Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2023; 29(23): 3715-3732
Published online Jun 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i23.3715
Published online Jun 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i23.3715
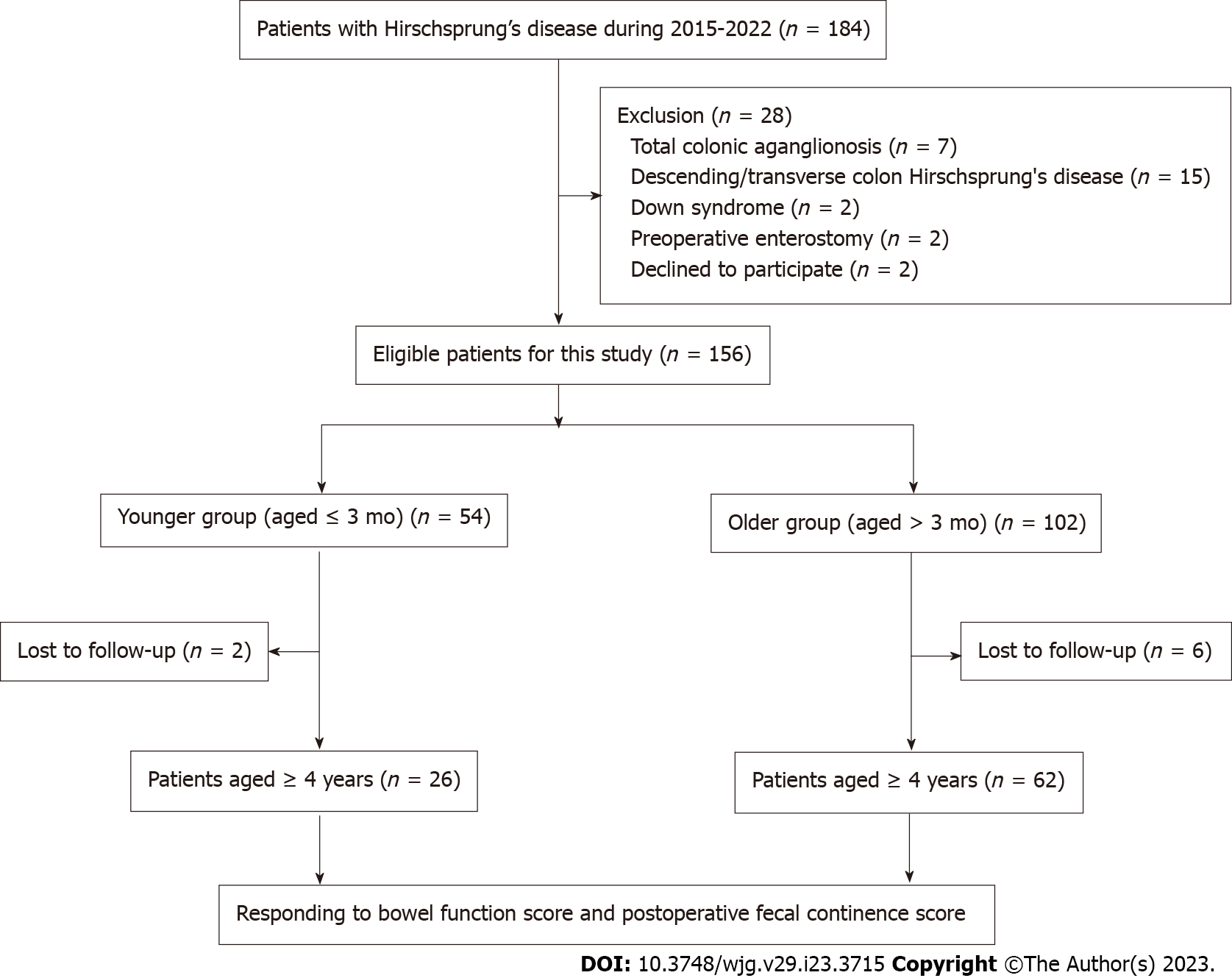
Figure 1 Flowchart of patient selection.
Figure 2 Trocar site in robotic-assisted proctosigmoidectomy.
There are three trocar ports, including a straight-cut umbilical trocar and two 8 mm working trocars located 5 cm from the umbilical trocar on either side.
Figure 3 Diagram of pelvic dissection planes and intraoperative images of pelvic dissection.
A: Pelvic dissection plane of robotic-assisted proctosigmoidectomy is under the serosa of the rectum or proper rectal fascia extended serous layer below the peritoneal reflection; B: Pelvic dissection under robotic endoscopy; C: Pelvic dissection plane of conventional laparoscopic Soave surgery is performed tightly around the rectal wall; D: Pelvic dissection under laparoscopy.
Figure 4 The pelvic depth in robotic vision before and after pulling the rectum cranially; the depth becomes shallower after pulling.
A: Before pulling; B: After pulling.
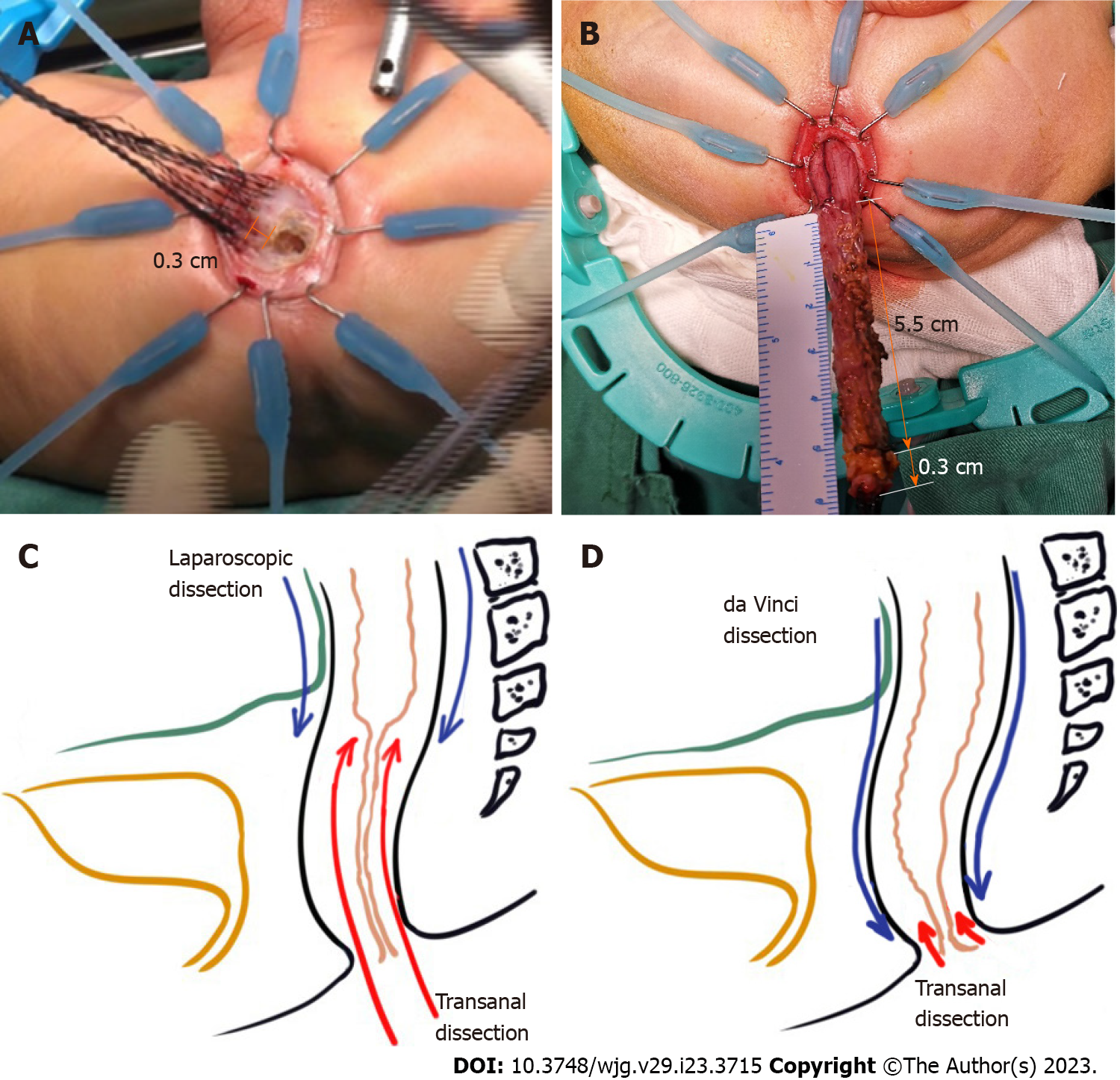
Figure 5 Comparison of two minimally invasive approaches and dissection length measurement of robotic-assisted proctosigmoidec
Figure 6 Short- to medium-term outcomes of robotic-assisted proctosigmoidectomy.
A: Occurrence of normal stool frequency at 1-6 years after surgery; B: Occurrence of enterocolitis at 1-6 years after surgery; C: Annual postoperative fecal continence score analysis among patients aged 4 years or more.
- Citation: Zhang MX, Zhang X, Chang XP, Zeng JX, Bian HQ, Cao GQ, Li S, Chi SQ, Zhou Y, Rong LY, Wan L, Tang ST. Robotic-assisted proctosigmoidectomy for Hirschsprung’s disease: A multicenter prospective study. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(23): 3715-3732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i23/3715.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i23.3715