Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3145-3156
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3145
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3145
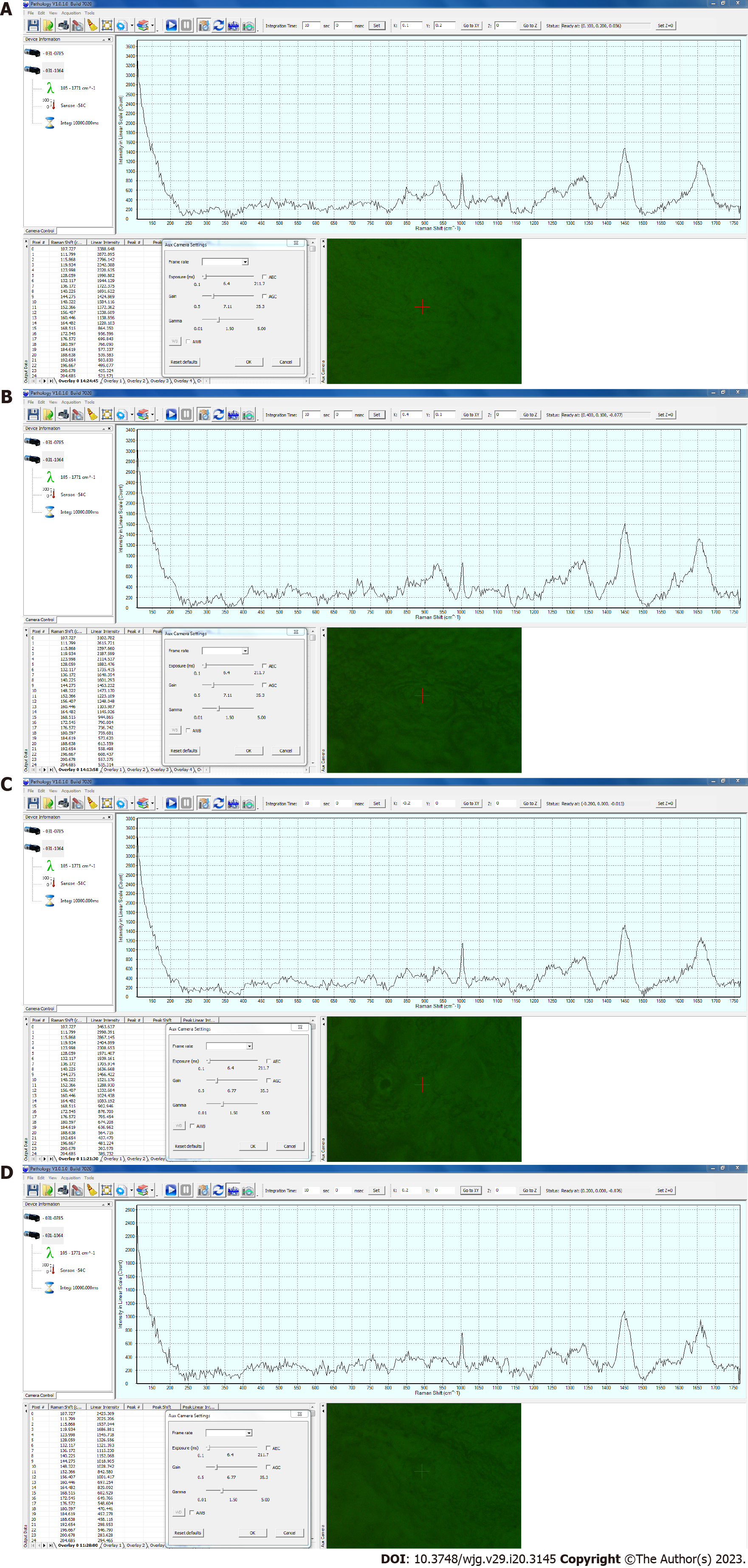
Figure 1 Example of Raman spectra.
Screenshots from the software window illustrating the Raman shift plotted against the intensity on a linear scale. A: Normal esophageal mucosa; B: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; C: Normal stomach mucosa; D: Stomach adenocarcinoma.
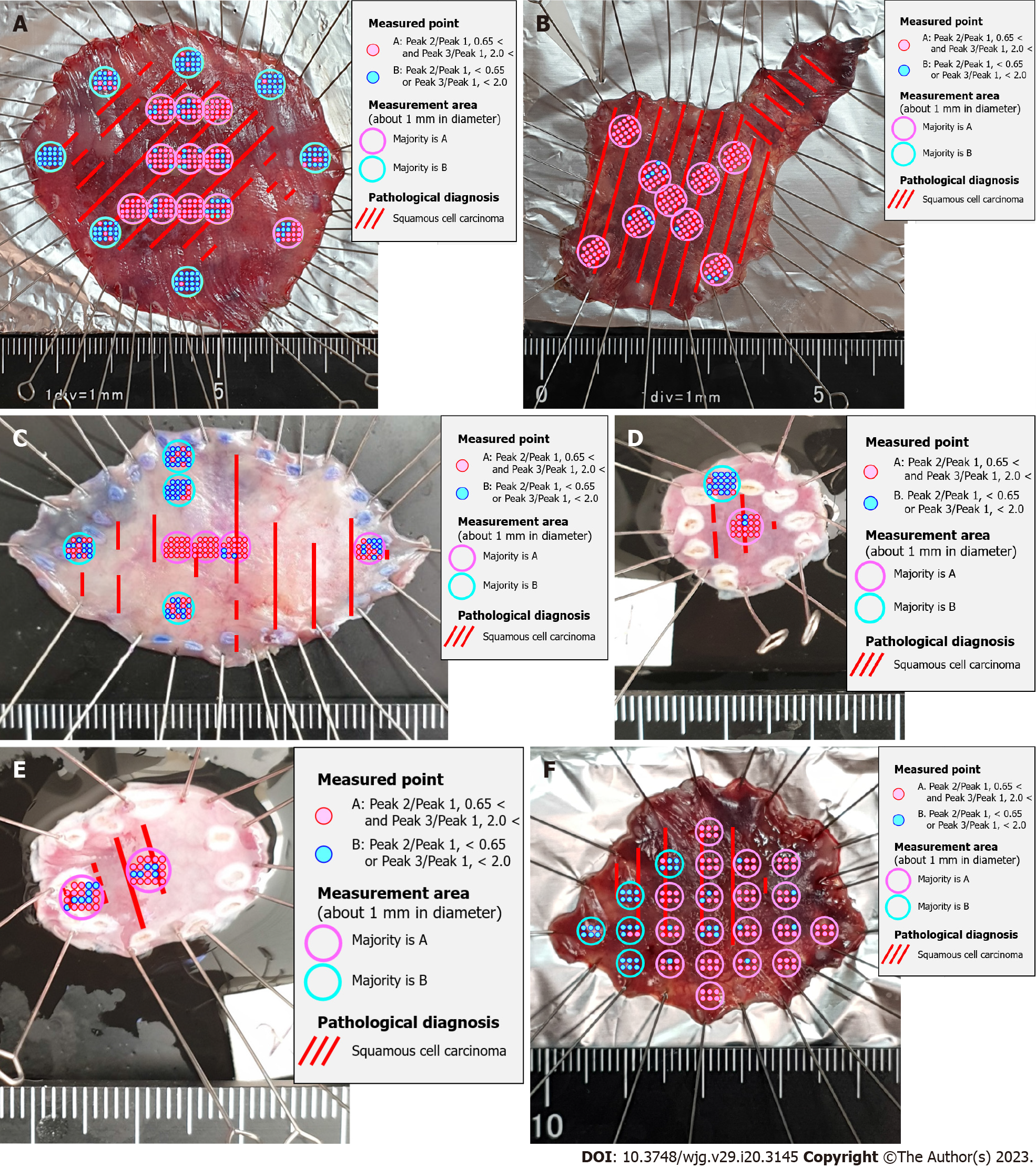
Figure 2 Comparison of Raman spectroscopic analysis and pathological diagnosis of sample Eso [squamous cell carcinoma, pT1a(LPM)-pT1b(SM)].
A: Eso-1; B: Eso-2; C: Eso-3; D: Eso-4; E: Eso-5; F: Eso-6.
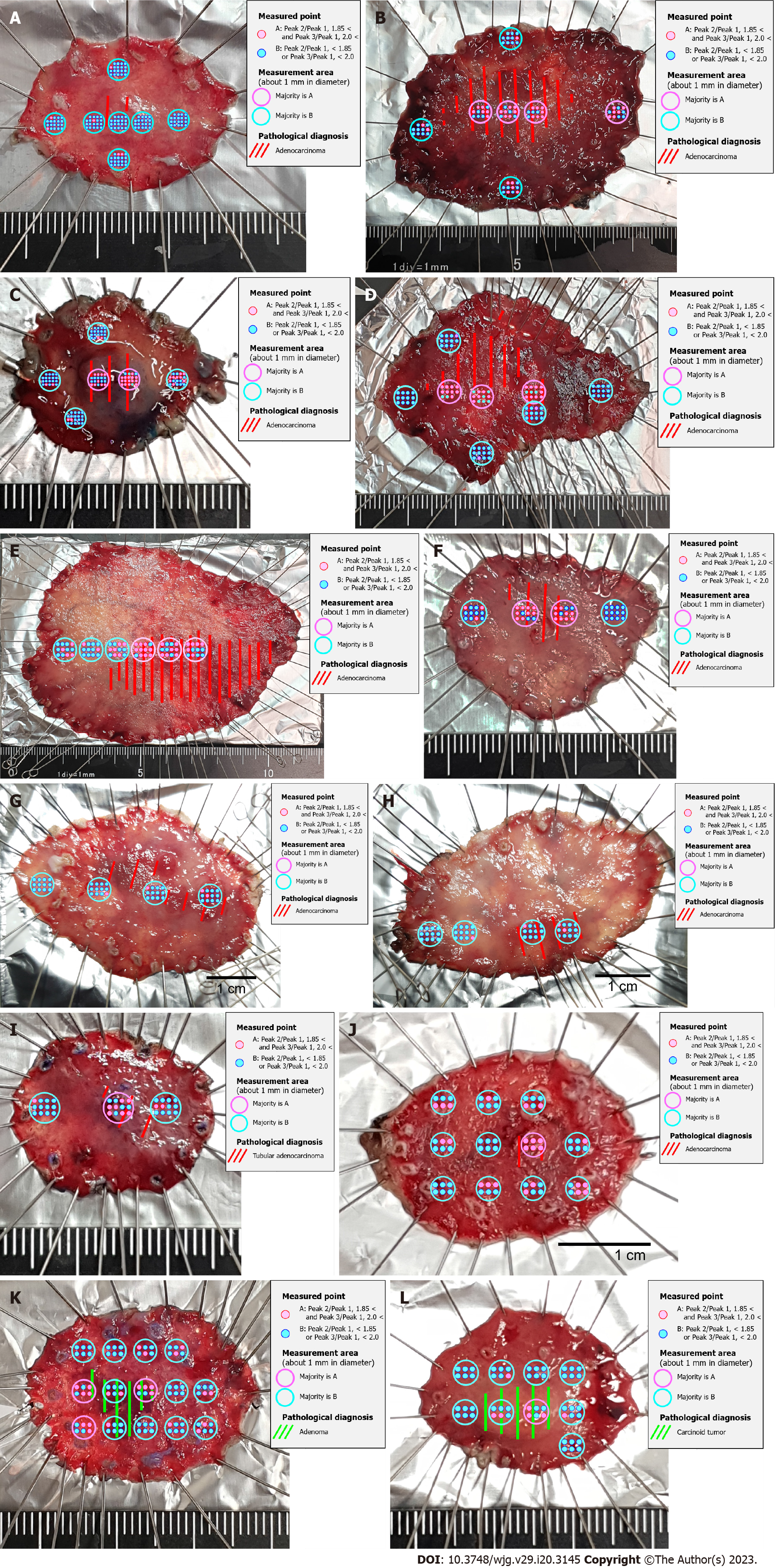
Figure 3 Comparison of Raman spectroscopic analysis and pathological diagnosis of sample Sto (well-differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma, pT1a-pT1b1; tubular adenoma; carcinoid tumor, NET G1).
A: Sto-1; B: Sto-2; C: Sto-3; D: Sto-4; E: Sto-5; F: Sto-6; G: Sto-7; H: Sto-8; I: Sto-9; J: Sto-10; K: Sto-11; L: Sto-12.
- Citation: Ito H, Uragami N, Miyazaki T, Shimamura Y, Ikeda H, Nishikawa Y, Onimaru M, Matsuo K, Isozaki M, Yang W, Issha K, Kimura S, Kawamura M, Yokoyama N, Kushima M, Inoue H. Determination of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric adenocarcinoma on raw tissue using Raman spectroscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3145-3156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3145.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3145