Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2023; 29(11): 1735-1744
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1735
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1735
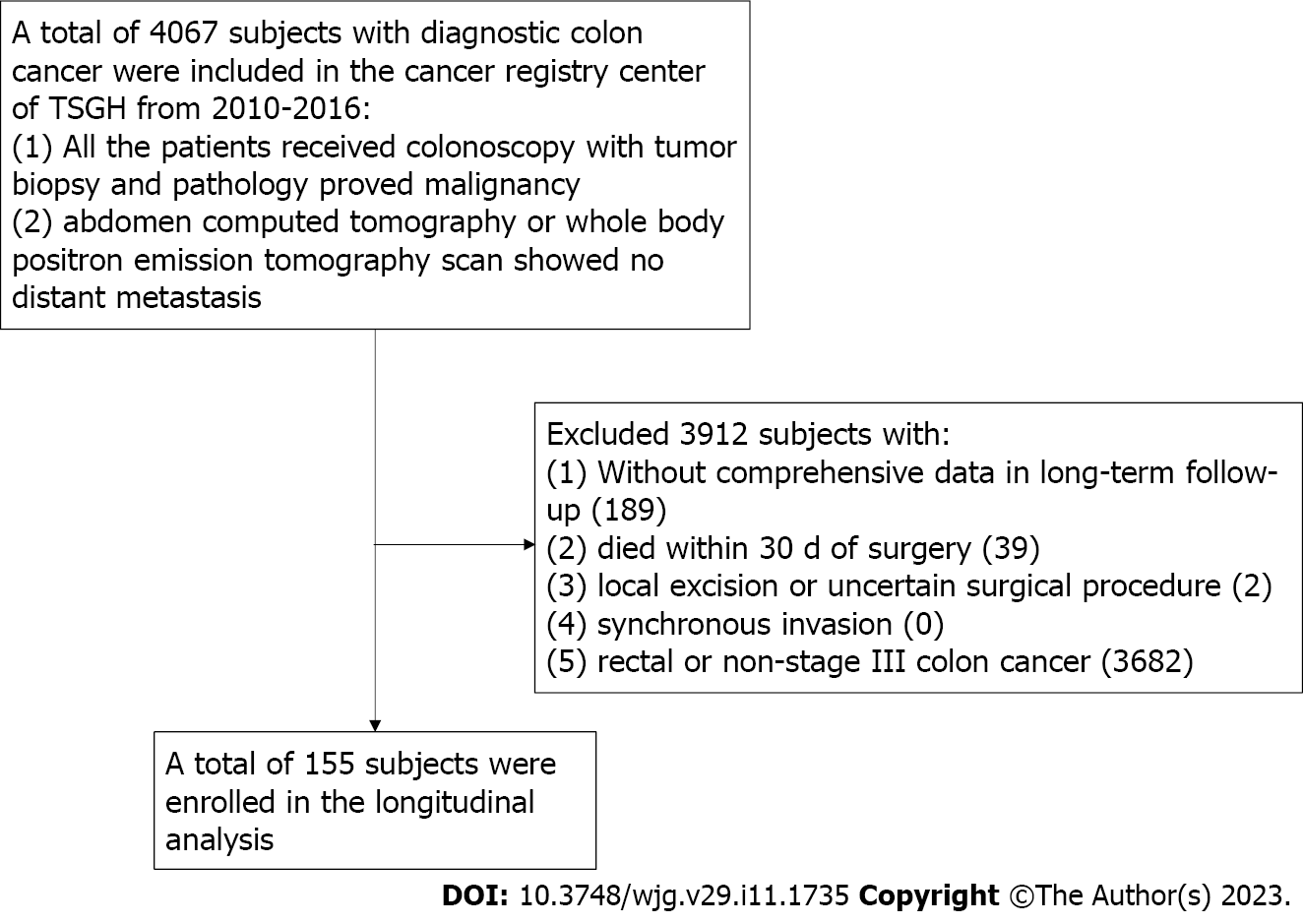
Figure 1 Description of the study flowchart.
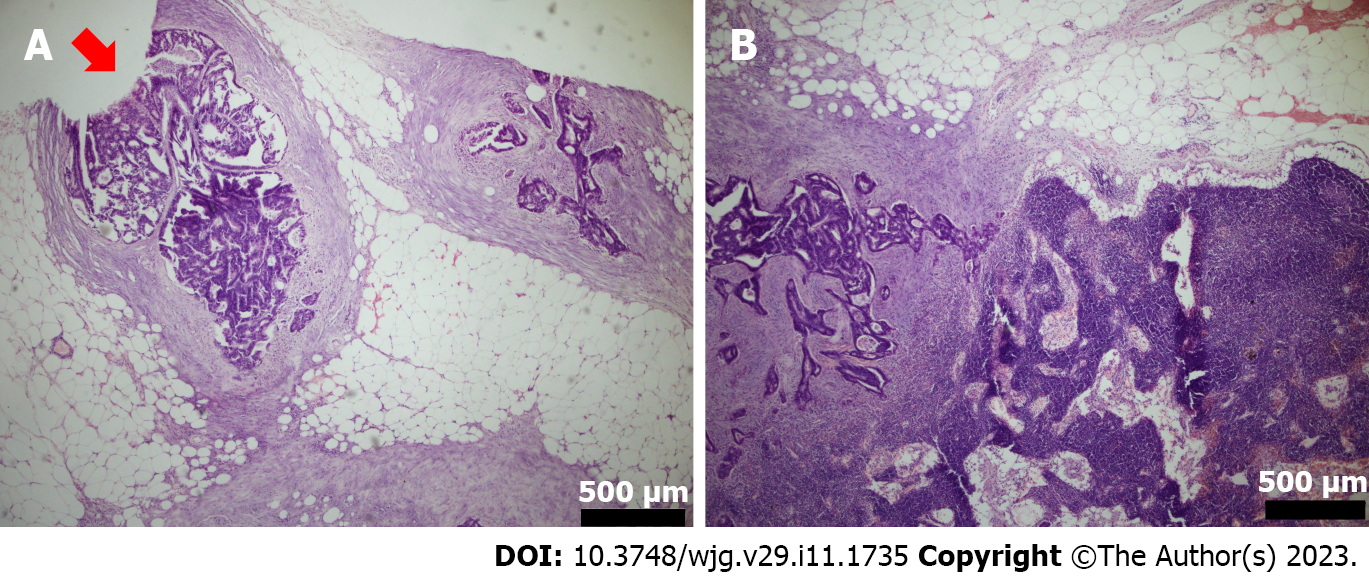
Figure 2 Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
A: The hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of N1c; B: The HE staining of non-N1c.
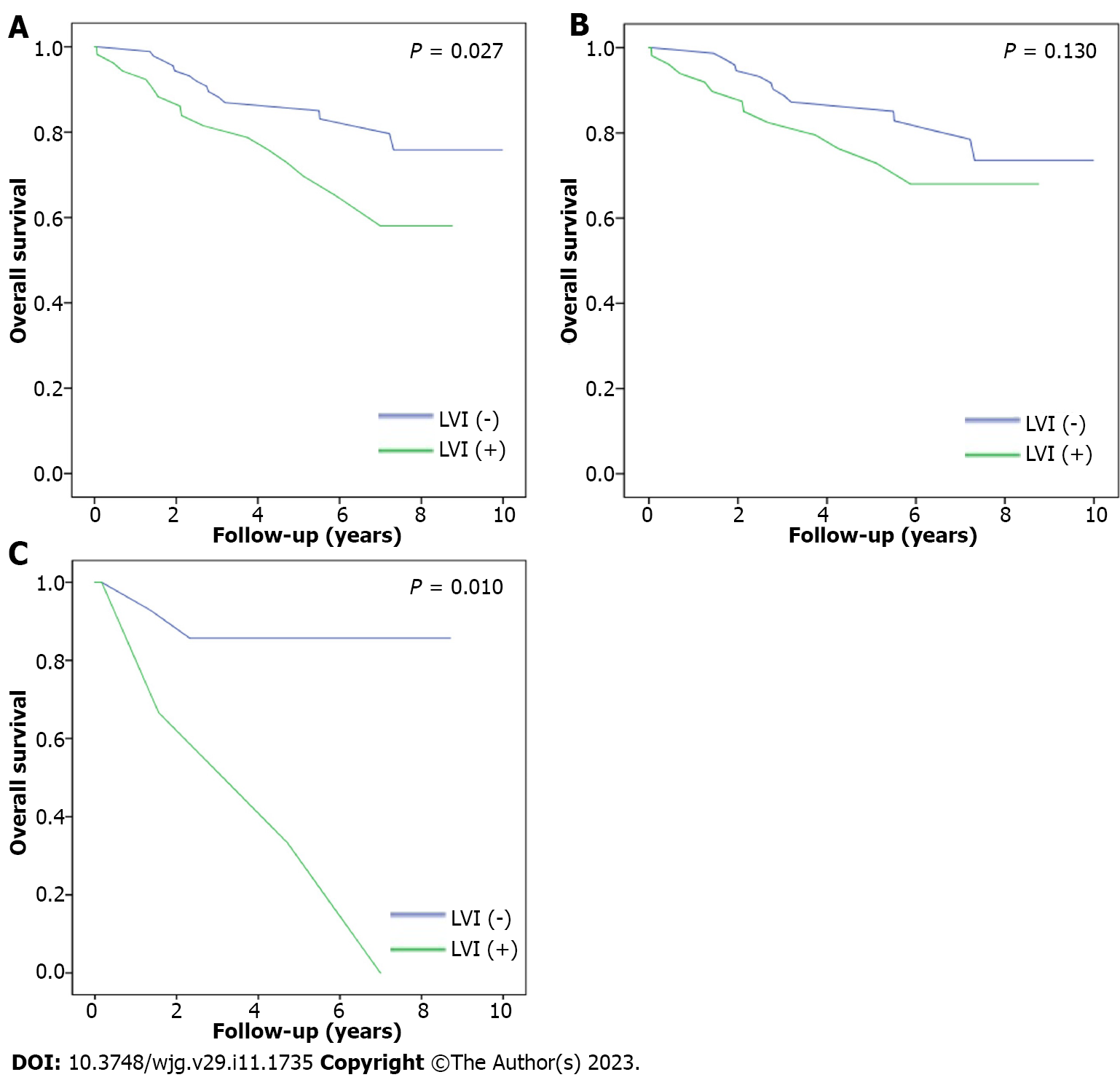
Figure 3 Overall survival.
A: The overall survival of the patient with/without lymphovascular invasion (LVI); B: The overall survival of the non-N1c patient with/without LVI; C: The overall survival of the N1c patient with/without LVI.
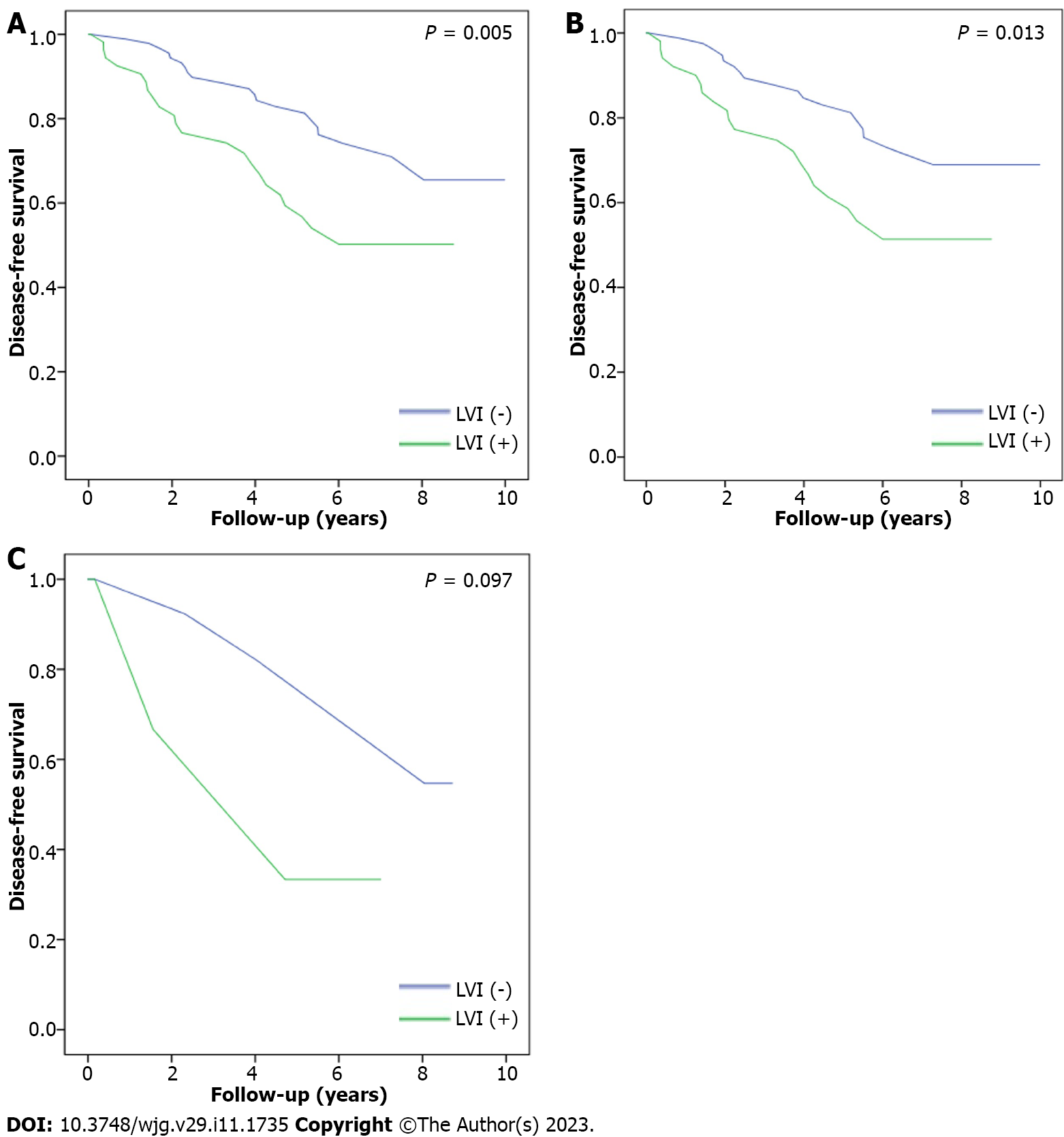
Figure 4 Disease-free survival.
A: The disease-free survival of the patients with/without lymphovascular invasion (LVI); B: The disease-free survival of the non-N1c patient with/without LVI; C: The disease-free survival of the N1c patient with/without LVI.
- Citation: Jhuang YH, Chou YC, Lin YC, Hu JM, Pu TW, Chen CY. Risk factors predict microscopic extranodal tumor deposits in advanced stage III colon cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1735-1744
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i11/1735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1735