Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2023; 29(27): 4252-4270
Published online Jul 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4252
Published online Jul 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4252
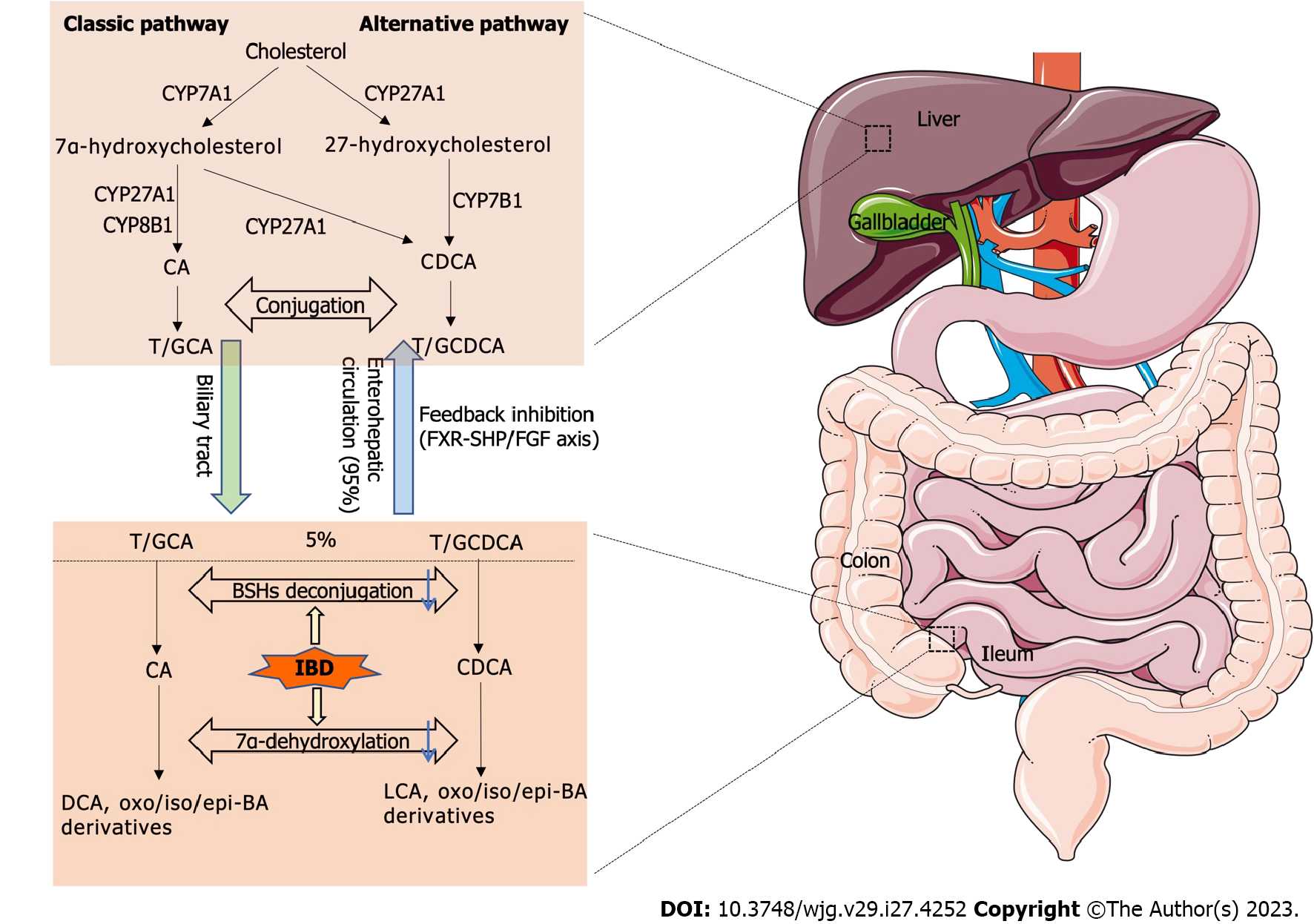
Figure 1 Synthesis, recirculation, and microbial modification of bile acids in the gut.
Bile acids are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver. In the classical pathway, cholesterol-7α-hydroxylase converts cholesterol to 7α-hydroxycholesterol, which is then metabolized to cholic acid via mitochondrial sterol-27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) or CYP8A1, or to chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) via CYP27A1. In the alternative pathway, CYP27A1 begins the conversion of cholesterol to 27-hydroxycholesterol, which is then metabolized to CDCA by oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase. These primary bile acids are then conjugated with taurine or glycine and then released into the bile for secretion into the duodenum. At the end of the ileum, 95% of the conjugated bile acids (BAs) are reabsorbed through the enterohepatic circulation, while the remaining 5% depolymerizes and enters the colon, where BAs undergo a series of chemical modifications by intestinal bacteria, including catabolism, desulfurization, dehydrogenation, dehydroxylation, and exo-embedding reactions to form secondary bile acids (mainly lithocholic acid and deoxycholic acid) and their oxidative, isomeric, and exo-derivatives. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; CA: Cholic acid; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; GCA: Glycocholic acid; TCA: Taurocholic acid; GCDCA: Glycochenodeoxycholic acid; TCDCA: Taurochenodeoxycholic acid; DCA: Deoxycholic acid; LCA: Lithocholic acid; BA: Bile acid; CYP7A1: Cholesterol-7α-hydroxylase; CYP27A1: Mitochondrial sterol-27-hydroxylase; CYP8B1: Sterol-12α-hydroxylase; CYP7B1: Oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase; BSHs: Bile salt hydrolases; FXR: Farnesol X receptor; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; SHP: Small isomeric partner.
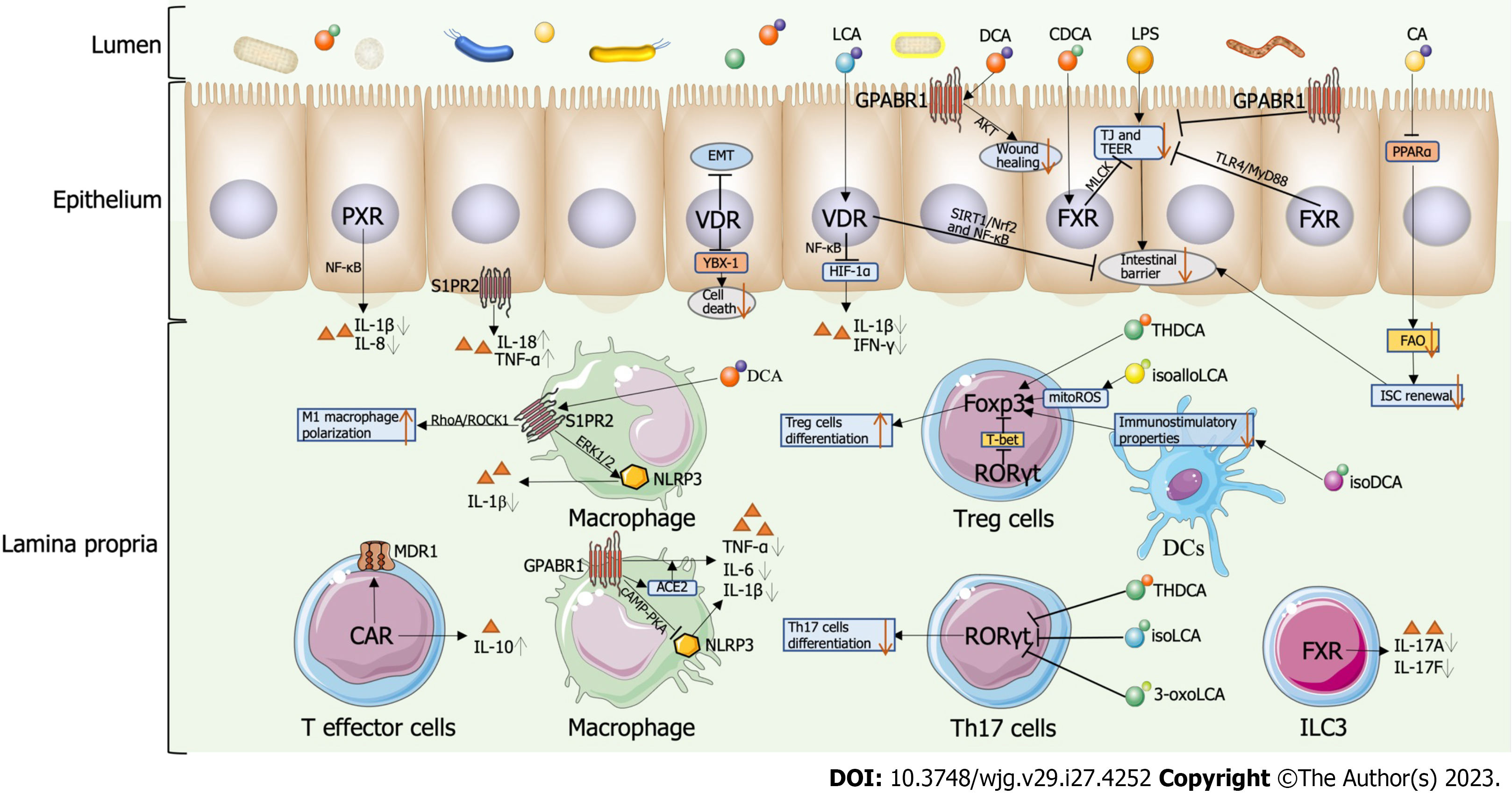
Figure 2 Emerging role of bile acids and their receptors.
DCA: Deoxycholic acid; LCA: Lithocholic acid; CA: Cholic acid; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; isoLCA: Isolithocholic acid; isoalloLCA: Isoallolithocholic acid; 3-oxoLCA: 3-oxolithocholic acid; isoDCA: 3β-hydroxydeoxycholic acid; THDCA: Taurohyodeoxycholic acid; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; GPABR1: G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1; PXR: Pregnane X receptor; VDR: Vitamin D receptor; RORγt: Retinoid-related orphan receptor γt; CAR: Costitutive androstane receptor; S1PR2: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2; Th17 cells: T helper 17 cells; Treg cells: Regulatory T cells; ILC3: Innate lymphocyte type 3; DCs: Dendritic cells; ISC: Intestinal stem cell; YBX-1: Y box binding protein 1; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; NLRP3: The NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3; mitoROS: Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FAO: Fatty acid oxidation; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TJ: Tight junction; TEER: Trans-epithelial electrical resistance; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4.
- Citation: Long XQ, Liu MZ, Liu ZH, Xia LZ, Lu SP, Xu XP, Wu MH. Bile acids and their receptors: Potential therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(27): 4252-4270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i27/4252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4252