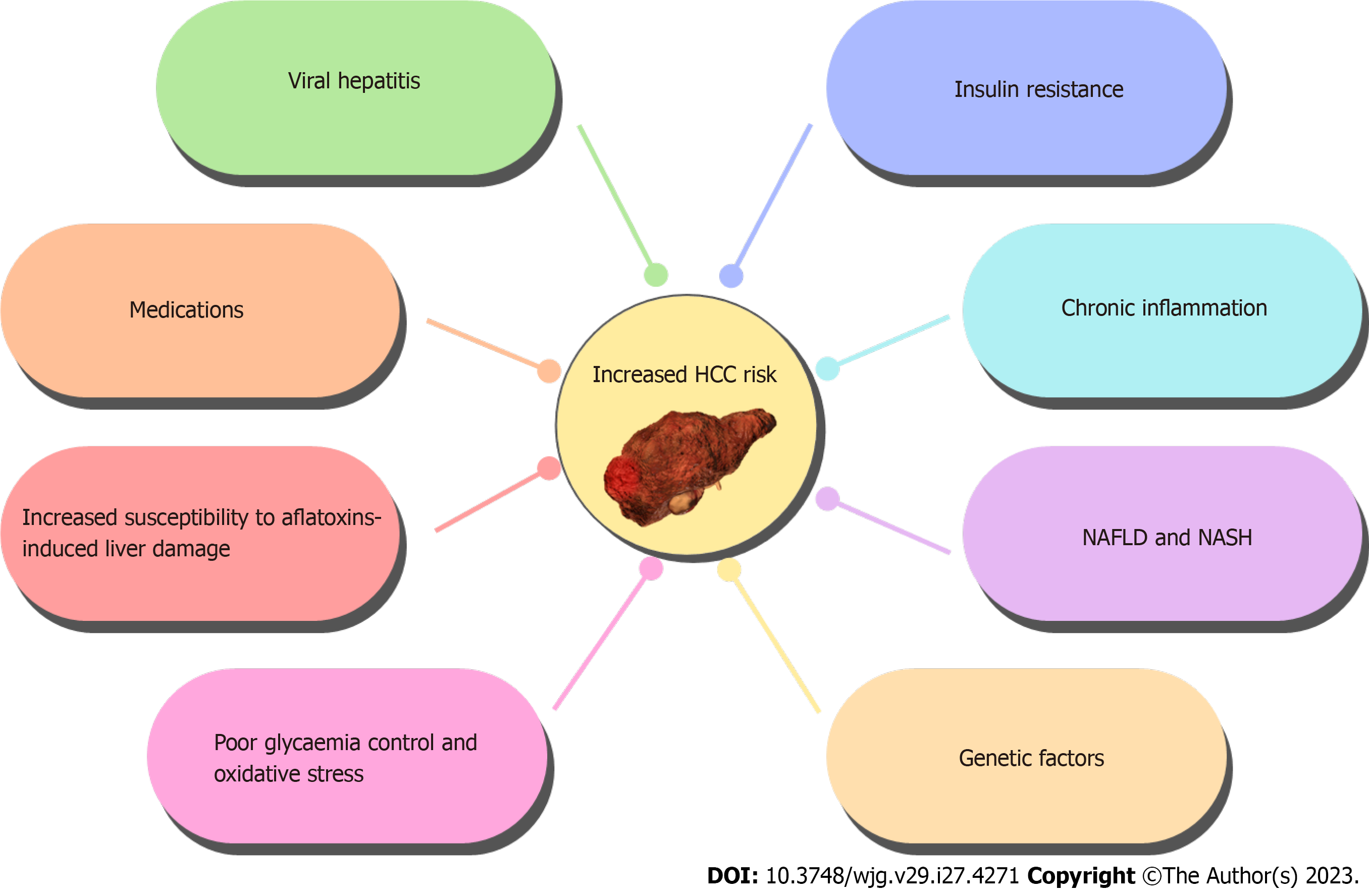
Figure 1 Factors contributing to increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients.
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
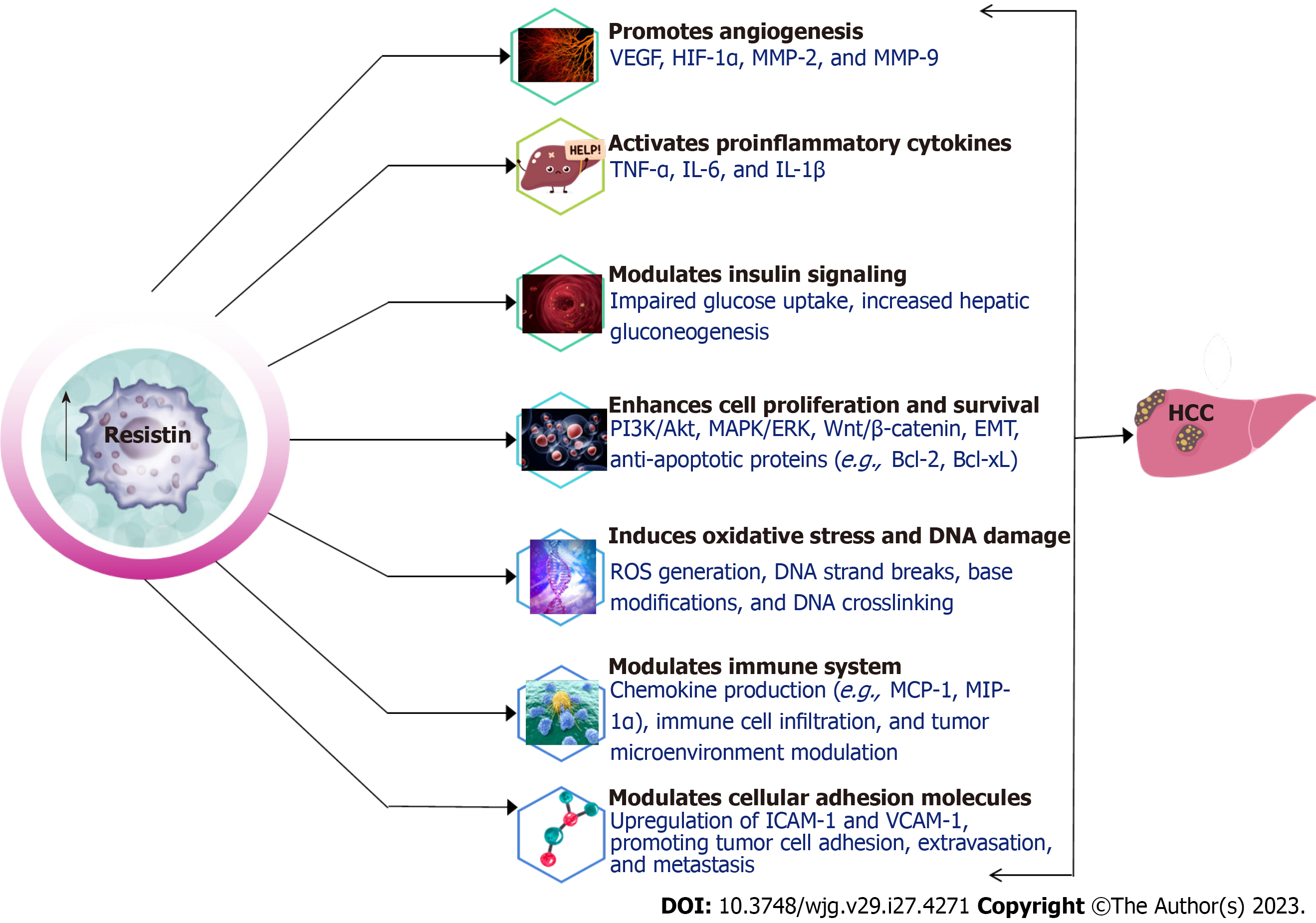
Figure 2 Mechanisms of resistin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; MMP-2: Matrix metalloproteinases-2; MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinases -9; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin -6; IL-1β: Interleukin--1β; ROS: Reactive-oxygen species; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MIP-α: Macrophage inflammatory protein-alpha; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Abdalla MMI. Serum resistin and the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(27): 4271-4288
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i27/4271.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4271