Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2023; 29(17): 2616-2627
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616
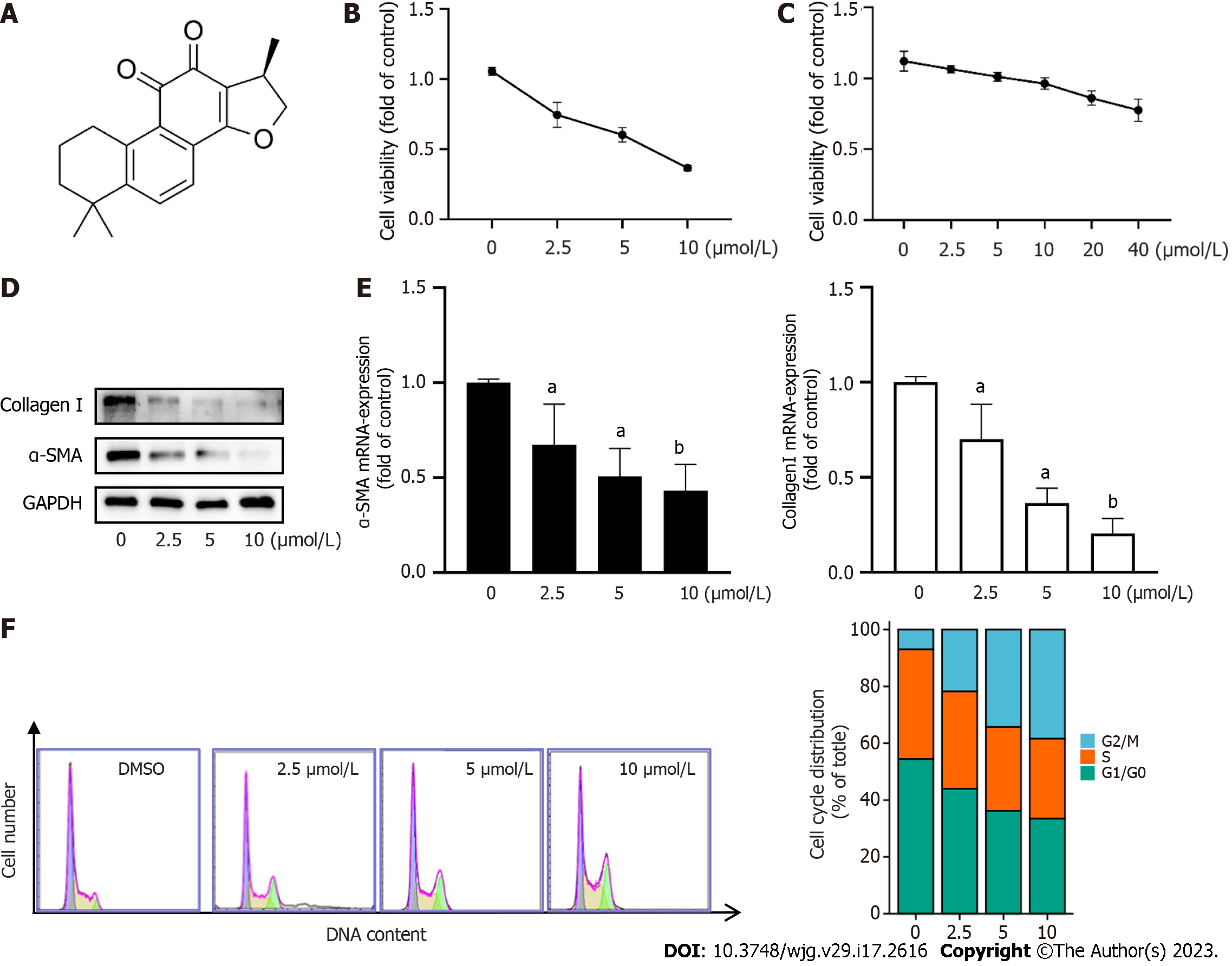
Figure 1 Cryptotanshinone reduces collagen deposition and induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M checkpoint.
A: Chemical structure of cryptotanshinone; B: CCK8 assay for LX2 cell viability; C: CCK8 assay for cell viability of LO2; D: Protein levels of collagen I and α-SMA were determined using Western blot analysis; E: mRNA levels of α-SMA and collagen I were determined using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); F: The percentage of cell cycle distribution was determined using flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 versus control.
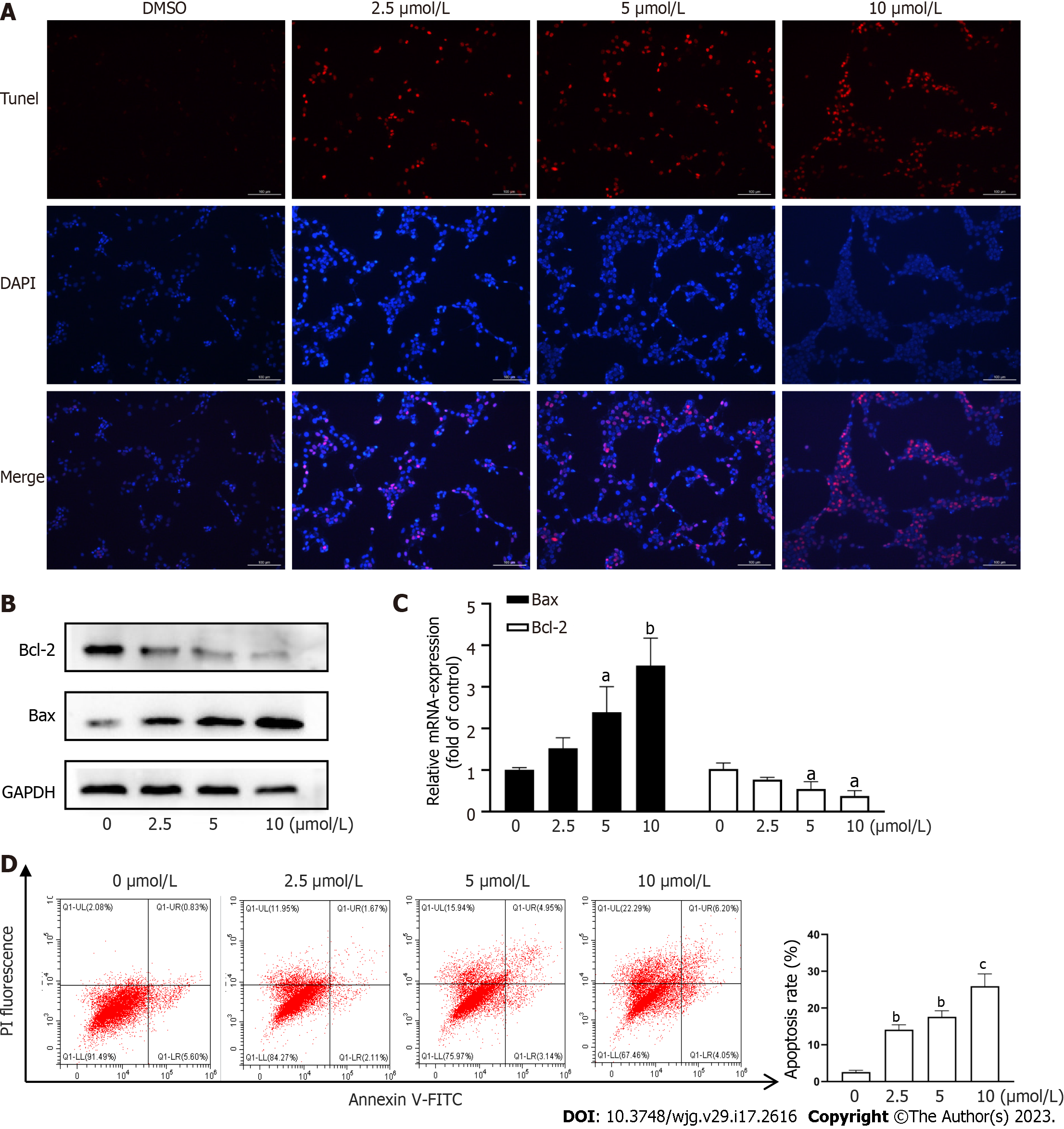
Figure 2 Cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells.
A: TUNEL staining to assess LX2 apoptosis. Red fluorescence indicates apoptotic cells. Scale baes: 100μm; B: Western blot analysis of Bcl-2 and Bax protein expression in LX2 cells; C: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis of Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA levels in LX2 cells; D: Flow cytometric analysis of LX2 cell apoptosis using fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled Annexin-V/propidium iodide staining. Cells located in the right two quadrants of each figure were considered apoptotic cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 versus control.
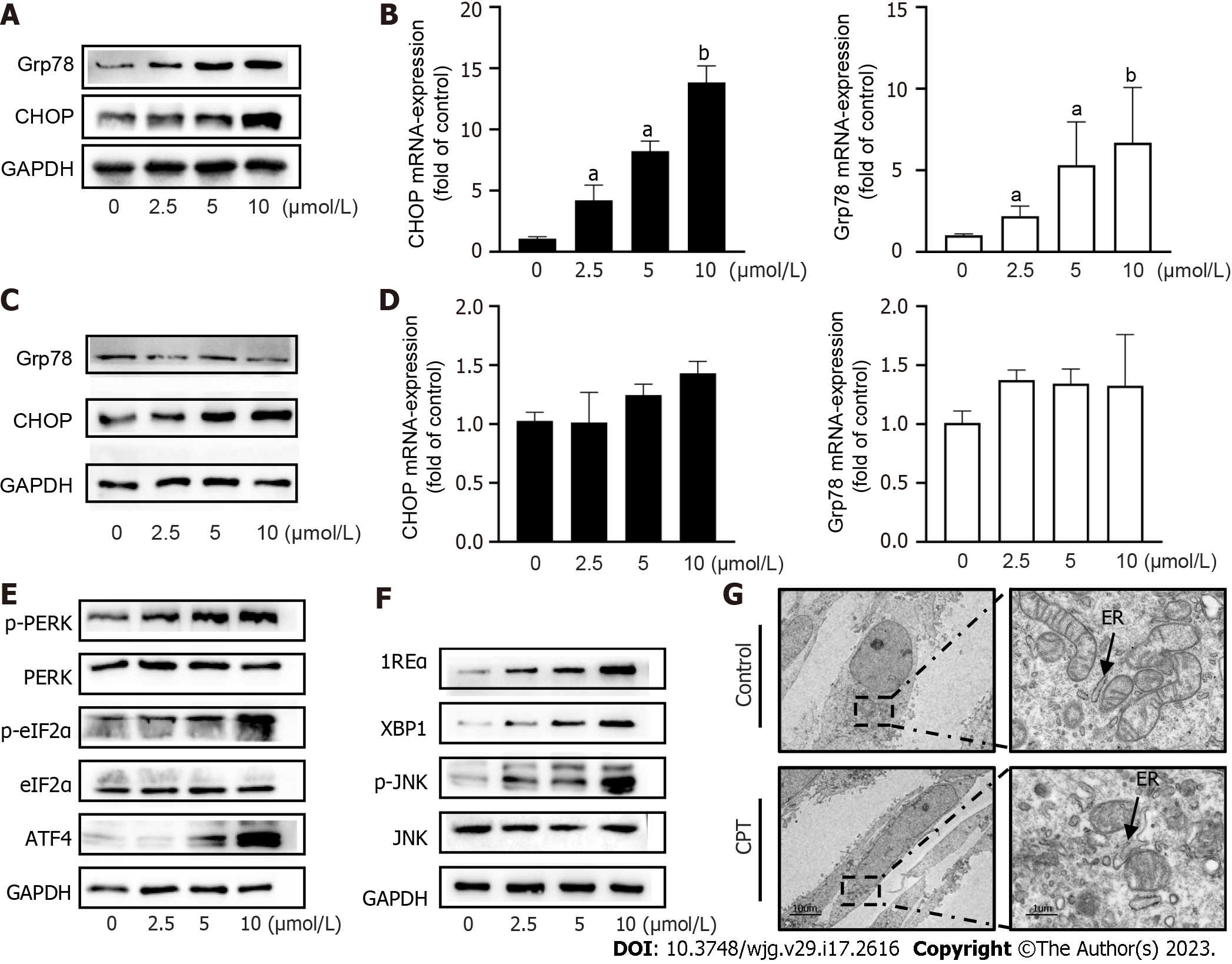
Figure 3 Cryptotanshinone activates the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in activated LX2 cells.
A: Western blot analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-related protein expression in LX2 cells; B: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of Grp78 and CHOP mRNA levels in LX2 cells; C: Western blot analysis of ERS-related protein expression in LO2 cells; D: RT-PCR analysis of Grp78 and CHOP mRNA levels in LO2 cells; E and F: Western blot analyses of ATF4, PERK, and IRE1 signaling pathways in hepatic stellate cells; G: Transmission electron microscopy showing that CPT caused ER swelling and destruction of the mitochondrial membrane integrity. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 versus control. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
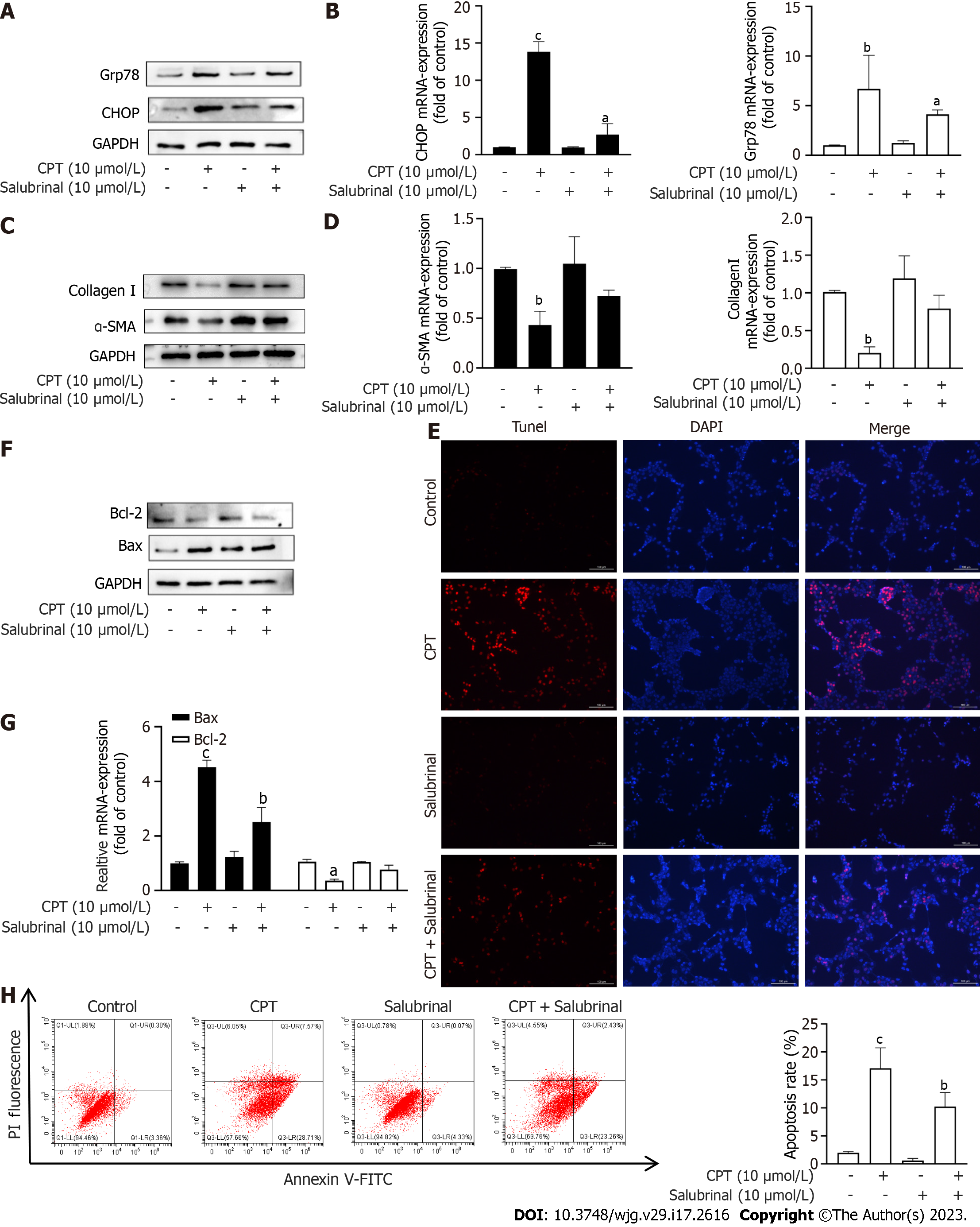
Figure 4 The endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway leads to LX2 cell apoptosis and reduces collagen deposition induced by cryptotanshinone.
A: Protein expression of Grp78 and CHOP was determined using Western blot analysis; B: mRNA levels of Grp78 and CHOP were determined using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); C: Protein expression of collagen type I and α-SMA was determined using Western blot analysis; D: mRNA levels of α-SMA and collagen I were determined using RT-PCR; E: TUNEL staining was used to assess LX2 cell apoptosis. Red fluorescence indicates apoptotic cells. Scale bars: 100 μm; F: Protein expression of Bax and Bcl2 was determined using Western blot analysis; G: mRNA levels of Bax and Bcl2 were determined using RT-PCR; H: Flow cytometry data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 versus control. CPT: Cryptotanshinone; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
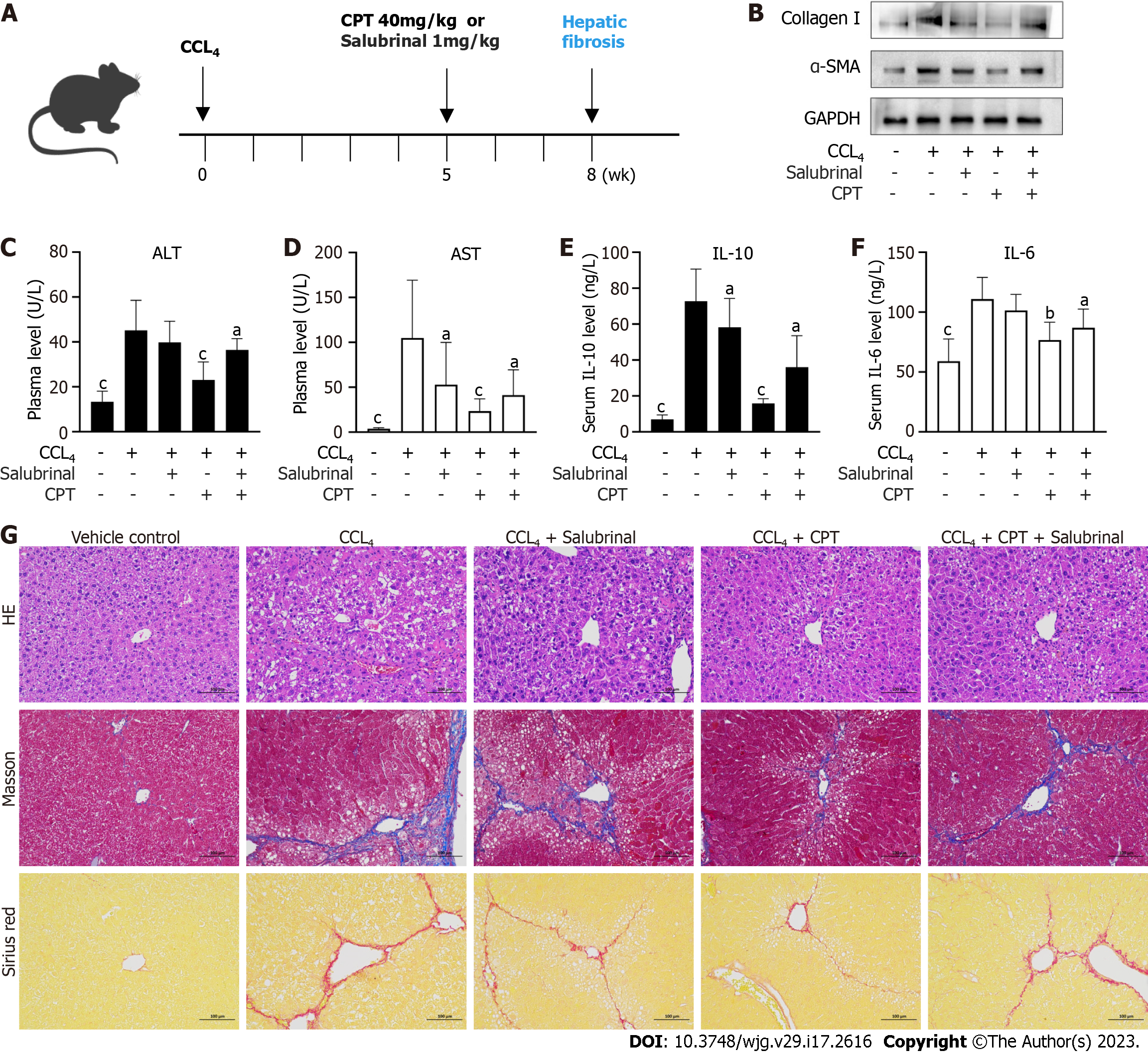
Figure 5 Cryptotanshinone protects the liver against carbon tetrachloride-induced injury and inflammation.
Cryptotanshinone (CPT) alleviates hepatic fibrotic injury in mice. Mice were injected with carbon tetrachloride (CCL4) for 8 wk to induce liver fibrosis. During weeks 5 through 8, mice in the treatment groups were given CPT (40 mg/kg) or salubrinal (1 mg/kg). A: CPT treatment protocol in the CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mouse model; B: Western blot analysis of α-SMA and collagen I in the liver tissue; C: Determination of serum alanine aminotransferase levels; D: Determination of serum aspartate aminotransferase levels; E: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) measurement of IL-6 levels in the serum; F: ELISA measurement of IL-10 levels in the serum; G: Liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, Masson reagents, and Sirius red. Scale baes: 100 μm. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 compared with the CCL4 group. CPT: Cryptotanshinone; CCL4: Carbon tetrachloride.
- Citation: Hou XX, Li YW, Song JL, Zhang W, Liu R, Yuan H, Feng TT, Jiang ZY, Li WT, Zhu CL. Cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells via modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(17): 2616-2627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i17/2616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616